Dosing & Uses
Dosage Forms & Strengths
oral suspension
- 40mg/mL (105mL)
tablet, delayed-release
- 100mg
injectable solution
- 18mg/mL (300mg/16.7mL-vial)
Invasive Aspergillus & Candida Infections
Oral suspension or delayed-release tablets are indicated for prophylaxis of invasive Aspergillus and Candida infections in patients who are at high risk of developing these infections due to being severely immunocompromised (eg, hematopoietic stem cell transplant recipients with GVHD, hematologic malignancies with prolonged neutropenia from chemotherapy)
Oral suspension: 200 mg (5 mL) PO TID
Tablet: 300 mg PO BID on Day 1, then 300 mg PO qDay
IV: 300 mg IV BID on Day 1, then 300 mg IV qDay (see IV preparation and administration)
Duration of therapy is based on recovery from neutropenia or immunosuppression
Oropharyngeal Candidiasis
Oral suspension is indicated for oropharyngeal candidiasis
100 mg (2.5 mL) PO BID on Day 1, then 100 mg PO qDay for 13 days
Refractory to itraconazole and/or fluconazole: 400 mg (10 mL) PO BID; duration based on severity of underlying disease and clinical response
Dosage Modifications
Renal impairment
-
Tablets or oral suspension
- Severe (eGFR <20 mL/min): Due to variability, closely monitor for breakthrough fungal infections
-
Injection
- Moderate-to-severe (eGFR <50 mL/min): Avoid unless benefit outweighs the risks
- Accumulation of IV vehicle (betadex sulfobutyl ether sodium [SBECD]), expected to occur
- If unavoidable, closely monitor serum creatinine; if increases occur, consider switching to oral therapy
Hepatic impairment
- Mild-to-severe (Child-Pugh A to C): No dosage adjustment necessary; no specific study was conducted with the injection or tablets
Orphan Designations
Treatment of invasive aspergillosis
Treatment of zygomycosis
Sponsor
- Merck, Sharp & Dohme Corp; 1 Merck Drive; Whitehouse Station, New Jersey 08889
Dosage Forms & Strengths
oral suspension
- 40mg/mL (105mL)
oral suspension, delayed-release
- 300mg
- Reconstituted concentration: ~30 mg/mL
tablet, delayed-release
- 100mg
injectable solution
- 18mg/mL (300mg/16.7mL-vial)
Invasive Aspergillus & Candida Infections
Indicated for prophylaxis of invasive Aspergillus and Candida infections in patients who are at high risk of developing these infections due to being severely immunocompromised (eg, hematopoietic stem cell transplant recipients with GVHD, hematologic malignancies with prolonged neutropenia from chemotherapy)
IV
- <2 years: Safety and efficacy not established
-
≥2 years
- Loading dose: 6 mg/kg IV BID on Day 1; not to exceed 300 mg BID, then
- Maintenance dose: 6 mg/kg IV qDay starting on the Day 2; not to exceed 300 mg qDay
- Duration of therapy is based on recovery from neutropenia or immunosuppression
Tablets
- <2 years: Safety and efficacy not established
-
≥2 years and >40 kg
- Loading dose: 300 mg PO BID on Day 1, then
- Maintenance dose: 300 mg PO qDay starting on the Day 2
- Duration of therapy is based on recovery from neutropenia or immunosuppression
Oral suspension
- <13 years: Safety and efficacy not established
-
≥13 years
- Loading and maintenance dose: 200 mg PO TID
- Duration of therapy is based on recovery from neutropenia or immunosuppression
Delayed-release oral suspension
- <2 years: Safety and efficacy not established
-
≥2 years and ≤40 kg
- 10 to <12 kg: 90 mg PO BID on Day 1, then 90 mg PO qDay starting on Day 2
- 12 to <17 kg: 120 mg PO BID on Day 1, then 120 mg PO qDay starting on Day 2
- 17 to <21 kg: 150 mg PO BID on Day 1, then 150 mg PO qDay starting on Day 2
- 21 to <26 kg: 180 mg PO BID on Day 1, then 180 mg PO qDay starting on Day 2
- 26 to <36 kg: 210 mg PO BID on Day 1, then 210 mg PO qDay starting on Day 2
- 36-40 kg: 240 mg PO BID on Day 1, then 240 mg PO qDay starting on Day 2
- Duration of therapy is based on recovery from neutropenia or immunosuppression
Oropharyngeal Candidiasis
Oral suspension is indicated for oropharyngeal candidiasis
<13 years: Safety and efficacy not established
≥13 years
- Oral suspension: 100 mg (2.5 mL) PO BID on Day 1, then 100 mg PO qDay for 13 days
- Refractory to itraconazole and/or fluconazole: 400 mg (10 mL) PO BID; duration based on severity of underlying disease and clinical response
Dosage Modifications
Renal impairment
-
Tablets or oral suspension
- Severe (eGFR <20 mL/min): Due to variability, closely monitor for breakthrough fungal infections
Hepatic impairment
- Mild-to-severe (Child-Pugh A to C): No dosage adjustment necessary; no specific study was conducted with the injection or tablets
Interactions
Interaction Checker
No Results
Contraindicated
Serious - Use Alternative
Significant - Monitor Closely
Minor
Contraindicated (39)
- alfuzosin
alfuzosin and posaconazole both increase QTc interval. Contraindicated.
- asenapine
asenapine and posaconazole both increase QTc interval. Contraindicated.
- bromocriptine
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of bromocriptine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Contraindicated.
- buprenorphine buccal
buprenorphine buccal and posaconazole both increase QTc interval. Contraindicated.
- buprenorphine subdermal implant
buprenorphine subdermal implant and posaconazole both increase QTc interval. Contraindicated.
- buprenorphine transdermal
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of buprenorphine transdermal by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Contraindicated.
- buprenorphine, long-acting injection
buprenorphine, long-acting injection and posaconazole both increase QTc interval. Contraindicated.
- ceritinib
ceritinib and posaconazole both increase QTc interval. Contraindicated.
- cobimetinib
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of cobimetinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Contraindicated. Avoid coadministration with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors with (increases cobimetinib systemic exposure by 6.7-fold).
- conivaptan
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of conivaptan by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Contraindicated. Coadministration of conivaptan with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors is contraindicated.
- crizotinib
crizotinib and posaconazole both increase QTc interval. Contraindicated.
- dihydroergotamine
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of dihydroergotamine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Contraindicated.
- dihydroergotamine intranasal
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of dihydroergotamine intranasal by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Contraindicated.
- efavirenz
efavirenz and posaconazole both increase QTc interval. Contraindicated.
- eliglustat
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of eliglustat by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Contraindicated. Strong CYP3A4 inhibitors are contraindicated with eliglustat poor or intermediate metabolizers; reduce eliglustat dose from 84 mg BID to 84 mg once daily in extensive metabolizers; eliglustat is contraindiated if strong or moderate CYP2D6 inhibitors are given concomitantly with strong or moderate CYP3A inhibitors
- ergoloid mesylates
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of ergoloid mesylates by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Contraindicated.
- ergonovine
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of ergonovine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Contraindicated.
- finerenone
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of finerenone by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Contraindicated.
- flibanserin
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of flibanserin by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Contraindicated. Coadministration of flibanserin with moderate or strong CYP3A4 inhibitors is contraindicated. Severe hypotension or syncope can occur.
- gepirone
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of gepirone by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Contraindicated.
- isavuconazonium sulfate
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of isavuconazonium sulfate by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Contraindicated.
- ivabradine
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of ivabradine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Contraindicated. Coadministration of ivabradine with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors is contraindicated.
- lomitapide
posaconazole increases levels of lomitapide by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Contraindicated. Increases lomitapide levels several folds.
- lonafarnib
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of lonafarnib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Contraindicated. Lonafarnib is a sensitive CYP3A4 substrate. Coadministration with strong or moderate CYP3A4 inhibitors is contraindicated.
- lovastatin
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of lovastatin by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Contraindicated. Strong CYP3A4 inhibitors increase systemic statin exposure and risk of myopathy, including rhabdomyolysis
- lurasidone
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of lurasidone by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Contraindicated. Coadministration of lurasidone and strong CYP3A4 inhibitors is contraindicated.
- mavacamten
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of mavacamten by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Contraindicated. Strong CYP3A4 inhibitors may increase mavacamten systemic exposure, resulting in heart failure due to systolic dysfunction.
- methylergonovine
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of methylergonovine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Contraindicated.
- mirtazapine
mirtazapine and posaconazole both increase QTc interval. Contraindicated.
- naloxegol
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of naloxegol by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Contraindicated. Coadministration of naloxegol with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors can significantly increase naloxegol systemic exposure which may precipitate opioid withdrawal symptoms
- ondansetron
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of ondansetron by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Contraindicated.
- pacritinib
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of pacritinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Contraindicated.
- regorafenib
posaconazole, regorafenib. affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Contraindicated. Strong CYP3A4 inhibitors increase regorafenib levels and decrease exposure of the active metabolites M-2 and M-5.
- ribociclib
ribociclib increases toxicity of posaconazole by QTc interval. Contraindicated.
- simvastatin
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of simvastatin by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Contraindicated. Contraindicated. Increased risk for rhabdomyolysis with drugs that increase simvastatin systemic exposure
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of simvastatin by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Contraindicated. Contraindicated. Increased risk for rhabdomyolysis with drugs that increase simvastatin systemic exposure - sunitinib
sunitinib and posaconazole both increase QTc interval. Contraindicated.
- venetoclax
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of venetoclax by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Contraindicated. Use of strong CYP3A4 inhibitors is contraindicated with venetoclax during the initial ramp-up dosing phase. If a strong CYP3A inhibitor must be used after the ramp-up phase, reduce the venetoclax dose by at least 75%.
- venlafaxine
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of venlafaxine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Contraindicated.
- voclosporin
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of voclosporin by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Contraindicated.
Serious - Use Alternative (166)
- acalabrutinib
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of acalabrutinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid coadministration of acalabrutinib with strong CYP3A inhibitors. If a strong CYP3A inhibitor must be used short-term (eg, up to 7 days), temporarily interrupt treatment with acalabrutinib.
- adagrasib
adagrasib will increase the level or effect of posaconazole by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid coadministration of adagrasib, a CYP3A4 substrate, with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors until adagrasib concentrations have reached steady-state (after ~8 days). If steady state is not reached, concomitant use of strong CYP3A4 inhibitors will increase adagrasib concentrations and risk of its toxicities
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of adagrasib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid coadministration of adagrasib, a CYP3A4 substrate, with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors until adagrasib concentrations have reached steady-state (after ~8 days). If steady state is not reached, concomitant use of strong CYP3A4 inhibitors will increase adagrasib concentrations and risk of its toxicities
adagrasib, posaconazole. Either increases effects of the other by QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Each drug prolongs the QTc interval, which may increased the risk of Torsade de pointes, other serious arryhthmias, and sudden death. If coadministration unavoidable, more frequent monitoring is recommended for such patients. - ado-trastuzumab emtansine
posaconazole increases levels of ado-trastuzumab emtansine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. DM1, the cytotoxic component, is metabolized mainly by CYP3A4; strong CYP3A4 inhibitors may increase DM1 exposure and toxicity.
- afatinib
posaconazole increases levels of afatinib by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Reduce afatinib daily dose by 10 mg if not tolerated when coadministered with P-gp inhibitors.
- amiodarone
amiodarone and posaconazole both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- amisulpride
amisulpride and posaconazole both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. ECG monitoring is recommended if coadministered.
- anagrelide
anagrelide and posaconazole both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- apixaban
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of apixaban by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. If taking apixaban dose >2.5 mg BID, decrease dose by 50% if coadministered with strong dual inhibitors of CYP3A4 and P-gp; if currently taking apixaban 2.5 mg PO BID, avoid coadministration with strong dual inhibitors of CYP3A4 and P-gp
- aripiprazole
aripiprazole and posaconazole both increase QTc interval. Contraindicated.
- arsenic trioxide
arsenic trioxide and posaconazole both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- artemether
artemether and posaconazole both increase QTc interval. Contraindicated.
- asenapine transdermal
asenapine transdermal and posaconazole both increase QTc interval. Contraindicated.
- avanafil
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of avanafil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. CYP3A4 inhibitors may reduce avanafil clearance increasing systemic exposure to avanafil; significantly increased levels may result in significant adverse events including severe hypotension, syncope, visual changes, and priapism. Coadministration with strong CYP3A4 is contraindicated.
- avapritinib
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of avapritinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid coadministration of avapritinib with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors.
- axitinib
posaconazole increases levels of axitinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. If unable to avoid coadministration with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors, reduce axitinib dose by 50%.
- bedaquiline
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of bedaquiline by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid coadministration of bedaquiline with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors for >14 consecutive days, unless the benefit of treatment outweighs the risk
- bosutinib
posaconazole increases levels of bosutinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Strong CYP3A4 inhibitors increases bosutinib plasma concentration ~5-fold.
