skeleton System.pdf (skeleton system wow)
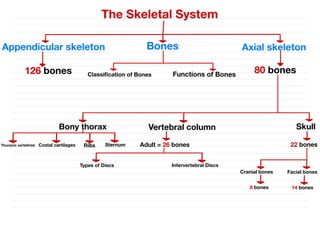
- 1. The Skeletal System Axial skeleton Appendicular skeleton 80 bones 126 bones Bones Functions of Bones Classification of Bones Skull Vertebral column Bony thorax 22 bones Adult = 26 bones Cranial bones Facial bones 8 bones 14 bones Types of Discs Intervertebral Discs Sternum Ribs Costal cartilages Thoracic vertebrae - - - & & - - - & & - & & & & & & - & & & & & &
- 2. The Skeletal System • Parts of the skeletal system include : 1–Bones (skeleton) 2–Joints 3–Cartilages 4–Ligaments • Divided into two divisions : A- Axial skeleton – 80 bones B- Appendicular skeleton – 126 bones & X & · /341144 - SISI ·
- 4. ع ن د ا ل ح د ي ث ع ن " bones " ف ق ط ، ن ش ي ر إ ل ى ا ل ع ظ ا م ب ش ك ل ف ر د ي . أ م ا ع ن د ا س ت خ د ا م أ و " skeleton " ، ف إ ن ن ا ن ش ي ر إ ل ى ا ل ه ي ك ل ا ل ع ظ م ي ك ك ل م ت ك ا م ل ي ت ض م ن ا ل ع ظ ا م و ا أل ج ز ا ء ا مل س ا ن د ة ا أل خ ر ى . Functions of Bones 1- Framework : –Supports muscle , fat and skin 2- Protection : –Surrounds vital organs like skull , ribs , pelvis 110) : -5) 3. // :& 2.) 504) 2all
- 5. 3- Movement : –Muscles attach to bones to provide movement 4- Mineral homeostasis : –Stores and maintain minerals (Calcium & phosphorus) **Mineral homeostasis** ا ل ت و ا ز ن ا مل ع د ن ي ، ي ش ي ر إ ل ى ا ل ح ف ا ظ ع ل ى ا ل ت و ا ز ن ا أل م ث ل ل ت ر ك ي ز ا مل ع ا د ن ا أل س ا س ي ة ف ي ا ل ج س م . ا مل ع ا د ن م ث ل ا ل ك ا ل س ي و م ، ا ل ف و س ف و ر ، ا ل ب و ت ا س ي و م ، ا ل ص و د ي و م ، و ا مل غ ن ي س ي و م ، ت ل ع ب د و ر ا ً ح ي و ي ا ً ف ي ا ل ع د ي د م ن و ظ ا ئ ف ا ل ج س م ب م ا ف ي ذ ل ك ب ن ا ء ا ل ع ظ ا م ، ن ق ل ا إل ش ا ر ا ت ا ل ع ص ب ي ة ، ت ق ل ص ا ل ع ض ال ت ، و ت ن ظ ي م ت و ا ز ن ا ل س و ا ئ ل . 5- Production of blood cells : –Red bone marrow –produes Red and white blood cells and platelets & %1 : i % j - = 90= + /4 - 2 - . . z Es -- · = S
- 7. 6- Storage : –Calcium –Yellow bone marrow – has adipocytes– stores fat. - * * ن خ ا ع ا ل ع ظ م ا أل ح م ر * * : ي و ج د ف ي ن ه ا ي ا ت ا ل ع ظ ا م ا ل ط و ي ل ة ) م ث ل ا ل ف خ ذ و ا ل ذ ر ا ع ( . - * * ن خ ا ع ا ل ع ظ م ا أل ص ف ر * * : ي و ج د ف ي و س ط ا ل ع ظ ا م ا ل ط و ي ل ة ) م ث ل ا ل ف خ ذ و ا ل ذ ر ا ع ( . 25 + j j + &S
- 8. Classification of Bones 1- Long bones –Typically, longer than wide –Have a shaft with heads at both ends –Contain mostly compact bone Examples : Femur , humerus Compact Bobe : و ه ي ا ل ط ب ق ة ا ل خ ا ر ج ي ة ا ل ق و ي ة و ا مل ت ي ن ة ل ل ع ظ م · - a /61 - -1 e SS 6 j s 50 . . &j. 2 . 0-94 %1944 & ⑳
- 9. Long bones : Have a shaft with heads at both ends ا ل ع ظ ا م ا ل ط و ي ل ة ه ي أ ن و ا ع م ن ا ل ع ظ ا م ت ت م ي ز ب و ج و د ع م و د أ و " ش ا ف ت " و ر ؤ و س ع ل ى ك ل م ن ط ر ف ي ه ا . ه ذ ه ا ل ع ظ ا م ت ش م ل ع ظ ا م ا ل ذ ر ا ع و ا ل ف خ ذ و ا ل س ا ق ، و ت س ا ع د ف ي د ع م ا ل ج س م و ح ر ك ت ه .
