|
|
Compounds of arsenic:
arsenic (II) sulphide
- Formula as commonly written: As4S4
- Hill system formula: As4S4
- CAS registry number: [12279-90-2]
- Formula weight: 427.95
- Class: sulphide
Synonyms
- arsenic (II) sulphide
- arsenic sulphide
- diarsenic disulphide
- tetraarsenic tetrasulphide
Physical properties
- Colour: red
- Appearance: crystalline solid
- Melting point: 320°C
- Boiling point: 565°C
- Density: 3500 kg m-3
Suppliers
Coming soon...
Element analysis and oxidation numbers
For each compound, and where possible, a formal oxidation number for each element is given, but the usefulness of this number is limited, especially so for p-block elements in particular. Based upon that oxidation number, an electronic configuration is also given but note that for more exotic compounds you should view this as a guide only.
| Element |
% |
Formal oxidation state |
Formal electronic configuration |
|
As |
70.03 |
2 |
[Ar].3d10.4s2.4p1 |
|
S |
29.97 |
-2 |
[Ne].3s2.3p6 |
Synthesis
Not available
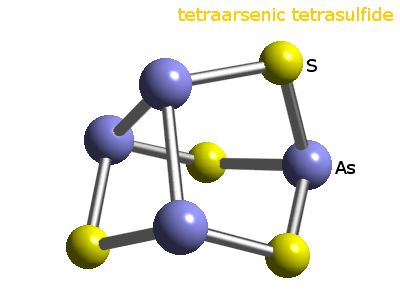
Solid state structure
- Geometry of arsenic:
- Prototypical structure:
Isotope pattern
What follows is the calculated isotope pattern for the As4S4 unit with the most intense ion set to 100%.
Formula: As4S4
mass %
428 100.0 __________________________________________________
429 3.2 __
430 17.8 _________
431 0.4
432 1.3 _
433 0.0
434 0.0
References
The data on these compounds pages are assembled and adapted from the primary literature and several other sources including the following.
- R.T. Sanderson in Chemical Periodicity, Reinhold, New York, USA, 1960.
- N.N. Greenwood and A. Earnshaw in Chemistry of the Elements, 2nd edition, Butterworth, UK, 1997.
- F.A. Cotton, G. Wilkinson, C.A. Murillo, and M. Bochmann, in Advanced Inorganic Chemistry, John Wiley & Sons, 1999.
- A.F. Trotman-Dickenson, (ed.) in Comprehensive Inorganic Chemistry, Pergamon, Oxford, UK, 1973.
- R.W.G. Wyckoff, in Crystal Structures, volume 1, Interscience, John Wiley & Sons, 1963.
- A.R.West in Basic solid state chemistry Chemistry, John Wiley & Sons, 1999.
- A.F. Wells in Structural inorganic chemistry, 4th edition, Oxford, UK, 1975.
- J.D.H. Donnay, (ed.) in Crystal data determinative tables, ACA monograph number 5, American Crystallographic Association, USA, 1963.
- D.R. Lide, (ed.) in Chemical Rubber Company handbook of chemistry and physics, CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida, USA, 77th edition, 1996.
- J.W. Mellor in A comprehensive treatise on inorganic and theoretical chemistry, volumes 1-16, Longmans, London, UK, 1922-1937.
- J.E. Macintyre (ed.) in Dictionary of inorganic compounds, volumes 1-3, Chapman & Hall, London, UK, 1992.
|
|
|