- brigatinib
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of brigatinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. If concomitant use of a strong CYP3A inhibitor cannot be avoided, reduce the brigatinib once daily dose by about 50% (ie, from 180 mg to 90 mg, or from 90 mg to 60 mg). After discontinuation of a strong CYP3A inhibitor, resume the brigatinib dose that was tolerated prior to initiating the strong CYP3A inhibitor.
- buprenorphine
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of buprenorphine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Contraindicated.
buprenorphine and posaconazole both increase QTc interval. Contraindicated. - buprenorphine transdermal
buprenorphine transdermal and posaconazole both increase QTc interval. Contraindicated.
- cabazitaxel
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of cabazitaxel by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Coadministration of cabazitaxel with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors should be avoided.
- cabozantinib
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of cabozantinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid coadministration of cabozantinib with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors. If a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor is required, decrease cabozantinib dose by 40 mg/day (Cometriq) or by 20 mg/day (Cabometyx). Resume previous dose 2-3 days after strong CYP3A4 inhibitor discontinued.
- calcitriol
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of calcitriol by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- capivasertib
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of capivasertib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. If unable to avoid coadministration of capivasertib with strong CYP3A inhibitors, reduce capivasertib dose and monitor for adverse effects.
- ceritinib
posaconazole increases levels of ceritinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid if possible; if concomitant use is unavoidable, reduce ceritinib dose by ~33%; after discontinuation of strong CYP3A inhibitor, resume at previous dose.
- chloroquine
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of chloroquine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- citalopram
citalopram and posaconazole both increase QTc interval. Contraindicated.
- clozapine
clozapine and posaconazole both increase QTc interval. Contraindicated.
- cobicistat
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of cobicistat by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- colchicine
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of colchicine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid use of colchicine with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors. If coadministration is necessary, decrease colchicine dose or frequency as recommended in prescribing information. Use of any colchicine product in conjunction with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors is contraindicated in patients with renal or hepatic impairment.
- copanlisib
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of copanlisib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. If concomitant use with strong CYP3A inhibitors cannot be avoided, reduce copanlisib dose to 45 mg.
- dabrafenib
posaconazole increases levels of dabrafenib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- daridorexant
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of daridorexant by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- desflurane
desflurane and posaconazole both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- disopyramide
disopyramide and posaconazole both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- dronedarone
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of dronedarone by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
dronedarone will increase the level or effect of posaconazole by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. The use of dronedarone in combination with other medications that can prolong the QT interval is considered contraindicated. Coadministration may result in additive effects and increased risk of ventricular arrhythmias including torsade de pointes. - edoxaban
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of edoxaban by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Dose adjustment may be required with strong P-gp inhibitors. DVT/PE treatment: Decrease dose to 30 mg PO once daily. NVAF: No dose reduction recommended
- elacestrant
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of elacestrant by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- elbasvir/grazoprevir
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of elbasvir/grazoprevir by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- eliglustat
eliglustat and posaconazole both increase QTc interval. Contraindicated.
- elvitegravir/cobicistat/emtricitabine/tenofovir DF
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of elvitegravir/cobicistat/emtricitabine/tenofovir DF by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- encorafenib
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of encorafenib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. If concomitant use of a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor is unavoidable, reduce encorafenib dose to one-third of the dose (eg, reduce from 450 mg/day to 150 mg/day). After discontinuing the inhibitor for 3-5 elimination half-lives, resume previous encorafenib dose.
encorafenib and posaconazole both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. - entrectinib
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of entrectinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid coadministration of strong CYP3A4 inhibitors with entrectinib, a CYP3A4 substrate. If coadministration unavoidable, reduce entrectinib dose to 100 mg/day for patients aged 12 y or older with BSA >1.50m2. Resume previous entrectinib dose after discontinuing strong CYP3A inhibitor for 3-5 elimination half-lives.
entrectinib and posaconazole both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. - erdafitinib
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of erdafitinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. If unable to avoid coadministration with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors, monitor closely for adverse reactions and consider decreasing dose accordingly. If strong CYP3A4 inhibitor is discontinued, consider increasing erdafitinib dose in the absence of any drug-related toxicities.
- ergotamine
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of ergotamine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- eribulin
eribulin and posaconazole both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- erythromycin base
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of erythromycin base by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- erythromycin ethylsuccinate
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of erythromycin ethylsuccinate by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- erythromycin lactobionate
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of erythromycin lactobionate by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- erythromycin stearate
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of erythromycin stearate by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- eszopiclone
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of eszopiclone by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- everolimus
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of everolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- fedratinib
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of fedratinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. If unable to avoid fedratinib coadministration with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors, decrease fedratinib dose to 200 mg/day. If CYP3A4 inhibitor discontinued, increase fedratinib dose to 300 mg/day for 2 weeks, and then 400 mg/day thereafter as tolerated.
- felbamate
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of felbamate by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- fentanyl
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of fentanyl by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. If coadministration of CYP3A4 inhibitors with fentanyl is necessary, monitor patients for respiratory depression and sedation at frequent intervals and consider fentanyl dose adjustments until stable drug effects are achieved.
- fentanyl intranasal
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of fentanyl intranasal by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. If coadministration of CYP3A4 inhibitors with fentanyl is necessary, monitor patients for respiratory depression and sedation at frequent intervals and consider fentanyl dose adjustments until stable drug effects are achieved.
- fentanyl transdermal
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of fentanyl transdermal by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. If coadministration of CYP3A4 inhibitors with fentanyl is necessary, monitor patients for respiratory depression and sedation at frequent intervals and consider fentanyl dose adjustments until stable drug effects are achieved.
- fentanyl transmucosal
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of fentanyl transmucosal by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. If coadministration of CYP3A4 inhibitors with fentanyl is necessary, monitor patients for respiratory depression and sedation at frequent intervals and consider fentanyl dose adjustments until stable drug effects are achieved.
- fexinidazole
posaconazole will decrease the level or effect of fexinidazole by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. If unable to avoid coadministration, monitor fexinidazole for decreased efficacy owing to decreased plasma concentrations of active M1 and M2 metabolites.
- flunisolide inhaled
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of flunisolide inhaled by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- fluticasone intranasal
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of fluticasone intranasal by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Strong CYP3A4 inhibitors may increase systemic corticosteroid adverse effects; monitor for signs/symptoms of high corticosteroid concentrations including Cushing type signs/symptoms.
- futibatinib
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of futibatinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Coadministration of futibatinib with drugs that are dual P-gp and strong CYP3A inhibitors may increase incidence/severity of futibatinib toxicities.
- gilteritinib
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of gilteritinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Consider alternatives to any strong CYP3A4 inhibitor when coadministered with gilteritinib. If such a combination cannot be avoided, closely monitor for gilteritinib-related adverse effects. Interrupt and reduce gilteritinib dosage in patients with serious or life-threatening toxicity.
gilteritinib and posaconazole both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. - glasdegib
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of glasdegib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Consider alternate therapies that are not strong CYP3A inhibitors or monitor for increased risk of adverse effects, including QTc interval prolongation.
- haloperidol
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of haloperidol by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Contraindicated.
- hydroxychloroquine sulfate
hydroxychloroquine sulfate and posaconazole both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- ibrutinib
posaconazole increases levels of ibrutinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Coadministration with posaconazole suspension at doses of 100 mg qDay, 100 mg BID, or 200 mg BID, reduce ibrutinib dose to 140 mg qDay (B-cell malignancies) or 280 mg qDay (graft versus host disease [GvHD]). Coadministration with posaconazole suspension at doses of 200 mg TID, 400 mg BID , posaconazole 300 mg IV qDay, posaconazole delayed-release tablets 300 mg qDay reduce ibrutinib dose to 70 mg qDay (B-cell malignancies) or 140 mg qDay (GvHD). After CYP3A inhibitor discontinuation, resume previous dose of ibrutinib.
- ibutilide
ibutilide and posaconazole both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- idelalisib
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of idelalisib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. If coadministered with strong CYP3A inhibitors, monitor for signs of idelalisib toxicity; follow recommendations for dosage modifications if adverse reactions occur
- indapamide
indapamide and posaconazole both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- infigratinib (DSC)
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of infigratinib (DSC) by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- irinotecan
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of irinotecan by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- irinotecan liposomal
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of irinotecan liposomal by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- isoflurane
isoflurane and posaconazole both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- ivosidenib
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of ivosidenib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid coadministration of strong CYP3A4 inhibitors with ivosidenib or replace with alternate therapies. If coadministration of a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor is unavoidable, reduce ivosidenib dose to 250 mg qDay. If the strong inhibitor is discontinued, increase ivosidenib dose (after at least 5 half-lives of the strong CYP3A4 inhibitor) to the recommended dose of 500 mg qDay. Monitor for increased risk of QTc interval prolongation.
ivosidenib and posaconazole both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid coadministration of QTc prolonging drugs with ivosidenib or replace with alternate therapies. If coadministration of a QTc prolonging drug is unavoidable, monitor for increased risk of QTc interval prolongation. - ketamine
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of ketamine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- larotrectinib
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of larotrectinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. If coadministration of larotrectinib with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors is unavoidable, reduce larotrectinib dose by 50%. Resume prior larotrectinib dose once CYP3A4 inhibitor discontinued for 3-5 half-lives.
- lasmiditan
lasmiditan increases levels of posaconazole by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- lefamulin
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of lefamulin by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid coadministration of lefamulin with strong CYP3A inhibitors.
- lemborexant
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of lemborexant by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid coadministration of lemborexant with moderate or strong CYP3A inhibitors.
- leniolisib
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of leniolisib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- lorlatinib
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of lorlatinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid coadministering lorlatinib with strong CYP3A inhibitors. If unavoidable, reduce lorlatinib dose by 25 mg/day. If strong CYP3A inhibitor discontinued, increase to previous lorlatinib (dose after 3 plasma half-lives of strong CYP3A inhibitor). See monograph for further details.
- lumacaftor/ivacaftor
lumacaftor/ivacaftor will decrease the level or effect of posaconazole by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- lurbinectedin
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of lurbinectedin by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. If coadministration unavoidable, reduce lurbinectedin dose by 50%. After strong CYP3A inhibitor discontinued for 5 half-lives, increase lurbinectedin to dose used before coadministration.
- macimorelin
macimorelin and posaconazole both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Macimorelin causes an increase of ~11 msec in the corrected QT interval. Avoid coadministration with drugs that prolong QT interval, which could increase risk for developing torsade de pointes-type ventricular tachycardia. Allow sufficient washout time of drugs that are known to prolong the QT interval before administering macimorelin.
- macitentan
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of macitentan by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid coadministering macitentan with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors
- mefloquine
mefloquine increases toxicity of posaconazole by QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Mefloquine may enhance the QTc prolonging effect of high risk QTc prolonging agents.
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of mefloquine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Potential for increased toxicity. Avoid coadministration during and for 15 weeks after discontinuing mefloquine. - midazolam intranasal
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of midazolam intranasal by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Coadministration of strong CYP3A4 inhibitors with midazolam intranasal causes higher midazolam systemic exposure, which may prolong sedation.
- midostaurin
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of midostaurin by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. If coadministration with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors cannot be avoided, monitor midostaurin for increased risk of adverse reactions, especially during the first week of treatment.
- mirtazapine
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of mirtazapine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Contraindicated.
- mobocertinib
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of mobocertinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
mobocertinib and posaconazole both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. If coadministration unavoidable, reduce mobocertinib dose and monitor QTc interval more frequently. - neratinib
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of neratinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid coadministration of neratinib with strong/moderate CYP3A4 inhibitors.
- nirogacestat
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of nirogacestat by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- olaparib
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of olaparib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. If coadministration with strong CYP3A inhibitors cannot be avoided, reduce olaparib dose to 150 mg (capsule) or 100 mg (tablet) PO BID. Do not substitute tablets with capsules.
- omaveloxolone
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of omaveloxolone by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. If unavoidable, reduce omaveloxolone dose to 50 mg/day. Closely monitor and discontinue if adverse effects emerge.
- ombitasvir/paritaprevir/ritonavir
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of ombitasvir/paritaprevir/ritonavir by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- ombitasvir/paritaprevir/ritonavir & dasabuvir (DSC)
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of ombitasvir/paritaprevir/ritonavir & dasabuvir (DSC) by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- ondansetron
posaconazole and ondansetron both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid with congenital long QT syndrome; ECG monitoring recommended with concomitant medications that prolong QT interval, electrolyte abnormalities, CHF, or bradyarrhythmias. Potential for increased ondansetron levels.
- osimertinib
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of osimertinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid coadministration of osimertinib with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors. If no other alternative treatment exists, monitor patient more closely for adverse effects.
- oxaliplatin
oxaliplatin and posaconazole both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- oxycodone
posaconazole increases levels of oxycodone by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Oxycodone dose reduction may be warranted when coadministered with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors.