- 10. 2- Short bones –Generally , cube-shape –Contain mostly spongy bone Examples: Carpals , tarsals and cuneiforms ع ظ ا م ا ل ر س غ ) Carpals ( و ع ظ ا م ا ل ق د م ) Tarsals ( ه و أ ن ع ظ ا م ا ل ر س غ ت و ج د ف ي ا ل ي د ، ب ي ن م ا ع ظ ا م ا ل ق د م ت و ج د ف ي ا ل ق د م . و ك ال ه م ا ي ش ك ل م ف ا ص ل ا ل ر س غ و ا ل ق د م ع ل ى ا ل ت و ا ل ي ، م م ا ي س ه م ف ي د ع م ا ل ح ر ك ة و ا ال س ت ق ر ا ر ف ي ا ل ج س م . · 95. 50 . is 1 i 6 . 1 & 15191 2 & T ⑭
- 11. · ·
- 12. 3- Flat bones –Thin and flattened , usually curved –Thin layers of compact bone around a layer of spongy bone •Examples: Skull , ribs , sternum 28 - & -bis - - -- - 26 Je - + / -2/1204 4:44
- 13. 4- Irregular bones –Irregular in shape –Do not fit into other bone classification categories Example: Vertebrae and hip - - ... & / X(2 -5 - - -15 - 1 J , %
- 14. Do not fit into other bone classification categories : ا ل ع ظ ا م ا ل غ ي ر م ن ت ظ م ة ه ي ت ل ك ا ل ع ظ ا م ا ل ت ي ال ت ن د ر ج ت ح ت أ ي ف ئ ة أ خ ر ى م ن ت ص ن ي ف ا ت ا ل ع ظ ا م . ع ا د ة ً م ا ت ك و ن ه ذ ه ا ل ع ظ ا م ذ ا ت أ ش ك ا ل و ه ي ا ك ل ف ر ي د ة ت م ي ل إ ل ى ع د م ت ط ا ب ق ا ل ن م ط ا ل ذ ي ي م ك ن ت ص ن ي ف ه ب ه . ع ل ى س ب ي ل ا مل ث ا ل ، ا ل ف ق ر ا ت و ا ل ع ظ ا م ا ل و ج ه ي ة ت ُ ع ت ب ر ع ظ ا م ً ا غ ي ر م ن ت ظ م ة ؛ ف ه ي ال ت ت ب ع ا أل ش ك ا ل ا ل ن م ط ي ة ل ل ع ظ ا م ا ل ط و ي ل ة أ و ا ل ق ص ي ر ة أ و ا مل س ط ح ة 5- sesamoid bone : Example : patella • patella : ا ل ر ض ف ة ه و ا ل ع ظ م ا مل ت ح ر ك ف ي ر أ س ا ل ر ك ب ة ** - - -5)
- 15. The Axial Skeleton • Forms the longitudinal part of the body • Divided into three parts : 1– Skull 2– Vertebral column 3– Bony thorax م ص ط ل ح " Bony thorax " ي ش ي ر إ ل ى ا ل ه ي ك ل ا ل ع ظ م ي ف ي ا ل ج ز ء ا ل ع ل و ي م ن ا ل ج س م ، و ي ت ك و ن م ن ا ل ق ف ص ا ل ص د ر ي و ا أل ض ال ع و ا ل ع م و د ا ل ف ق ر ي . 80 bones -16 14 % 4 B & 5 . /sy/ 2 . % . /1 5 . x 1 Do
- 16. 1- Skull • The cranial and facial bones protect and support special sense organs and the brain. • Besides forming the large cranial cavity, the skull also forms several smaller cavities – Nasal cavity – Orbits (eye sockets) – Para nasal sinuses – Small cavities which house organs involved in hearing and equilibrium • Consists of 22 bones ·11 d 160 > // , & 2351 ! & . 111 4 1 j S ni 5 .. 97j - 116141 . % + / & 3 ..j ; 1 + 1 + = 19 -Si
- 18. • Bones of the skull are grouped into two categories : 1- Cranial bones : Eight cranial bones form the cranial cavity a - Frontal bone b - two parietal bones c - two temporal bones d - occipital bone e - sphenoid bone f - ethmoid bone - ...... /19 & . z . 11 ... · -St -4 , 15. - - 55/ 5 ./
- 19. • Frontal Bone : — Forms the forehead • Parietal Bones : — Form the sides and roof of the cranial cavity • Temporal Bones : — Form the lateral aspects and floor of the cranium • Occipital Bone : — Forms the posterior part and most of the base of the cranium • Sphenoid Bone : — Lies at the middle part of the base of the skull · .I - &.../ 2- 1x.11 e * - 2 . % . 11 & .. j -12 / & Wi ..3 / 51.1 / & i . &/1 , . /1 g :5 % . 8 . / 5541 / & . &11 1 / :55 % . % . 1
- 20. • Ethmoid Bone : 1- A major superior supporting structure of the nasal cavity 2- Contain thin projections called conchae which are lined by mucous membranes 3- location : on the midline in the anterior part of the cranial floor medial to the orbits 4- function : Increased surface area in the nasal cavity helps to humidify inhaled air - ,9940 4x .. - 5 . 5 : = /36 .- . . x & & dj · &11 . 28 . 30 · 5. - . j - 156)
- 22. 2- Facial bones : Fourteen facial bones form the face a - Two nasal bones b - two maxillae c - two zygomatic bones d - the mandible e - two lacrimal bones f - two palatine bones g - two inferior nasal conchae and vomer -51 es 14 & 5 6 / - 11 - " 1 b.
- 23. • Immovable joints called sutures fuse most of the skull bones together ا مل ف ا ص ل غ ي ر ا مل ت ح ر ك ة ، و ا ل ت ي ت س م ى ا ل غ ر ز ) sutures ( ، ه ي ن ق ا ط ا ل ت ق ا ء ب ني ع ظ ا م ا ل ج م ج م ة . ت ت م ي ز ه ذ ه ا ل غ ر ز ب ك و ن ه ا م ف ا ص ل ل ي ف ي ة ص ل ب ة ت ر ب ط ع ظ ا م ا ل ج م ج م ة ب إ ح ك ا م ، م م ا ي و ف ر ا ل ح م ا ي ة ل ل د م ا غ . خ ال ل ن م و ا إل ن س ا ن ، ت ك و ن ه ذ ه ا ل غ ر ز أ ك ث ر م ر و ن ة ، م م ا ي س م ح ل ل ج م ج م ة ب ا ل ن م و م ع ن م و ا ل د م ا غ . و م ع م ر و ر ا ل و ق ت ، ت ب د أ ه ذ ه ا ل غ ر ز ب ا ل ت ح و ل إ ل ى ع ظ ا م غ ي ر م ت ح ر ك ة ، م م ا ي ؤ د ي إ ل ى ت م ا س ك ع ظ ا م ا ل ج م ج م ة ب ش ك ل د ا ئ م و ث ا ب ت . ه ذ ا ا ل ت ح و ل إ ل ى ع ظ ا م غ ي ر م ت ح ر ك ة ي س ا ه م ف ي ت ق و ي ة ا ل ب ن ي ة ا ل ع ا م ة ل ل ج م ج م ة و ح م ا ي ت ه ا م ن ا إل ص ا ب ا ت . & - / 2 ,
- 24. • The skull provides large areas of attachment for muscles that move various parts of the head ا ل ج م ج م ة ت و ف ر م س ا ح ا ت و ا س ع ة ال ر ت ب ا ط ا ل ع ض ال ت ا ل ت ي ت ح ر ك أ ج ز ا ء م خ ت ل ف ة م ن ا ل ر أ س . ه ذ ه ا ل ع ض ال ت ت ش م ل ا ل ع ض ال ت ا مل س ؤ و ل ة ع ن ت ع ا ب ي ر ا ل و ج ه ، م ث ل ا ال ب ت س ا م و ا ل ع ب و س ، و ك ذ ل ك ا ل ع ض ال ت ا ل ت ي ت س ا ه م ف ي ح ر ك ة ا ل ف ك و ا ل ل س ا ن ، م م ا ي م ك ن ن ا م ن ا مل ض غ و ا ل ك ال م . و ج و د ه ذ ه ا مل س ا ح ا ت ا ل و ا س ع ة ي ت ي ح ت ث ب ي ت ا ل ع ض ال ت ب ش ك ل ق و ي و م ت ني ، م م ا ي س ا ع د ع ل ى أ د ا ء ا ل ح ر ك ا ت ا ل د ق ي ق ة و ا مل ع ق د ة ا ل ت ي ت ت ط ل ب ه ا و ظ ا ئ ف ا ل ر أ س ا مل خ ت ل ف ة . - Iis andiS G 5 % 1 0 -is