- palbociclib
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of palbociclib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid coadministration of palbociclib with strong CYP3A inhibitors. If unable to avoid, reduce palbociclib dose to 75 mg/day.
- palovarotene
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of palovarotene by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- panobinostat
posaconazole and panobinostat both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Panobinostat is known to significantly prolong QT interval. Panobinostat prescribing information states use with drugs known to prolong QTc is not recommended.
- pazopanib
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of pazopanib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid coadministration of pazopanib with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors if possible; if must coadminister, decrease pazopanib dose to 400 mg/day
- pemigatinib
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of pemigatinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. If coadministration with strong or moderate CYP3A4 inhibitors is unavoidable, reduce pemigatinib dose (refer to drug monograph dosage modifications). After discontinuing the CYP3A4 inhibitor for 3 elimination half-lives, may resume previous pemigatinib dose.
- pentamidine
pentamidine and posaconazole both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- pexidartinib
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of pexidartinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. If coadministration with strong or moderate CYP3A4 inhibitors is unavoidable, reduce pexidartinib dose (refer to drug monograph dosage modifications). After discontinuing the CYP3A4 inhibitor for 3 elimination half-lives, may resume previous pexidartinib dose.
- phenytoin
phenytoin will decrease the level or effect of posaconazole by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- pimavanserin
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of pimavanserin by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Decrease dose to 17 mg/day if pimavanserin is coadministered with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors.
- pimozide
pimozide and posaconazole both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
posaconazole increases levels of pimozide by decreasing metabolism. Contraindicated. Risk of QT interval prolongation. - pirtobrutinib
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of pirtobrutinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. If coadministration is unavoidable, reduce pirtobrutinib by 50 mg. If current pirtobrutinib dose is 50 mg qDay, discontinue pirtobrutinib for duration of strong CYP3A inhibitor use. Once strong CYP3A inhibitor discontinued for 5 half-lives, resume pirtobrutinib at the dose taken before initiating the strong CYP3A inhibitor.
- pitolisant
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of pitolisant by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- pomalidomide
posaconazole increases levels of pomalidomide by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
posaconazole increases levels of pomalidomide by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. - ponatinib
posaconazole increases levels of ponatinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Decrease ponatinib starting dose to 30 mg qDay if coadministration with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors cannot be avoided.
- pralsetinib
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of pralsetinib by Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Combined CYP3A4 and P-gp inhibitors increase levels of pralsetinib, a CYP3A4 and P-gp substrate. If unable to avoid, reduce dose (see pralsetinib prescribing information). After combined P-gp and strong CYP3A4 inhibitor discontinued, resume previous pralsetinib dose.
- procainamide
posaconazole and procainamide both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- quinidine
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of quinidine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Contraindicated. Use of posaconazole in combination with drugs that both prolong the QT interval and are substrates for CYP3A4 is contraindicated
quinidine will increase the level or effect of posaconazole by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
quinidine and posaconazole both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. - ranolazine
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of ranolazine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- red yeast rice
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of red yeast rice by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. May increase creatine kinase levels and increase risk of myopathy or rhabdomyolysis; red yeast rice contains monocolin K (reportedly identical to lovastatin)
- repotrectinib
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of repotrectinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Discontinue strong or moderate CYP3A inhibitors and wait 3-5 elimination half-lives before initiating repotrectinib.
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of repotrectinib by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. - ribociclib
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of ribociclib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. If a strong CYP3A inhibitor must be coadministered with ribociclib, reduce the ribociclib starting dose to 400 mg/day.
- rifabutin
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of rifabutin by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- rimegepant
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of rimegepant by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of rimegepant by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. - riociguat
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of riociguat by decreasing metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Coadministration of riociguat (substrate of CYP isoenzymes 1A1, 2C8, 3A, 2J2) with strong CYP inhibitors may require a decreased initial dose of 0.5 mg PO TID; monitor for signs of hypotension and reduce dose if needed
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of riociguat by Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Coadministration of riociguat (an ABCG2 [BCRP] substrate) with strong ABCG2 inhibitors may require a decreased initial dose of 0.5 mg PO TID; monitor for signs of hypotension and reduce dose if needed - rivaroxaban
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of rivaroxaban by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- ruxolitinib
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of ruxolitinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Reduce ruxolitinib starting dose to 10 mg BID with platelet count 100 X 10^9/L or more and concurrent use of strong CYP3A4 inhibitors; avoid with platelet counts <100 X 10^9/L
- ruxolitinib topical
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of ruxolitinib topical by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Reduce ruxolitinib starting dose to 10 mg BID with platelet count 100 X 10^9/L or more and concurrent use of strong CYP3A4 inhibitors; avoid with platelet counts <100 X 10^9/L
- Saccharomyces boulardii
posaconazole decreases effects of Saccharomyces boulardii by unspecified interaction mechanism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Systemic or oral antifungals may decrease activity of probiotic.
- selpercatinib
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of selpercatinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- selumetinib
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of selumetinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. If coadministration with strong or moderate CYP3A4 inhibitors cannot be avoided, reduce selumetinib dosage (refer to selumetinib monograph for further information). After discontinuation of the strong or moderate CYP3A4 inhibitor for 3 elimination half-lives, resume selumetinib dose that was taken before initiating the inhibitor.
- sevoflurane
sevoflurane and posaconazole both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- silodosin
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of silodosin by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- siponimod
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of siponimod by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Coadministration of siponimod with a moderate or strong CYP3A4 inhibitor PLUS a moderate or strong CYP2C9 inhibitor is not recommended.
siponimod and posaconazole both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. - sirolimus
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of sirolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- solifenacin
solifenacin and posaconazole both increase QTc interval. Contraindicated.
- sonidegib
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of sonidegib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid coadministration of sonidegib with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors.
- sorafenib
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of sorafenib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- sotalol
posaconazole and sotalol both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- sotorasib
sotorasib will decrease the level or effect of posaconazole by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. If use is unavoidable, refer to the prescribing information of the P-gp substrate for dosage modifications.
- sparsentan
posaconazole, sparsentan. Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. If unavoidable, interrupt treatment with sparsentan. When resuming sparsentan, consider dose titration. .
- stiripentol
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of stiripentol by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- suvorexant
posaconazole increases levels of suvorexant by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Suvorexant not recommended with use of strong CYP3A4 inhibitors.
- tacrolimus
tacrolimus and posaconazole both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- tamsulosin
posaconazole increases levels of tamsulosin by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- tazemetostat
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of tazemetostat by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- teniposide
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of teniposide by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- tepotinib
tepotinib will increase the level or effect of posaconazole by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. If concomitant use unavoidable, reduce the P-gp substrate dosage if recommended in its approved product labeling.
- tetrabenazine
tetrabenazine and posaconazole both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- tiagabine
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of tiagabine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- tofacitinib
posaconazole increases levels of tofacitinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Reduce tofacitinib dose to 5 mg qDay when coadministered with potent CYP3A4 inhibitors.
- tolvaptan
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of tolvaptan by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- trabectedin
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of trabectedin by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. If strong CYP3A inhibitor must be used, short-term (eg, less than 14 days), administer strong CYP3A inhibitor 1 week after trabectedin infusion, and discontinue the day prior to next trabectedin infusion
- tramadol
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of tramadol by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- trazodone
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of trazodone by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- ubrogepant
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of ubrogepant by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Contraindicated.
- umeclidinium bromide/vilanterol inhaled
posaconazole increases toxicity of umeclidinium bromide/vilanterol inhaled by QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Exercise extreme caution when vilanterol coadministered with drugs that prolong QTc interval; adrenergic agonist effects on the cardiovascular system may be potentiated.
- vandetanib
posaconazole, vandetanib. Either increases toxicity of the other by QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid coadministration with drugs known to prolong QT interval; if a drug known to prolong QT interval must be used, more frequent ECG monitoring is recommended.
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of vandetanib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. - vemurafenib
vemurafenib and posaconazole both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Concomitant use of vemurafenib with drugs that prolong QT interval is not recommended. Posaconazole may also increase levels of vemurafenib.
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of vemurafenib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Contraindicated. - vilanterol/fluticasone furoate inhaled
posaconazole increases toxicity of vilanterol/fluticasone furoate inhaled by QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Exercise extreme caution when vilanterol coadministered with drugs that prolong QTc interval; adrenergic agonist effects on the cardiovascular system may be potentiated.
- vilazodone
posaconazole increases levels of vilazodone by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Strong CYP3A4 inhibitors may increase vilazodone plasma levels by 50% - Reduce daily dose to 20 mg.
- vinblastine
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of vinblastine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. increased risk of neurotoxicity, development of SIADH and other adverse effects
- vincristine
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of vincristine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. increased risk of neurotoxicity, development of SIADH and other adverse effects
- vincristine liposomal
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of vincristine liposomal by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. increased risk of neurotoxicity, development of SIADH and other adverse effects
- vorapaxar
posaconazole increases levels of vorapaxar by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- voriconazole
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of voriconazole by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Contraindicated.
Monitor Closely (320)
- abemaciclib
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of abemaciclib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Strong CYP3A4 inhibitors increase plasma levels of abemaciclib and its metabolites. Abemaciclib dose reduction required. If a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor is discontinued, increase abemaciclib to the dose prior to initiating the strong inhibitor.
- albuterol
albuterol and posaconazole both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- alfuzosin
posaconazole and alfuzosin both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- almotriptan
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of almotriptan by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- alprazolam
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of alprazolam by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- aluminum hydroxide
aluminum hydroxide will decrease the level or effect of posaconazole by increasing gastric pH. Applies only to oral form of both agents. Use Caution/Monitor.
- amiodarone
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of amiodarone by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
amiodarone will increase the level or effect of posaconazole by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor. - amitriptyline
amitriptyline and posaconazole both increase QTc interval. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- amlodipine
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of amlodipine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- amoxapine
amoxapine and posaconazole both increase QTc interval. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- apalutamide
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of apalutamide by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Coadministration of apalutamide with strong CYP3A4 or CYP2C8 inhibitors does not require initial dosage modification; however, dose reduction may be needed based on tolerability.
- aprepitant
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of aprepitant by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- arformoterol
arformoterol and posaconazole both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- aripiprazole
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of aripiprazole by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- artemether/lumefantrine
artemether/lumefantrine and posaconazole both increase QTc interval. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of artemether/lumefantrine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. - atogepant
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of atogepant by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Recommended atogepant dosage is 10 mg PO qDay when coadministered with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors.
- atomoxetine
atomoxetine and posaconazole both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- atorvastatin
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of atorvastatin by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- bazedoxifene/conjugated estrogens
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of bazedoxifene/conjugated estrogens by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- bedaquiline
posaconazole and bedaquiline both increase QTc interval. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. ECG should be monitored closely
- benzhydrocodone/acetaminophen
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of benzhydrocodone/acetaminophen by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Coadministration with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors may increase hydrocodone (benzhydrocodone is prodrug of hydrocodone) plasma concentrations and can result in potentially fatal respiratory depression.
- berotralstat
posaconazole increases levels of berotralstat by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
berotralstat will increase the level or effect of posaconazole by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor. Monitor or titrate P-gp substrate dose if coadministered. - betrixaban
posaconazole increases levels of betrixaban by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor. Decrease betrixaban dose to 80 mg PO once, then 40 mg PO qDay if coadministered with a P-gp inhibitor.
- bexarotene
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of bexarotene by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- bortezomib
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of bortezomib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- brentuximab vedotin
posaconazole increases levels of brentuximab vedotin by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Monitor patients for adverse reactions. .
- brexpiprazole
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of brexpiprazole by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Administer half of the usual brexpiprazole dose when coadministered with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors. If also administered with a strong/moderate CYP2D6 inhibitor, administer a quarter of brexpiprazole dose.
- budesonide
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of budesonide by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- buprenorphine subdermal implant
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of buprenorphine subdermal implant by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Monitor patients already on buprenorphine subdermal implant who require newly-initiated treatment with CYP3A4 inhibitors for signs and symptoms of overmedication. If the dose of the concomitant CYP3A4 inhibitor cannot be reduced or discontinued, implant removal may be necessary and the patient should then be treated with a buprenorphine dosage form that permits dose adjustments. If a CYP3A4 inhibitor is discontinued in a patient who has been stabilized on buprenorphine, monitor the patient for withdrawal.
- buprenorphine, long-acting injection
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of buprenorphine, long-acting injection by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Patients who transfer to buprenorphine long-acting injection from transmucosal buprenorphine coadministered with CYP3A4 inhibitors should be monitored to ensure buprenorphine plasma levels are adequate. Within 2 weeks, if signs and symptoms of buprenorphine toxicity or overdose occur and the concomitant CYP3A4 inhibitor cannot be reduced or discontinued, transition the patient back to a buprenorphine formulation that permits dose adjustments.