- 25. • Skull and facial bones provide attachment for muscles that produce facial expressions. ع ظ ا م ا ل ج م ج م ة و ا ل و ج ه ت و ف ر ن ق ا ط ا ر ت ك ا ز ل ل ع ض ال ت ا ل ت ي ت ن ت ج ت ع ا ب ي ر ا ل و ج ه . ه ذ ه ا ل ع ض ال ت ، ا مل ع ر و ف ة ب ا س م ع ض ال ت ا ل و ج ه أ و ع ض ال ت ا ل ت ع ا ب ي ر ا ل و ج ه ي ة ، ت ر ت ب ط م ب ا ش ر ة ب ع ظ ا م ا ل و ج ه و ا ل ج ل د . ع ن د م ا ت ن ق ب ض ه ذ ه ا ل ع ض ال ت ، ت س ح ب ا ل ج ل د و ت س ب ب ت ع ا ب ي ر م خ ت ل ف ة م ث ل ا ال ب ت س ا م ، ا ل ع ب و س ، ا ل ح ز ن ، ا ل د ه ش ة ، و غ ي ر ه ا . ا ل ع ض ال ت ا ل ر ئ ي س ي ة ا ل ت ي ت س ا ه م ف ي ت ع ا ب ي ر ا ل و ج ه ت ش م ل 1- Orbicularis oris 2- Orbicularis oculi 3- Zygomaticus major 4- Frontalis · ·3.4 - Wi 12 . . . 5 N ... ·
- 26. • The facial bones form the framework of the face and provide support for the entrances to the digestive and respiratory systems. ع ظ ا م ا ل و ج ه ت و ف ر ا ل د ع م ل ل م د ا خ ل إ ل ى ا ل ج ه ا ز ي ن ا ل ه ض م ي و ا ل ت ن ف س ي ، و ذ ل ك ي ش م ل : 1 . * * ا ل ف م * * : ع ظ ا م ا ل ف ك ا ل ع ل و ي ) Maxilla ( و ا ل ف ك ا ل س ف ل ي ) Mandible ( ت ش ك ل ت ج و ي ف ا ل ف م و ت ح م ل ا أل س ن ا ن ، م م ا ي س م ح ب ت ن ا و ل ا ل ط ع ا م و م ض غ ه . ا ل ف م ه و ا مل د خ ل ا ل ر ئ ي س ي ل ل ج ه ا ز ا ل ه ض م ي ، ح ي ث ي ت م إ د خ ا ل ا ل ط ع ا م و ا ل ش ر ا ب . 2 . * * ا أل ن ف * * : ا ل ع ظ ا م ا أل ن ف ي ة ) Nasal bones ( و ع ظ ا م أ خ ر ى م ث ل ا ل ع ظ م ا ل ح ن ك ي ) Palatine ( ت س ا ه م ف ي ت ش ك ي ل ت ج و ي ف ا أل ن ف . ا أل ن ف ه و ا مل د خ ل ا ل ر ئ ي س ي ل ل ج ه ا ز ا ل ت ن ف س ي ، ح ي ث ي د خ ل ا ل ه و ا ء إ ل ى ا ل ر ئ ت ني . ب ذ ل ك ، ت و ف ر ع ظ ا م ا ل و ج ه ب ن ي ة ص ل ب ة و م س ت ق ر ة ت د ع م ه ذ ه ا مل د ا خ ل ا ل ح ي و ي ة ، م م ا ي م ك ن ا ل ج س م م ن أ د ا ء و ظ ا ئ ف ا ل ت ن ف س و ا ل ه ض م ب ش ك ل ف ع ا ل . · / !251 - 55451 15
- 29. Sutures of the Skull Sutures : are a type of fibrous joint that are unique to the skull. They are immovable and fuse completely around the age of 20. - 1 25 % 1961 [1 % ... 2 . 2 . 1. = /
- 30. • These joints are important in the context of trauma, as they represent points of potential weakness in the skull. The main sutures in the adult skull are: 1- Coronal suture : fuses the frontal bone with the two parietal bones. 2- Sagittal suture : fuses both parietal bones to each other. 3- Lambdoid suture : fuses the occipital bone to the two parietal bones. · - 18 . 4 b. -d 1 < 51 ↑ & * & . . & .