- buspirone
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of buspirone by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- busulfan
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of busulfan by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- calcifediol
posaconazole, calcifediol. affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. CYP450 inhibitors may inhibit enzymes involved in vitamin D metabolism (CYP24A1 and CYP27B1). This may alter serum levels of calcifediol and decrease the conversion of calcifediol to calcitriol. Dose adjustment of calcifediol may be required, and serum 25hydroxyvitamin D, intact PTH, and serum calcium concentrations should be closely monitored when initiating or discontinuing a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor.
- calcium carbonate
calcium carbonate will decrease the level or effect of posaconazole by increasing gastric pH. Applies only to oral form of both agents. Use Caution/Monitor.
- cannabidiol
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of cannabidiol by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Consider reducing the cannabidiol dose when coadministered with a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor.
- capmatinib
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of capmatinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- carbamazepine
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
carbamazepine decreases levels of posaconazole by increasing metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. - cariprazine
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of cariprazine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Coadministration with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors requires cariprazine dose reduction. See Dosage Modification section in drug monograph.
- ceritinib
posaconazole increases levels of ceritinib by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
- chlordiazepoxide
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of chlordiazepoxide by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- chlorpromazine
chlorpromazine and posaconazole both increase QTc interval. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- chlorpropamide
posaconazole increases levels of chlorpropamide by decreasing metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- ciclesonide inhaled
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of ciclesonide inhaled by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- cilostazol
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of cilostazol by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- cimetidine
cimetidine will decrease the level or effect of posaconazole by increasing gastric pH. Applies only to oral form of both agents. Use Caution/Monitor.
- cinacalcet
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of cinacalcet by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- citalopram
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of citalopram by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Combination may increase risk of serotonin syndrome or neuroleptic malignant syndrome like reactions. ECG monitoring is recommended, along with drugs that may prolong the QT interval.
- clarithromycin
clarithromycin will increase the level or effect of posaconazole by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
clarithromycin and posaconazole both increase QTc interval. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. - clomipramine
clomipramine and posaconazole both increase QTc interval. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- clonazepam
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of clonazepam by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- clopidogrel
posaconazole will decrease the level or effect of clopidogrel by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Inhibition of CYP3A4 will reduce clopidogrel bioactivation
- clorazepate
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of clorazepate by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- clotrimazole
clotrimazole will decrease the level or effect of posaconazole by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
- clozapine
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of clozapine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- conjugated estrogens
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of conjugated estrogens by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- conjugated estrogens, vaginal
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of conjugated estrogens, vaginal by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- cortisone
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of cortisone by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- crizotinib
posaconazole increases levels of crizotinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Concomitant use of strong CYP3A inhibitors should be avoided. ECG monitoring is recommended, along with drugs that may prolong the QT interval.
- cyclosporine
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of cyclosporine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Perform frequent monitoring of cyclosporine trough concentrations during and at discontinuation of posaconazole treatment and cyclosporine dose adjusted accordingly.
cyclosporine will increase the level or effect of posaconazole by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor. - dabigatran
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of dabigatran by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor. Atrial fibrillation: Avoid coadministering dabigatran with P-gp inhibitors if CrCl <30 mL/min. DVT/PE treatment: Avoid coadministering dabigatran with P-gp inhibitors if CrCl <50 mL/min
- danicopan
danicopan will increase the level or effect of posaconazole by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor. Danicopan increases plasma concentrations of P-gp substrates; consider dose reduction of P-gp substrates where minimal concentration changes may lead to serious adverse reactions.
- darifenacin
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of darifenacin by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- darolutamide
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of darolutamide by Other (see comment). Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Darolutamide is a P-gp and CYP3A4 substrate. Closely monitor for increased adverse reactions and modify dose of darolutamide as needed when coadministered with drugs that are both P-gp and strong or moderate CYP3A4 inhibitors.
- darunavir
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of darunavir by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Monitor for increased darunavir or cobicistat adverse reactions.
- dasatinib
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of dasatinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
dasatinib and posaconazole both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. - deflazacort
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of deflazacort by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Decrease deflazacort dose to one-third of the recommended dose if coadministered with moderate or strong CYP3A4 inhibitors.
posaconazole and deflazacort both decrease serum potassium. Use Caution/Monitor. - degarelix
degarelix and posaconazole both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- desipramine
desipramine and posaconazole both increase QTc interval. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- deutetrabenazine
deutetrabenazine and posaconazole both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. At the maximum recommended dose, deutetrabenazine does not prolong QT interval to a clinically relevant extent. Certain circumstances may increase risk of torsade de pointes and/or sudden death in association with drugs that prolong the QTc interval (eg, bradycardia, hypokalemia or hypomagnesemia, coadministration with other drugs that prolong QTc interval, presence of congenital QT prolongation).
- dexamethasone
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of dexamethasone by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- dexlansoprazole
dexlansoprazole will decrease the level or effect of posaconazole by increasing gastric pH. Applies only to oral form of both agents. Use Caution/Monitor.
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of dexlansoprazole by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. - diazepam
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of diazepam by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- diazepam intranasal
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of diazepam intranasal by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Strong or moderate CYP3A4 inhibitors may decrease rate of diazepam elimination, thereby increasing adverse reactions to diazepam.
- dichlorphenamide
dichlorphenamide and posaconazole both decrease serum potassium. Use Caution/Monitor.
- dienogest/estradiol valerate
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of dienogest/estradiol valerate by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Monitor for potential adverse effects such as nausea, irregular uterine bleeding, breast tenderness and headache.
- digoxin
posaconazole increases levels of digoxin by decreasing metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- diltiazem
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of diltiazem by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- dofetilide
dofetilide and posaconazole both increase QTc interval. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- dolasetron
dolasetron and posaconazole both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- donepezil
donepezil and posaconazole both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- doravirine
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of doravirine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Coadministration of doravirine and CYP3A4 inhibitors may increase plasma concentrations and toxicities of doravirine.
- doxepin
doxepin and posaconazole both increase QTc interval. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- dronabinol
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of dronabinol by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Dronabinol is a CYP3A4 substrate.
- dronedarone
dronedarone and posaconazole both increase QTc interval. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- droperidol
droperidol and posaconazole both increase QTc interval. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- duvelisib
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of duvelisib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Coadministration with a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor increases duvelisib AUC, which may increase the risk of duvelisib toxicities. Reduce duvelisib dose to 15 mg BID when coadministered with a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor.
- elagolix
elagolix will increase the level or effect of posaconazole by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of elagolix by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Coadministration of elagolix 200 mg BID with strong CYP3A inhibitors for >1 month is not recommended. Limit elagolix dose to 150 mg qDay and CYP3A inhibitor duration of use to 6 months if coadministered. - eletriptan
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of eletriptan by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- eliglustat
eliglustat increases levels of posaconazole by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Monitor therapeutic drug concentrations, as indicated, or consider reducing the dosage of the P-gp substrate and titrate to clinical effect.
- elvitegravir
posaconazole increases levels of elvitegravir by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Elvitegravir is a CYP3A4 substrate; if coadministered with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors may increase levels.
- enfortumab vedotin
posaconazole increases toxicity of enfortumab vedotin by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Enfortumab vedotin is an antibody-drug conjugate that releases monomethylauristatin E (MMAE) via proteolytic cleavage. MMAE is primarily metabolized by CYP3A4 in vitro. Coadministration with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors may increase free MMAE exposure, which may increase the incidence or severity of toxicities.
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of enfortumab vedotin by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Coadministration with dual P-gp and strong CYP3A4 inhibitors may increase unconjugated small molecule microtubule disrupting agent, monomethyl auristatin E (MMAE) exposure, which may increase the risk of enfortumab vedotin toxicities. Closely monitor for signs of toxicities. - enzalutamide
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of enzalutamide by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- epinephrine
epinephrine and posaconazole both increase QTc interval. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- epinephrine racemic
epinephrine racemic and posaconazole both increase QTc interval. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- erlotinib
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of erlotinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- erythromycin base
erythromycin base will increase the level or effect of posaconazole by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
erythromycin base and posaconazole both increase QTc interval. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. - erythromycin ethylsuccinate
erythromycin ethylsuccinate will increase the level or effect of posaconazole by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
erythromycin ethylsuccinate and posaconazole both increase QTc interval. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. - erythromycin lactobionate
erythromycin lactobionate will increase the level or effect of posaconazole by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
erythromycin lactobionate and posaconazole both increase QTc interval. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. - erythromycin stearate
erythromycin stearate will increase the level or effect of posaconazole by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
erythromycin stearate and posaconazole both increase QTc interval. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. - escitalopram
escitalopram increases toxicity of posaconazole by QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of escitalopram by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. - esomeprazole
esomeprazole will decrease the level or effect of posaconazole by increasing gastric pH. Applies only to oral form of both agents. Use Caution/Monitor.
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of esomeprazole by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. - estradiol
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of estradiol by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- estradiol vaginal
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of estradiol vaginal by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Coadministration with CYP3A4 inhibitors may increase plasma concentrations of estrogens and toxicities.
- estrogens conjugated synthetic
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of estrogens conjugated synthetic by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- estrogens esterified
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of estrogens esterified by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- estropipate
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of estropipate by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- ethinylestradiol
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of ethinylestradiol by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- ethosuximide
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of ethosuximide by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- ethotoin
ethotoin decreases levels of posaconazole by increasing metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- etonogestrel
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of etonogestrel by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- etoposide
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of etoposide by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- etravirine
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of etravirine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- ezogabine
ezogabine, posaconazole. Either increases toxicity of the other by QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. Slight and transient QT-prolongation observed with ezogabine, particularly when dose titrated to 1200 mg/day. QT interval should be monitored when ezogabine is prescribed with agents known to increase QT interval.
- famotidine
famotidine will decrease the level or effect of posaconazole by increasing gastric pH. Applies only to oral form of both agents. Use Caution/Monitor.
- felodipine
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of felodipine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
felodipine will increase the level or effect of posaconazole by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor. - fesoterodine
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of fesoterodine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- fingolimod
fingolimod and posaconazole both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- flecainide
flecainide and posaconazole both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- fluconazole
fluconazole and posaconazole both increase QTc interval. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- fludrocortisone
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of fludrocortisone by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- fluoxetine
fluoxetine and posaconazole both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- fluphenazine
fluphenazine and posaconazole both increase QTc interval. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- flurazepam
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of flurazepam by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- flutamide
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of flutamide by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- fluticasone furoate
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of fluticasone furoate by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Strong CYP3A4 inhibitors may increase fluticasone systemic exposure
- fluticasone inhaled
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of fluticasone inhaled by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Strong CYP3A4 inhibitors may increase fluticasone systemic exposure
- fluvoxamine
fluvoxamine and posaconazole both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- formoterol
formoterol and posaconazole both increase QTc interval. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- fosamprenavir
fosamprenavir decreases levels of posaconazole by unknown mechanism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Combination may decrease posaconazole plasma concentrations. If administered concomitantly, monitor closely for breakthrough fungal infections.
- fosaprepitant
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of fosaprepitant by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- foscarnet
foscarnet and posaconazole both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- fosphenytoin
fosphenytoin will decrease the level or effect of posaconazole by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
fosphenytoin decreases levels of posaconazole by increasing metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. - fostamatinib
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of fostamatinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Strong CYP3A4 inhibitors may increase exposure to R406 (fostamatinib major active metabolite). Monitor for toxicities that may require fostamatinib dose reduction.
fostamatinib will increase the level or effect of posaconazole by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor. Concomitant use of fostamatinib may increase concentrations of P-gp substrates. Monitor for toxicities of the P-gp substrate drug that may require dosage reduction when given concurrently with fostamatinib. - gefitinib
posaconazole increases levels of gefitinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Coadministration of strong CYP3A4 inhibitors may increase risk for gefitinib adverse effects.
- gemifloxacin
gemifloxacin and posaconazole both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- gepirone
gepirone and posaconazole both increase QTc interval. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- glecaprevir/pibrentasvir
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of glecaprevir/pibrentasvir by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
glecaprevir/pibrentasvir will increase the level or effect of posaconazole by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor. - glimepiride
posaconazole increases levels of glimepiride by decreasing metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- glipizide
posaconazole increases levels of glipizide by decreasing metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- glyburide
posaconazole increases levels of glyburide by decreasing metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- granisetron
granisetron and posaconazole both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- guanfacine
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of guanfacine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Strong or moderate CYP3A4 inhibitors significantly increase guanfacine plasma concentrations. FDA-approved labeling for extended-release (ER) guanfacine recommends that, if coadministered, the guanfacine dosage should be decreased to half of the recommended dose. Specific recommendations for immediate-release (IR) guanfacine are not available.
- haloperidol
haloperidol and posaconazole both increase QTc interval. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- hydrocodone
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of hydrocodone by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Coadministration with CYP3A4 inhibitors may increase hydrocodone plasma concentrations and can result in potentially fatal respiratory depression
- hydrocortisone
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of hydrocortisone by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- hydroxyprogesterone caproate (DSC)
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of hydroxyprogesterone caproate (DSC) by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- hydroxyzine
hydroxyzine and posaconazole both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- ibuprofen/famotidine
ibuprofen/famotidine will decrease the level or effect of posaconazole by increasing gastric pH. Applies only to oral form of both agents. Use Caution/Monitor.
- ifosfamide
posaconazole will decrease the level or effect of ifosfamide by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Coadministration of CYP3A4 inhibitors may decrease the metabolism of ifosfamide to its active alkylating metabolites and decrease the efficacy of ifosfamide.
- iloperidone
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of iloperidone by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
iloperidone and posaconazole both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. - imipramine
imipramine and posaconazole both increase QTc interval. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- indacaterol, inhaled
indacaterol, inhaled, posaconazole. QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. Drugs that are known to prolong the QTc interval may have an increased the risk of ventricular arrhythmias.
- indinavir
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of indinavir by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
indinavir will increase the level or effect of posaconazole by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor. - istradefylline
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of istradefylline by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Do not exceed istradefylline 20 mg/day if coadministered with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors.
istradefylline will increase the level or effect of posaconazole by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor. Istradefylline 40 mg/day increased peak levels and AUC of P-gp substrates in clinical trials. Consider dose reduction of sensitive P-gp substrates. - itraconazole
itraconazole will increase the level or effect of posaconazole by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
itraconazole and posaconazole both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. - ivacaftor
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of ivacaftor by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Reduce ivacaftor dose if coadministered with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors. See specific ivacaftor-containing product for precise dosage modification.
ivacaftor increases levels of posaconazole by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor. Ivacaftor and its M1 metabolite has the potential to inhibit P-gp; may significantly increase systemic exposure to sensitive P-gp substrates with a narrow therapeutic index. - ixabepilone
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of ixabepilone by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- ketoconazole
ketoconazole will increase the level or effect of posaconazole by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
ketoconazole and posaconazole both increase QTc interval. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. - lacosamide
posaconazole, lacosamide. Either increases levels of the other by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Consider decreasing lacosamide dose when coadministered with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors.
- lansoprazole
lansoprazole will decrease the level or effect of posaconazole by increasing gastric pH. Applies only to oral form of both agents. Use Caution/Monitor.
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of lansoprazole by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. - lapatinib
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of lapatinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
lapatinib will increase the level or effect of posaconazole by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
lapatinib and posaconazole both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. - lenvatinib
posaconazole and lenvatinib both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. Lenvatinib prescribing information recommends monitoring ECG closely when coadministered with QT prolonging drugs.
- levamlodipine
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of levamlodipine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Coadministration with moderate and strong CYP3A inhibitors results in increased systemic exposure to amlodipine and may require dose reduction. Monitor for symptoms of hypotension and edema when amlodipine is coadministered with CYP3A inhibitors to determine the need for dose adjustment.
- levofloxacin
levofloxacin and posaconazole both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- levoketoconazole
levoketoconazole and posaconazole both increase QTc interval. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
levoketoconazole will increase the level or effect of posaconazole by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor. - levomilnacipran
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of levomilnacipran by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Do not exceed 80 mg/day of levomilnacipran when coadministered with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors
- levonorgestrel oral/ethinylestradiol/ferrous bisglycinate
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of levonorgestrel oral/ethinylestradiol/ferrous bisglycinate by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Coadministration with CYP3A4 inhibitors may increase the plasma hormone concentrations. Use of a nonhormonal contraceptive is recommended.
- lithium
lithium and posaconazole both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- lofepramine
lofepramine and posaconazole both increase QTc interval. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- lopinavir
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of lopinavir by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- loratadine
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of loratadine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
loratadine will increase the level or effect of posaconazole by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor. - lumacaftor/ivacaftor
posaconazole increases levels of lumacaftor/ivacaftor by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Strong CYP3A inhibitors do not impact lumacaftor exposure, but increased ivacaftor exposure by 4.3-fold. Due to the induction effect of lumacaftor on CYP3A, at steady-state the net exposure of ivacaftor is not expected to exceed that when given in the absence of lumacaftor at a dose of 150 mg q12hr (the approved dose of ivacaftor monotherapy). Therefore, no dose adjustment is necessary when CYP3A inhibitors are initiated in patients currently taking lumacaftor/ivacaftor. However, when initiating lumacaftor/ivacaftor in patients taking strong CYP3A inhibitors, reduce the dose to 1 tablet daily (lumacaftor 200 mg/ivacaftor 125 mg total daily dose) for the first week of treatment to allow for the steady-state induction effect of lumacaftor. Following this period, continue with the recommended daily dose. No dose adjustment is required for moderate or weak CYP3A4 inhibitors.
- lumateperone
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of lumateperone by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Reduce lumateperone dose to 10.5 mg/day if coadministered with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors.
- lumefantrine
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of lumefantrine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
lumefantrine and posaconazole both increase QTc interval. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. - maprotiline
maprotiline and posaconazole both increase QTc interval. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- maraviroc
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of maraviroc by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Decrease maraviroc dose to 150 mg BID when coadministered with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors
- marijuana
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of marijuana by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- medroxyprogesterone
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of medroxyprogesterone by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Use alternative if available.
- mestranol
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of mestranol by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- methadone
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of methadone by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
methadone and posaconazole both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. - methylprednisolone
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of methylprednisolone by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- metoclopramide
metoclopramide decreases levels of posaconazole by inhibition of GI absorption. Applies only to oral form of both agents. Use Caution/Monitor.
- metoclopramide intranasal
metoclopramide intranasal will increase the level or effect of posaconazole by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Metoclopramide may decrease the absorption of posaconazole PO suspension. Monitor for reduced therapeutic effect of posaconazole PO suspension.
- midazolam
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of midazolam by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- mifepristone
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of mifepristone by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Do not exceed mifepristone 300 mg/day for Cushing syndrome when coadministered with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors; combination may also prolong QT interval. Use alternatives if available
- mirvetuximab soravtansine
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of mirvetuximab soravtansine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Coadministration with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors may increase unconjugated DM4 (a CYP3A4 substrate and the cytotoxic component of the antibody drug conjugate for mirvetuximab soravtansine) exposure, which may increase the risk of adverse reactions.
- modafinil
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of modafinil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- mometasone, intranasal
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of mometasone, intranasal by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- moxifloxacin
moxifloxacin and posaconazole both increase QTc interval. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- naldemedine
posaconazole increases levels of naldemedine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Monitor naldemedine for potential adverse effects if coadministered with strong or moderate CYP3A4 inhibitors.
posaconazole increases levels of naldemedine by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor. Monitor naldemedine for potential adverse effects if coadministered with P-gp inhibitors. - nefazodone
nefazodone will increase the level or effect of posaconazole by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of nefazodone by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. - nelfinavir
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of nelfinavir by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- netupitant/palonosetron
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of netupitant/palonosetron by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Netupitant is mainly metabolized by CYP3A4; no dosage adjustment is required
- nevirapine
posaconazole increases levels of nevirapine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Potential for increased toxicity. .
- nicardipine
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of nicardipine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
nicardipine will increase the level or effect of posaconazole by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor. - nifedipine
nifedipine will decrease the level or effect of posaconazole by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
- nilotinib
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of nilotinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
nilotinib will increase the level or effect of posaconazole by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
nilotinib and posaconazole both increase QTc interval. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. - nintedanib
posaconazole increases levels of nintedanib by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. If nintedanib adverse effects occur, management may require interruption, dose reduction, or discontinuation of therapy .
- nisoldipine
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of nisoldipine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- nizatidine
nizatidine will decrease the level or effect of posaconazole by increasing gastric pH. Applies only to oral form of both agents. Use Caution/Monitor.
- norgestrel
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of norgestrel by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Strong or moderate CYP3A4 inhibitors may increase systemic concentration of norgestrel, which may increase risk for adverse effects
- nortriptyline
nortriptyline and posaconazole both increase QTc interval. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- octreotide
octreotide and posaconazole both increase QTc interval. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- octreotide (Antidote)
octreotide (Antidote) and posaconazole both increase QTc interval. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- ofloxacin
ofloxacin and posaconazole both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- olanzapine
olanzapine and posaconazole both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- oliceridine
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of oliceridine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. If concomitant use is necessary, may require less frequent oliceridine dosing. Closely monitor for respiratory depression and sedation and titrate subsequent doses accordingly. If inhibitor is discontinued, consider increase oliceridine dosage until stable drug effects are achieved. Monitor for signs of opioid withdrawal.
- olodaterol inhaled
posaconazole and olodaterol inhaled both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. Drugs that prolong the QTc interval and may potentiate the effects of beta2 agonists on the cardiovascular system; increased risk of ventricular arrhythmias
- omeprazole
omeprazole will decrease the level or effect of posaconazole by increasing gastric pH. Applies only to oral form of both agents. Use Caution/Monitor.
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of omeprazole by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. - osilodrostat
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of osilodrostat by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Reduce dose of osilodrostat, a CYP3A4 substrate, by half when coadministered with a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor.
- osimertinib
osimertinib and posaconazole both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. Conduct periodic monitoring with ECGs and electrolytes in patients taking drugs known to prolong the QTc interval.
- ospemifene
posaconazole increases levels of ospemifene by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- ozanimod
ozanimod and posaconazole both increase QTc interval. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. The potential additive effects on heart rate, treatment with ozanimod should generally not be initiated in patients who are concurrently treated with QT prolonging drugs with known arrhythmogenic properties.
- paliperidone
paliperidone and posaconazole both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- panobinostat
posaconazole increases levels of panobinostat by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Reduce panobinostat starting dose to 10 mg if coadministered with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors.
- pantoprazole
pantoprazole will decrease the level or effect of posaconazole by increasing gastric pH. Applies only to oral form of both agents. Use Caution/Monitor.
- paricalcitol
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of paricalcitol by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- paroxetine
paroxetine and posaconazole both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- pasireotide
posaconazole and pasireotide both increase QTc interval. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- perampanel
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of perampanel by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- perphenazine
perphenazine and posaconazole both increase QTc interval. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- phenobarbital
phenobarbital will decrease the level or effect of posaconazole by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
phenobarbital decreases levels of posaconazole by increasing metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. - phenytoin
phenytoin decreases levels of posaconazole by increasing metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- polatuzumab vedotin
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of polatuzumab vedotin by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Polatuzumab undergoes catabolism to small peptides, amino acids, monomethyl auristatin E (MMAE), and unconjugated MMAE-related catabolites. MMAE is a CYP3A4 substrate. Coadministration of polatuzumab vedotin with a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor may increase unconjugated MMAE AUC, which may increase polatuzumab vedotin toxicities.
- ponatinib
ponatinib increases levels of posaconazole by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
- praziquantel
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of praziquantel by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- prednisolone
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of prednisolone by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- prednisone
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of prednisone by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- primaquine
primaquine and posaconazole both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- primidone
primidone decreases levels of posaconazole by increasing metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- prochlorperazine
prochlorperazine and posaconazole both increase QTc interval. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- progesterone intravaginal gel
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of progesterone intravaginal gel by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- progesterone micronized
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of progesterone micronized by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- progesterone, natural
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of progesterone, natural by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- promazine
promazine and posaconazole both increase QTc interval. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- promethazine
promethazine and posaconazole both increase QTc interval. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- protriptyline
protriptyline and posaconazole both increase QTc interval. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- quazepam
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of quazepam by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- quercetin
quercetin will decrease the level or effect of posaconazole by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
- quetiapine
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of quetiapine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
quetiapine, posaconazole. Either increases toxicity of the other by QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. Avoid use with drugs that prolong QT and in patients with risk factors for prolonged QT interval. Postmarketing cases show QT prolongation with overdose in patients with concomitant illness or with drugs known to cause electrolyte imbalance or prolong QT. - quinine
posaconazole and quinine both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- quizartinib
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of quizartinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Reduce quizartinib dosage to 26.5 mg qDay (if current dosage is 53 mg/day) or 17.7 mg qDay (if current dosage is 26.5 mg/day or 35.4 mg/day) when coadministered with strong CYP3A inhibitors. If current dosage is 17.7 mg qDay, interrupt quizartinib for the duration of strong CYP3A inhibitor use. After discontinuation of a strong CYP3A inhibitor for 5 half-lives, resume quizartinib dose that was taken before initiating the strong inhibitor.
quizartinib, posaconazole. Either increases effects of the other by QTc interval. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Monitor patients more frequently with ECG if coadministered with QT prolonging drugs. - rabeprazole
rabeprazole will decrease the level or effect of posaconazole by increasing gastric pH. Applies only to oral form of both agents. Use Caution/Monitor.