- 31. ف ي ا ل س ي ا ق ا ل ط ب ي ، ي ش ي ر “ trauma ” إ ل ى ا إل ص ا ب ا ت ا ل ج س د ي ة ا ل ت ي ي ت ع ر ض ل ه ا ا ل ش خ ص ن ت ي ج ة ل ح ا د ث أ و ح د ث م ؤ ل م ، م ث ل ا ل ك س و ر ، ا ل ج ر و ح ، أ و ا إل ص ا ب ا ت ا ل ر أ س ي ة . • In neonates, the incompletely fused suture joints give rise to membranous gaps between the bones, known as fontanelles. The two major fontanelles are: 1- Frontal fontanelle : located at the junction of the coronal and sagittal sutures 2- Occipital fontanelle : located at the junction of the sagittal and lambdoid sutures st51.. 36 y - 19 -4 - - . hsi vi 5 . 5 .K2 . 4 .
- 32. 2- Vertebral Column • Also called the spine , backbone , or spinal column Functions : 1- Protect the spinal cord 2- Support the head 3- Serve as a point of attachment for the ribs, pelvic girdle, and muscles Sky) - -8/ -1 di - . . . [201p -
- 33. • The vertebral column is curved to varying degrees in different locations A- Curves increase the column strength B- Help maintain balance in the upright position C- Absorb shocks during walking, and help protect the vertebrae from fracture - - - . = 5 . 3 2 S -- - - .. long s 4b2117151 5 - . = gas-
- 34. • Composed of a series of bones called vertebrae (Adult=26) A- 7 cervical are in the neck region B- 12 thoracic are posterior to the thoracic cavity C- 5 lumbar support the lower back D- 1 sacrum consists of five fused sacral vertebrae E- 1 coccyx consists of four fused coccygeal vertebrae - - - -/ = = (1d & - & i S + - .. J -3) & - i -2120
- 36. Intervertebral Discs • Location : Found between the bodies of adjacent vertebrae • Function : 1- Form strong joints 2- Permit various movements of the vertebral column 3- Absorb vertical shock • Vertebrae typically consist of : 1- A Body (weight bearing) 2- A vertebral arch (surrounds the spinal cord) 3- Several processes (points of attachment for muscles) Body - . . / - (5) ... 9 - . 95.51i -5 % ↑ 2 - 6) -x14 - ) - . / 1 - = -5 - .
- 37. Types of Discs 1 - Normal Disc 2 - Degenerative Disc 3 - Bulging Disc 4 - Herniated Disc 5 - Thinning Disc 6 - Disc Degeneration with Osteophyte formation %>81 :4 ... ... ·.. S
- 40. 3- Thorax • Thoracic cage is formed by the : 1- Sternum 2- Ribs 3- Costal cartilages 4- Thoracic vertebrae Functions : 1- Enclose and protect the organs in the thoracic and abdominal cavities. 2- Provide support for the bones of the upper limbs. 3- Play a role in breathing. - 1 1 - - -i &X T & .., -- -it T & s & s y &-1 . . I .. G S . >X/ 9 & 1 bX/ - & Tyga &.....
- 42. 1- Sternum : *Breastbone* Location : in the center of the thoracic wall • Consists of the manubrium, body, xiphoid process / · & s - 113 . -5- - · .. / 2 . 3 . j) -
- 43. 2- Ribs : • 12 Twelve pairs of ribs give structural support to the sides of the thoracic cavity • True ribs (7 pairs), False ribs (3 Pairs) and floating ribs(2 pairs) [04 · 6151 51) %, ·...It &8/1 - - / -
- 45. 3- Costal cartilages : • Costal cartilages contribute to the elasticity of the thoracic cage 15 . / - /