- ranolazine
ranolazine will increase the level or effect of posaconazole by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
posaconazole and ranolazine both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. - repaglinide
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of repaglinide by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- rifabutin
rifabutin decreases levels of posaconazole by increasing metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- rifampin
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of posaconazole by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
rifampin decreases levels of posaconazole by increasing metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. - rifaximin
posaconazole increases levels of rifaximin by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
- rilpivirine
posaconazole increases levels of rilpivirine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. No rilpivirine dose adjustment is required. Clinically monitor for breakthrough fungal infections when azole antifungals are co-administered with rilpivirine.
rilpivirine increases toxicity of posaconazole by QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. Rilpivirine should be used with caution when co-administered with a drug with a known risk of Torsade de Pointes. - ripretinib
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of ripretinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Coadministration with a strong CYP3A inhibitor will increase systemic exposure to ripretinib and its active metabolite (DP-5439), which may increase risk of adverse reactions.
- risperidone
posaconazole and risperidone both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- ritonavir
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of ritonavir by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
ritonavir will increase the level or effect of posaconazole by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor. - roflumilast topical
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of roflumilast topical by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- romidepsin
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of romidepsin by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
posaconazole and romidepsin both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. - salmeterol
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of salmeterol by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- saquinavir
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of saquinavir by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- sarecycline
sarecycline will increase the level or effect of posaconazole by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor. Monitor for toxicities of P-gp substrates that may require dosage reduction when coadministered with P-gp inhibitors.
- saxagliptin
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of saxagliptin by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Limit saxagliptin dose to 2.5 mg/day when coadministered with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors
- selpercatinib
selpercatinib increases toxicity of posaconazole by QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- sertraline
sertraline and posaconazole both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- sildenafil
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of sildenafil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- simvastatin
simvastatin will increase the level or effect of posaconazole by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
- sirolimus
sirolimus will increase the level or effect of posaconazole by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
- sodium bicarbonate
sodium bicarbonate will decrease the level or effect of posaconazole by increasing gastric pH. Applies only to oral form of both agents. Use Caution/Monitor.
- sodium citrate/citric acid
sodium citrate/citric acid will decrease the level or effect of posaconazole by increasing gastric pH. Applies only to oral form of both agents. Use Caution/Monitor.
- sodium sulfate/potassium chloride/magnesium sulfate/polyethylene glycol
posaconazole and sodium sulfate/potassium chloride/magnesium sulfate/polyethylene glycol both decrease serum potassium. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- sodium zirconium cyclosilicate
sodium zirconium cyclosilicate will decrease the level or effect of posaconazole by increasing gastric pH. Applies only to oral form of both agents. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Check specific recommendations for drugs that exhibit pH-dependent solubility that may affect their systemic exposure and efficacy. In general, administer drugs at least 2 hr before or after sodium zirconium cyclosilicate.
- sofosbuvir/velpatasvir
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of sofosbuvir/velpatasvir by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- solifenacin
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of solifenacin by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- sorafenib
sorafenib and posaconazole both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- St John's Wort
St John's Wort will decrease the level or effect of posaconazole by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
- stiripentol
stiripentol will increase the level or effect of posaconazole by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Consider reducing the dose of P-glycoprotein (P-gp) substrates, if adverse reactions are experienced when administered concomitantly with stiripentol.
- sufentanil SL
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of sufentanil SL by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Coadministration of sufentanil SL with any CYP3A4 inhibitor may increase sufentanil plasma concentration, and, thereby increase or prolonged adverse effects, including potentially fatal respiratory depression.
- sulfamethoxazole
sulfamethoxazole and posaconazole both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- sunitinib
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of sunitinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- tacrolimus
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
tacrolimus will increase the level or effect of posaconazole by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor. - tadalafil
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of tadalafil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- talazoparib
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of talazoparib by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor. Talazoparib is a P-glycoprotein (P-gp) substrate; coadministration with P-gp inhibitors may increase talazoparib systemic exposure.
- tamoxifen
posaconazole, tamoxifen. affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. CYP3A4 inhibition decreases metabolism of tamoxifen to N-desmethyl tamoxifen (active metabolite with similar biologic activity).
- tasimelteon
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of tasimelteon by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- telavancin
posaconazole and telavancin both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- temsirolimus
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of temsirolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- terbinafine
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of terbinafine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- tezacaftor
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of tezacaftor by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Adjust tezacaftor dosage regimen if coadministered with a strong CYP3A inhibitor.
- theophylline
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of theophylline by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- thioridazine
thioridazine and posaconazole both increase QTc interval. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- ticagrelor
posaconazole increases levels of ticagrelor by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Ticagrelor is metabolized by CYP3A4/5. Avoid use with strong CYP3A inhibitors.
- tinidazole
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of tinidazole by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- tipranavir
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of tipranavir by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- tisotumab vedotin
posaconazole increases levels of tisotumab vedotin by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Tisotumab vedotin?s active metabolite (MMAE) is a CYP3A4 substrate. Coadministration with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors may increase unconjugated MMAE systemic exposure and increase risk of adverse effects.
- tolazamide
posaconazole increases levels of tolazamide by decreasing metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- tolbutamide
posaconazole increases levels of tolbutamide by decreasing metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- tolterodine
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of tolterodine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- tolvaptan
tolvaptan will increase the level or effect of posaconazole by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
- toremifene
posaconazole increases levels of toremifene by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Metabolism of toremifene may be inhibited by drugs known to inhibit CYP3A4 hepatic enzymes.
- trazodone
trazodone will decrease the level or effect of posaconazole by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
trazodone and posaconazole both increase QTc interval. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. - triamcinolone acetonide injectable suspension
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of triamcinolone acetonide injectable suspension by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- triazolam
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of triazolam by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- trifluoperazine
trifluoperazine and posaconazole both increase QTc interval. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- trimethoprim
posaconazole and trimethoprim both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- trimipramine
trimipramine and posaconazole both increase QTc interval. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of trimipramine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. - tropisetron
posaconazole and tropisetron both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- tucatinib
tucatinib will increase the level or effect of posaconazole by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor. Consider reducing the dosage of P-gp substrates, where minimal concentration changes may lead to serious or life-threatening toxicities.
- ulipristal
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of ulipristal by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- umeclidinium bromide/vilanterol inhaled
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of umeclidinium bromide/vilanterol inhaled by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Vilanterol is a CYP3A4 substrate; coadministration with potent CYP3A4 inhibitors may increase systemic exposure
- upadacitinib
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of upadacitinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Caution if upadacitinib is coadministered with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors.
- valbenazine
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of valbenazine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Reduce valbenazine dose to 40 mg once daily when coadministered with a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor.
valbenazine and posaconazole both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. - vamorolone
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of vamorolone by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Reduce vamorolone starting dose to 4 mg/kg/day; not to exceed 200 mg/day if weight >50 kg.
- vardenafil
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of vardenafil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Vardenafil dose may need to be reduced if coadministered with moderate or strong CYP3A4 inhibitors
- velpatasvir
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of velpatasvir by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- venlafaxine
posaconazole and venlafaxine both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- verapamil
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of verapamil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
verapamil will increase the level or effect of posaconazole by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor. - vilanterol/fluticasone furoate inhaled
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of vilanterol/fluticasone furoate inhaled by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Fluticasone furoate and vilanterol are both CYP3A4 substrates; coadministration with potent CYP3A4 inhibitors may increase systemic exposure
- voclosporin
voclosporin, posaconazole. Either increases effects of the other by QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
voclosporin, posaconazole. Either increases toxicity of the other by nephrotoxicity and/or ototoxicity. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Coadministration with drugs associated with nephrotoxicity may increase the risk for acute and/or chronic nephrotoxicity. - voriconazole
posaconazole and voriconazole both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- vorinostat
vorinostat and posaconazole both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- warfarin
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of warfarin by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Warfarin's less potent R-enantiomer is metabolized in part by CYP3A4 (and also CYP1A2 and CYP2C19). Monitor INR more frequently if coadministered with inhibitors of these isoenzymes and adjust warfarin dose if needed.
- zanubrutinib
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of zanubrutinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Reduce zanubrutinib (a CYP3A4 substrate) to 80 mg once daily if coadministered with a strong CYP3A4 inhibitors. Interrupt dose as recommended for adverse reactions. After discontinuing the CYP3A4 inhibitor, resume previous zanubrutinib dose.
- ziprasidone
posaconazole and ziprasidone both increase QTc interval. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- zuranolone
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of zuranolone by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Reduce zuranolone dose if coadministered with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors.
Minor (73)
- alfentanil
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of alfentanil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- alfuzosin
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of alfuzosin by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- aliskiren
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of aliskiren by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- alosetron
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of alosetron by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- ambrisentan
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of ambrisentan by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- amikacin
posaconazole decreases levels of amikacin by unknown mechanism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- amitriptyline
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of amitriptyline by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- amobarbital
amobarbital decreases levels of posaconazole by inhibition of GI absorption. Applies only to oral form of both agents. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- armodafinil
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of armodafinil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- atazanavir
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of atazanavir by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- azithromycin
azithromycin and posaconazole both increase QTc interval. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- bosentan
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of bosentan by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- butabarbital
butabarbital decreases levels of posaconazole by inhibition of GI absorption. Applies only to oral form of both agents. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- butalbital
butalbital decreases levels of posaconazole by inhibition of GI absorption. Applies only to oral form of both agents. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- caffeine
posaconazole increases levels of caffeine by decreasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- cevimeline
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of cevimeline by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- chlordiazepoxide
posaconazole increases levels of chlordiazepoxide by decreasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- chloroquine
chloroquine increases toxicity of posaconazole by QTc interval. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- clarithromycin
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of clarithromycin by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- clomipramine
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of clomipramine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- dapsone
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of dapsone by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- didanosine
didanosine will decrease the level or effect of posaconazole by increasing gastric pH. Applies only to oral form of both agents. Minor/Significance Unknown. Applies to didanosine chewable tablets and powder for oral solution; administer 2 hr before or several hours after didanosine oral solution or chewable tablet administration
- disopyramide
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of disopyramide by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- docetaxel
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of docetaxel by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- donepezil
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of donepezil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- dutasteride
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of dutasteride by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- efavirenz
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of efavirenz by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- eplerenone
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of eplerenone by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- eucalyptus
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of eucalyptus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- finasteride
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of finasteride by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- food
food increases levels of posaconazole by enhancing GI absorption. Applies only to oral form of both agents. Minor/Significance Unknown. Desirable interaction coadministration with a high fat meal recommended.
- galantamine
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of galantamine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- ganaxolone
posaconazole, ganaxolone. affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown. Changes in ganaxolone exposures when coadministered with strong, moderate, or weak CYP3A4 inhibitors are not expected to be clinically significant.
- gentamicin
posaconazole decreases levels of gentamicin by unknown mechanism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- imatinib
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of imatinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- imipramine
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of imipramine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- isradipine
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of isradipine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- itraconazole
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of itraconazole by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- ixazomib
posaconazole, ixazomib. affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown. In clinical trials, coadministration of ixazomib with strong CYP3A inhibitors did not result in a clinically meaningful change in the systemic exposure of ixazomib.
- ketoconazole
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of ketoconazole by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- levoketoconazole
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of levoketoconazole by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- mestranol
posaconazole decreases effects of mestranol by increasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown. May also cause menstrual irregularities.
- montelukast
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of montelukast by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- neomycin PO
posaconazole decreases levels of neomycin PO by unknown mechanism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- nifedipine
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of nifedipine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- nimodipine
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of nimodipine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- nitrendipine
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of nitrendipine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- oxybutynin
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of oxybutynin by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- paclitaxel
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of paclitaxel by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- paclitaxel protein bound
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of paclitaxel protein bound by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- parecoxib
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of parecoxib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- paromomycin
posaconazole decreases levels of paromomycin by unknown mechanism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- pazopanib
pazopanib and posaconazole both increase QTc interval. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- pentobarbital
pentobarbital decreases levels of posaconazole by inhibition of GI absorption. Applies only to oral form of both agents. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- phenobarbital
phenobarbital decreases levels of posaconazole by inhibition of GI absorption. Applies only to oral form of both agents. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- pimozide
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of pimozide by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- pioglitazone
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of pioglitazone by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- primidone
primidone decreases levels of posaconazole by inhibition of GI absorption. Applies only to oral form of both agents. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- propafenone
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of propafenone by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- quinine
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of quinine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- rabeprazole
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of rabeprazole by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- ramelteon
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of ramelteon by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- rifabutin
posaconazole increases levels of rifabutin by decreasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- rifampin
posaconazole decreases levels of rifampin by inhibition of GI absorption. Applies only to oral form of both agents. Minor/Significance Unknown. Only applies to oral preparations of both agents.
- secobarbital
secobarbital decreases levels of posaconazole by inhibition of GI absorption. Applies only to oral form of both agents. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- streptomycin
posaconazole decreases levels of streptomycin by unknown mechanism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- sufentanil
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of sufentanil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- tobramycin
posaconazole decreases levels of tobramycin by unknown mechanism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- vinorelbine
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of vinorelbine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- zaleplon
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of zaleplon by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- ziprasidone
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of ziprasidone by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- zolpidem
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of zolpidem by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- zonisamide
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of zonisamide by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
Adverse Effects
>10%
Injection
- Diarrhea (10-42%)
- Pyrexia (21-31%)
- Nausea (19-30%)
- Hypokalemia (22-28%)
- Rash (15-24%)
- Headache (14-21%)
- Vomiting (12-19%)
- Epistaxis (14-17%)
- Abdominal pain (13-17%)
- Peripheral edema (12-15%)
- Cough (9-13%)
- Constipation (8-13%)
- Hypomagnesemia (11-13%)
- Decreased appetite (10-12%)
- Hypertension (8-11%)
- Thrombocytopenia (7-11%)
- Upper abdominal pain (6-11%)
Oral suspension
- Fever (6-45%)
- Nausea (9-38%)
- Hypokalemia (30%)
- Thrombocytopenia (29%)
- Vomiting (7-29%)
- Headache (8-28%)
- Abdominal pain (5-27%)
- Coughing (3-25%)
- Anemia (2-25%)
- Neutropenia (4-23%)
- Constipation (21%)
- Dyspnea (1-20%)
- Rigors (<20%)
- Anorexia (2-19%)
- Rash (3-19%)
- Hypomagnesemia (18%)
- Hypertension (18%)
- ALT increased, Grade 3 or 4 (6-17%)
- AST >3x ULN (6-17%)
- Fatigue (2-17%)
- Insomnia (1-17%)
- Musculoskeletal pain (16%)
- Edema legs (15%)
- Epistaxis (14%)
- Hypotension (14%)
- Decrease weight (1-14%)
- Tachycardia (12%)
- Pharyngitis (12%)
- Oral candidiasis (<12%)
- Hyperglycemia (11%)
- Pruritus (11%)
- Petechiae (11%)
- Dizziness (11%)
- Arthralgia (11%)
- Herpes simplex (3-11%)
- ALT >3x ULN (3-11%)
- Pain (1-11%)
- Dehydration (1-11%)
Tablets
- Diarrhea (29%)
- Pyrexia (28%)
- Nausea (27%)
- Hypokalemia (22%)
- Cough (17%)
- Rash (16%)
- Peripheral edema (16%)
- Epistaxis (14%)
- Headache (14%)
- Mucosal inflammation (14%)
- Thrombocytopenia (14%)
- Vomiting (13%)
- Alkaline phosphatase >3x ULN (3-13%)
- Abdominal pain (11%)
- Hypertension 23 (11%)
1-10%
Injection
- Petechiae (8-10%)
- Anemia (7-10%)
- Dyspnea (7-10%)
Tablets
- Anemia (10%)
- Constipation (10%)
- Asthenia (10%)
- Chills (10%)
- Hypomagnesemia (10%)
Oral suspension
- Back pain (10%)
- Bilirubinemia (10%)
- Vaginal hemorrhage (10%)
- Dyspepsia (10%)
- Pneumonia (3-10%)
- Sweating increased (2-10%)
- Edema (9%)
- Hypocalcemia (9%)
- Bilirubin increased, Grade 3 or 4 (7-9%)
- Weakness (8%)
- Hemolytic uremic syndrome (<5%)
- Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (<5%)
- Neutropenia aggravated (<5%)
- Adrenal insufficiency (<5%)
- Paresthesia (<5%)
- Allergic reaction (<5%)
- Torsades de pointes (<5%)
- Pulmonary embolism (<5%)
- Pancreatitis (<5%)
- Bilirubinemia (<5%)
- Hepatic enzymes increased (<5%)
- Hepatic function abnormal (<5%)
- Hepatitis (<5%)
- Hepatomegaly (<5%)
- Jaundice (<5%)
- AST/ALT increased (<5%)
- Hypokalemia (<5%)
- Thrombocytopenia (<5%)
- Renal failure acute (<5%)
- Total bilirubin > 1.5x ULN (3-5%)
- AST, Grade 3 or 4 (3-4%)
- Alkaline phosphatase, Grade 3 or 4 (1-3%)
Postmarketing Reports
Pseudoaldosteronism
Warnings
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to posaconazole or other azoles
Coadministration with sirolimus; increases sirolimus blood concentrations by ~9-fold
CYP3A4 substrates that prolong the QT interval (eg, pimozide, quinidine)
Coadministration with the HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors (statins) that are primarily metabolized through CYP3A4 (eg, atorvastatin, lovastatin, simvastatin)
Concurrent use with ergot alkaloids
Coadministration with venetoclax in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) or small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL)
Use of delayed-release oral suspension in patients with known or suspected hereditary fructose intolerance (HFI)
Delayed-release oral suspension only
- Patients with known or suspected hereditary fructose intolerance (HFI)
Cautions
May prolong QT interval; cases of torsades de pointes reported
Hepatic reactions reported including mild-to-moderate elevations in ALT, AST, alkaline phosphatase, total bilirubin, and clinical hepatitis; consider discontinuing therapy in patients who develop abnormal LFTs or monitor LFTs during treatment
Closely monitor patients with severe renal impairment for breakthrough fungal infections due to the variability in exposure of the delayed-release tablets and oral suspension; avoid use of injection in patients with moderate or severe renal impairment (eGFR <50 mL/min); unless benefit outweighs risks
Electrolyte disturbances, especially those involving potassium, magnesium or calcium levels, should be monitored and corrected as necessary before and during posaconazole therapy
Closely monitor patients who have severe diarrhea or vomiting for breakthrough fungal infections when receiving delayed-release tablets, oral suspension, or delayed-release oral suspension
Use of delayed-release oral suspension in patients with HFI
- Delayed-release oral suspension contains sorbitol, an inactive ingredient, and may precipitate a metabolic crisis that may include, but is not limited to life-threatening hypoglycemia, hypophosphatemia, lactic acidosis, and hepatic failure in patients with HFI
- Review patient history of HFI symptoms (nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain) with sorbitol/fructose/sucrose exposure before using the delayed-release oral suspension
- Diagnosis of HFI may not yet be established in pediatric patients
Drug interactions overview
Posaconazole is a P-gp substrate and a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor; metabolized by UDP-glucuronidase
-
Rifabutin and phenytoin
- Avoid unless benefit outweighs risks
- Rifabutin and phenytoin may decrease posaconazole plasma concentrations by inducing UDP-glucuronidase
- Posaconazole may also increase rifabutin and phenytoin levels by inhibiting CYP3A4
-
Antiretroviral agents
- Efavirenz may induce UDP-glucuronidase and significantly decrease posaconazole plasma levels; avoid use
- Ritonavir and atazanavir are CYP3A4 substrates; posaconazole may increase plasma concentrations of these drugs; closely monitor for posaconazole-related toxicities if concurrently used
- Fosamprenavir may decrease posaconazole plasma concentration; closely monitor for breakthrough fungal infections
-
Benzodiazepines metabolized by CYP3A4
- Closely monitor
- Coadministration with midazolam increases midazolam plasma concentrations by ~5-fold; increased risk of prolonged hypnotic and sedative effects
-
CYP3A4 substrates that cause QT prolongation
- Contraindicated
- Coadministration with CYP3A4 substrates may result in increased plasma concentrations of these drugs, leading to QTc prolongation and cases of torsades de pointes
-
Immunosuppressants metabolized by CYP3A4
- Coadministration posaconazole with calcineurin inhibitors (eg, sirolimus, tacrolimus, cyclosporine) increases blood concentrations pf calcineurin inhibitors
- Sirolimus: Contraindicated
- Tacrolimus: Reduce tacrolimus dose to ~1/3 of original dose when initiating posaconazole; closely monitor tacrolimus trough concentrations during and at discontinuation of posaconazole treatment and adjust tacrolimus dose accordingly
- Cyclosporine: Reduce cyclosporine dose to ~ 3/4 of original dose when initiating cyclosporine; closely monitor tacrolimus trough concentrations during and at discontinuation of posaconazole treatment and adjust tacrolimus dose accordingly
-
HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors primarily metabolized through CYP3A4
- Contraindicated
- May increase plasma concentrations of simvastatin by ~10-fold
-
Ergot alkaloids
- Contraindicated
- May increase the plasma concentrations of ergot alkaloids which may lead to ergotism
-
Cimetidine and esomeprazole
- Oral suspension: Cimetidine (an H2-receptor antagonist) and esomeprazole (a proton pump inhibitor) decreased posaconazole plasma concentrations; avoid use of cimetidine and esomeprazole unless the benefit outweighs the risks
-
Vinca alkaloids
- Use with vinca alkaloids (eg, vinblastine, vincristine) may increase the plasma concentrations of vinca alkaloids and risks of neurotoxicity and other serious adverse reactions
- Reserve azole antifungals for patients receiving a vinca alkaloid, including vincristine, who have no alternative antifungal treatment options
-
Calcium channel blockers
- May increase the plasma concentrations of calcium channel blockers metabolized by CYP3A4 (eg, verapamil, diltiazem, nifedipine, nicardipine, felodipine)
- Closely monitor for adverse reactions and toxicity related to calcium channel blockers; consider dose reduction of calcium channel blockers
-
Digoxin
- Increased plasma concentrations of digoxin reported in patients receiving digoxin and posaconazole; closely monitor digoxin levels
-
Venetoclax toxicity
- Concomitant administration of Noxafil, a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor, with venetoclax may increase venetoclax toxicities, including the risk of tumor lysis syndrome (TLS), neutropenia, and serious infections; in patients with CLL/SLL, administration of Noxafil during initiation and the ramp-up phase of venetoclax is contraindicated; refer to the venetoclax labeling for safety monitoring and dose reduction in the steady daily dosing phase in CLL/SLL patients
- For patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML), dose reduction and safety monitoring are recommended across all dosing phases when coadministering Noxafil with venetoclax; refer to the venetoclax prescribing information for dosing instructions
Pregnancy & Lactation
Pregnancy
Available data in pregnant women are insufficient to establish a drug- associated risk of major birth defects, miscarriage, or adverse maternal or fetal outcomes; based on findings from animal data, therapy may cause fetal harm when administered to pregnant women
Animal data
- Skeletal malformations (cranial malformations and missing ribs) and maternal toxicity (reduced food consumption and reduced body weight gain) observed when dosed orally to pregnant rats; during organogenesis at doses greater than or equal to 1.4 times the 400 mg twice daily oral suspension regimen recommended in humans; in pregnant rabbits dosed orally during organogenesis, increased resorptions, reduced litter size, and reduced body weight gain of females were seen at doses 5 times the exposure achieved with the 400 mg twice daily oral suspension regimen; doses of ≥3 times the clinical exposure caused an increase in resorptions in these rabbits; based on animal data, advise pregnant women of potential risk to a fetus
Lactation
There are no data on presence of drug in human milk, effects on breastfed infant, or on milk production; drug is excreted in milk of lactating rats; when a drug is present in animal milk, it is likely that the drug will be present in human milk; developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with mother’s clinical need for drug and any potential adverse effects on breastfed child from drug or from underlying maternal condition
Pregnancy Categories
A: Generally acceptable. Controlled studies in pregnant women show no evidence of fetal risk.
B: May be acceptable. Either animal studies show no risk but human studies not available or animal studies showed minor risks and human studies done and showed no risk. C: Use with caution if benefits outweigh risks. Animal studies show risk and human studies not available or neither animal nor human studies done. D: Use in LIFE-THREATENING emergencies when no safer drug available. Positive evidence of human fetal risk. X: Do not use in pregnancy. Risks involved outweigh potential benefits. Safer alternatives exist. NA: Information not available.Pharmacology
Mechanism of Action
Inhibits fungal cell membrane sterol biosynthesis
Absorption
Increased by food
Peak plasma time: 3-5 hr (oral susp); 3-4 hr (tablet); 1.5 hr (IV)
Peak plasma concentration: 1590 ng/mL (IV)
Distribution
Protein bound: >98%
Vd: 287 L (oral); 261 L (IV)
Metabolism
Metabolized primarily by glucuronide conjugates
Strong CYP3A4 inhibitor
Elimination
Half-life: 35 hr (oral susp); 26-31 hr (tablet); 24.6 hr (IV)
Total body clearance: 51.2 L/hr (oral susp); 9.39 L/hr (tablet); 7.3 L/hr (IV)
Excretion: 71% feces; 13% urine
Administration
IV Incompatibilities
Lactated ringer (LR)
Dextrose 5% (D5W) with LR
4.2% sodium bicarbonate
IV Compatibility
IV solutions
- 0.45% NaCl
- 0.9% NaCl
- D5W
- D5W 0.45% NaCl
- D5W 0.9% NaCl
- D5W and 20 mEq potassium chloride
Y-site administration
-
Drugs
- Amikacin
- Caspofungin
- Ciprofloxacin
- Daptomycin
- Dobutamine
- Famotidine
- Gentamicin
- Hydromorphone
- Levofloxacin
- Lorazepam
- Meropenem
- Micafungin
- Morphine
- Norepinephrine
- Potassium chloride
- Vancomycin
IV Preparation
Equilibrate refrigerated vial to room temperature
Aseptically transfer 16.7 mL (300 mg) of solution to an IV bag/bottle containing ~150 mL of a compatible admixture diluent; final concentration of diluted IV bag is 1-2 mg/mL
Use of other infusion solutions may result in particulate formation
Injection is a single dose sterile solution without preservatives; once admixed, use product immediately; if not used immediately, refrigerate for up to 24 hours at 2-8ºC (36-46ºF)
Visually inspect product for particulate matter prior to administration; diluted solution ranges from colorless to yellow
IV Administration
IV infusion only; not for IV bolus injection
Administer through a 0.22 micron polyethersulfone (PES) or polyvinylidene difluoride (PVDF) filter
Administer via a central venous line, including a central venous catheter or peripherally inserted central catheter (PICC), by slow IV infusion over ~90 minutes
If a central venous catheter is not available, may administer through a peripheral venous catheter by slow IV infusion over 30 minutes only as a single dose in advance of central venous line placement or to bridge the period during which a central venous line is replaced or is in use for other IV treatment
When multiple dosing required, infusion should be done via central venous line
Oral Preparation
Oral suspension H4
- Shake well before use
- Administer with measured dosing spoon (marked doses of 2.5 mL and 5 mL)
- Rinse spoon with water after each administration and before storage
- Administer each dose during or immediately (ie, within 20 min) following a full meal to enhance absorption of the oral suspension
Delayed-release oral suspension
- Do not open packet in kit until ready to prepare
- Remove 9 mL of mixing liquid using the provided BLUE syringe
- ONLY use the mixing liquid in the kit to prepare delayed-release oral suspension
- Using the provided mixing cup, combine 9 mL of mixing liquid and the entire contents of one packet in the kit and mix
- Each single-use packet in the kit contains 300 mg of posaconazole to be suspended in 9 mL of mixing liquid giving a final concentration of ~30 mg/mL
- Shake mixing cup vigorously for 45 sec to mix powder and mixing liquid from kit; check to make sure the powder is mixed; mixture should look cloudy and free of clumps
- Reconstituted suspension must be used within 1 hr; discard unused portion of the prepared drug product
Oral Administration
Tablets and oral suspension are not interchangeable because of differences in dosing for each formulation
Tablets
- Take with food
- Swallow tablets whole; do not divide, crush, or chew
Oral suspension
- Take with a full meal or liquid nutritional supplement or an acidic carbonated beverage (eg, ginger ale) in patients unable to eat a full meal
- If unable to eat a full meal or tolerate an oral nutritional supplement or an acidic carbonated beverage and who do not have the option of taking delayed-release tablets or injection, consider an alternative antifungal therapy or closely monitor for breakthrough fungal infections
Delayed-release oral suspension
- Take with food
- Use 3-mL syringe (green) for doses ≤3 mL
- Use 10-mL syringe (blue) for doses >3 mL
- Administer dose orally within 1 r of mixing
- Not all the mixture in the mixing cup will be used
- Maximum dose that can be accurately withdrawn from mixing cup after reconstitution is 240 mg (8 mL)
- To ensure delivery of the correct dose, ONLY provided notched tip syringes must be used for preparation and administration
- Discard any remaining suspension; mixing cup and notched tip syringes may be hand washed and reused
- Alternatively, mixing cup may be discarded, and a similar mixing cup with a lid may be used for subsequent doses
- For additional supply, a separate box of notched tip syringes is provided with the kit
Missed dose
- >12 hr of next dose: Take as soon as possible
- <12 hr of next dose: Skip missed dose; go back to regular schedule; do not double dose
Storage
Unopened vials: Refrigerate at 2-8ºC (36-46ºF)
Tablets
- Store at 20-25ºC (36-46ºF), excursions permitted to 15-30ºC (59-86ºF)
Oral suspension
- Store at 25ºC (36-46ºF), excursions permitted to 15-30ºC (59-86ºF)
- Do not freeze
Delayed-release oral suspension
- Store entire kit at 20-25ºC (36-46ºF), excursions permitted to 15-30ºC (59-86ºF) in a clean, dry place
- Do not open foil packet containing delayed-release oral suspension until ready for use
- Once mixed, use within 1 hr; discard any unused drug
Diluted solution
- Vial is a single dose sterile solution without preservatives; once admixed, use immediately
- If not used immediately, refrigerate for up to 24 hr at 2-8ºC (36-46ºF)
Images
| BRAND | FORM. | UNIT PRICE | PILL IMAGE |
|---|---|---|---|
| posaconazole oral - | 100 mg tablet | 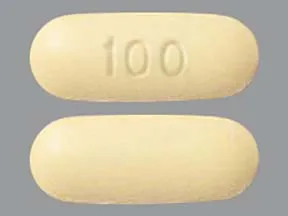 | |
| posaconazole oral - | 100 mg tablet |  | |
| posaconazole oral - | 100 mg tablet |  | |
| posaconazole oral - | 100 mg tablet |  | |
| posaconazole oral - | 100 mg tablet |  | |
| Noxafil oral - | 100 mg tablet |  | |
| Noxafil oral - | 200 mg/5 mL (40 mg/mL) suspension |  | |
| posaconazole intravenous - | 300 mg/16.7 mL vial |  | |
| Noxafil intravenous - | 300 mg/16.7 mL vial | 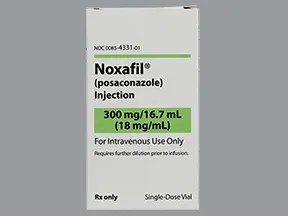 |
Copyright © 2010 First DataBank, Inc.
Patient Handout
posaconazole oral
POSACONAZOLE DELAYED-RELEASE - ORAL
(POE-sa-KON-a-zole)
COMMON BRAND NAME(S): Noxafil
USES: Posaconazole is used to prevent certain fungal infections in patients who have severely weakened immune systems (such as patients who have had chemotherapy). It belongs to a class of drugs known as azole antifungals. It works by stopping the growth of fungi.
HOW TO USE: Read the Patient Information Leaflet if available from your pharmacist before you start taking posaconazole and each time you get a refill. If you have any questions, ask your doctor or pharmacist.Take this medication by mouth with or without food as directed by your doctor, usually once daily. Do not crush or chew delayed-release tablets. Doing so can release all of the drug at once, increasing the risk of side effects. Swallow the whole tablet without crushing or chewing.The length of treatment is based on your medical condition.This medication works best when the amount of medicine in your body is kept at a constant level. Take this drug at evenly spaced intervals.The tablet and suspension forms of posaconazole may deliver different amounts of medication. Do not switch between the different forms of this medication without your doctor's permission and directions.Tell your doctor if you have severe diarrhea or vomiting. Posaconazole may not work as well.
SIDE EFFECTS: Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, headache, abdominal pain, dizziness, trouble sleeping, or stomach upset may occur. If any of these effects last or get worse, tell your doctor or pharmacist promptly.Remember that this medication has been prescribed because your doctor has judged that the benefit to you is greater than the risk of side effects. Many people using this medication do not have serious side effects.Tell your doctor right away if you have any serious side effects, including: unusual tiredness, easy bruising/bleeding, weakness, muscle cramps, mental/mood changes, swelling of the ankles/feet, signs of infection (such as chills, fever), vaginal bleeding, shortness of breath, increased thirst/urination.Get medical help right away if you have any very serious side effects, including: fast/irregular heartbeat, severe dizziness, fainting.Posaconazole has rarely caused very serious (possibly fatal) liver disease. Tell your doctor right away if you develop symptoms of liver disease, including: nausea/vomiting that doesn't stop, yellowing eyes/skin, dark urine, severe stomach/abdominal pain.A very serious allergic reaction to this drug is rare. However, get medical help right away if you notice any symptoms of a serious allergic reaction, including: rash, itching/swelling (especially of the face/tongue/throat), severe dizziness, trouble breathing.Posaconazole can commonly cause a mild rash that is usually not serious. However, you may not be able to tell it apart from a rare rash that could be a sign of a severe allergic reaction. Get medical help right away if you develop any rash.This is not a complete list of possible side effects. If you notice other effects not listed above, contact your doctor or pharmacist.In the US -Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or at www.fda.gov/medwatch.In Canada - Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to Health Canada at 1-866-234-2345.
PRECAUTIONS: Before taking posaconazole, tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are allergic to it; or to other azole antifungals (such as ketoconazole); or if you have any other allergies. This product may contain inactive ingredients, which can cause allergic reactions or other problems. Talk to your pharmacist for more details.Before using this medication, tell your doctor or pharmacist your medical history, especially of: liver disease, kidney disease.Posaconazole may cause a condition that affects the heart rhythm (QT prolongation). QT prolongation can rarely cause serious (rarely fatal) fast/irregular heartbeat and other symptoms (such as severe dizziness, fainting) that need medical attention right away.The risk of QT prolongation may be increased if you have certain medical conditions or are taking other drugs that may cause QT prolongation. Before using posaconazole, tell your doctor or pharmacist of all the drugs you take and if you have any of the following conditions: certain heart problems (heart failure, slow heartbeat, QT prolongation in the EKG), family history of certain heart problems (QT prolongation in the EKG, sudden cardiac death).Low levels of potassium or magnesium in the blood may also increase your risk of QT prolongation. This risk may increase if you use certain drugs (such as diuretics/"water pills") or if you have conditions such as severe sweating, diarrhea, or vomiting. Talk to your doctor about using posaconazole safely.This drug may make you dizzy. Alcohol or marijuana (cannabis) can make you more dizzy. Do not drive, use machinery, or do anything that needs alertness until you can do it safely. Avoid alcoholic beverages. Talk to your doctor if you are using marijuana (cannabis). Alcohol may also increase the risk of serious liver problems.Before having surgery, tell your doctor or dentist about all the products you use (including prescription drugs, nonprescription drugs, and herbal products).Older adults may be more sensitive to the side effects of this drug, especially QT prolongation (see above).During pregnancy, this medication should be used only when clearly needed. Discuss the risks and benefits with your doctor.It is unknown if this drug passes into breast milk. Consult your doctor before breastfeeding.
DRUG INTERACTIONS: Drug interactions may change how your medications work or increase your risk for serious side effects. This document does not contain all possible drug interactions. Keep a list of all the products you use (including prescription/nonprescription drugs and herbal products) and share it with your doctor and pharmacist. Do not start, stop, or change the dosage of any medicines without your doctor's approval.Other medications can affect the removal of posaconazole from your body, which may affect how posaconazole works. Examples include efavirenz, rifamycins (such as rifabutin), certain drugs used to treat seizures (such as phenytoin), among others.This drug can slow down the removal of other drugs from your body, which may affect how they work. Examples of affected drugs include certain alpha blockers (such as alfuzosin, silodosin, tamsulosin), certain benzodiazepines (such as midazolam), dronedarone, ergot alkaloids (such as ergotamine, dihydroergotamine), pimozide, quinidine, rivaroxaban, sirolimus, certain "statin" drugs (such as lovastatin, simvastatin), venetoclax, among others.Many drugs besides posaconazole may affect the heart rhythm (QT prolongation), including pacritinib, among others.
OVERDOSE: If someone has overdosed and has serious symptoms such as passing out or trouble breathing, call 911. Otherwise, call a poison control center right away. US residents can call 1-800-222-1222. Canada residents can call 1-844-764-7669.
NOTES: Do not share this medication with others.This medication has been prescribed for your current condition only. Do not use it later to prevent another infection unless your doctor tells you to.Lab and/or medical tests (such as liver function, blood mineral levels such as calcium, magnesium, potassium) should be done before you start using this medication and while you are using it. Keep all medical and lab appointments. Consult your doctor for more details.
MISSED DOSE: If you miss a dose, take it as soon as you remember. If it is within 12 hours of the next dose, skip the missed dose. Take your next dose at the regular time. Do not double the dose to catch up.
STORAGE: Store at room temperature away from light and moisture. Do not store in the bathroom. Keep all medications away from children and pets.Do not flush medications down the toilet or pour them into a drain unless instructed to do so. Properly discard this product when it is expired or no longer needed. Consult your pharmacist or local waste disposal company.
Information last revised May 2024. Copyright(c) 2024 First Databank, Inc.
IMPORTANT: HOW TO USE THIS INFORMATION: This is a summary and does NOT have all possible information about this product. This information does not assure that this product is safe, effective, or appropriate for you. This information is not individual medical advice and does not substitute for the advice of your health care professional. Always ask your health care professional for complete information about this product and your specific health needs.
Formulary
Adding plans allows you to compare formulary status to other drugs in the same class.
To view formulary information first create a list of plans. Your list will be saved and can be edited at any time.
Adding plans allows you to:
- View the formulary and any restrictions for each plan.
- Manage and view all your plans together – even plans in different states.
- Compare formulary status to other drugs in the same class.
- Access your plan list on any device – mobile or desktop.







