Dosing & Uses
Dosage Forms & Strengths
tablet, chewable (Epitol)
- 100mg
tablet, immediate-release (Tegretol)
- 200mg
tablet, extended-release (Tegretol XR)
- 100mg
- 200mg
- 400mg
capsule, extended-release (Equetro, Carbatrol)
- 100mg
- 200mg
- 300mg
oral suspension (Teril)
- 100mg/5mL
IV solution (Carnexiv)
- 10mg/mL (200mg/20mL single-dose vial)
Epilepsy
Indicated for the treatment of partial seizures with complex symptomatology (eg, psychomotor, temporal lobe), generalized tonic-clonic seizures (grand mal), and mixed seizure patterns, which include the seizure types listed here or other partial or generalized seizures
Maintenance dose range: 800-1200 mg/day PO in divided doses
Therapeutic range: 4-12 mg/L (16.9-50.8 micromoles/L)
Maximum dose of 1600 mg/day recommended (rarely, some patients have required 1.6-2.4 g/day)
Tablet (immediate-release)
- Initial: 200 mg PO q12hr
- Increase qWeek by 200 mg/day divided PO q6-8hr
Tablet/capsule (extended-release)
- Initial: 200 mg PO q12hr
- Increase qWeek by 200 mg/day PO divided q12hr
Oral suspension
- Initial: 10 mL (200 mg) PO q6hr
- Increase qWeek by up to 200 mg/day PO divided q6-8hr
IV solution
- Indicated as replacement therapy in adults for PO carbamazepine formulations, when PO administration is temporarily not feasible
-
Approved as temporary use (ie, ≤7 days) for the following seizure types
- Partial seizures with complex symptomatology
- Generalized tonic-clonic seizures
- Mixed seizure patterns which include the above, or other partial or generalized seizures
-
Dose
- The total daily dose of carbamazepine IV is 70% of the total daily PO dose from which patients are being
- Equally divide the total daily dose of the IV in four 30-minute infusions, separated by 6 hr
- Patients should be switched back to oral carbamazepine administration at their previous total daily oral dose and frequency of administration as soon as clinically appropriate
- IV administration has not been studies for >7 days
Limitations of use
- Not indicated for absence seizures (including atypical absence); carbamazepine has been associated with increased frequency of generalized convulsions in these patients
Trigeminal Neuralgia
Indicated for pain associated with trigeminal neuralgia; beneficial results have also been reported in glossopharyngeal neuralgia; carbamazepine is not a simple analgesic and should not be used for the relief of trivial aches or pains
Maintenance dose range: 400-800 mg/day PO in divided doses; attempts to reduce or discontinue the drug should be made at least every 3 months throughout the treatment period
Maximum dose of 1200 mg/day recommended
Tablet (immediate-release)
- Initial: 200 mg/day on day 1 divided q12hr
- Increase by up to 200 mg/day in increments of 100 mg q12hr, to dose range of 400-800 mg/day divided twice daily; not to exceed 1200 mg/day
Tablet/capsule (extended-release)
- Initial (XR tablet): 200 mg/day PO on day 1 divided q12hr
- Initial (XR capsules): 200 mg PO once on the first day; may increase dose by up to 200 mg/day using increments of 100 mg q12hr to reach an effective/tolerated dose; not to exceed 1200 mg/day
- Increase by up to 200 mg/day in increments of 100 mg q12hr, to dose range of 400-800 mg/day divided twice daily; not to exceed 1200 mg/day
Oral suspension
- Initial: 200 mg PO on day 1 divided q6hr
- Increase by up to 200 mg/day in increments of 50 mg q6hr, to dose range of 400-800 mg/day divided twice daily; not to exceed 1200 mg/day
Bipolar Mania
Equetro
- Indicated for treatment of patients with acute manic or mixed episodes associated with bipolar I disorder
- Initial: 200 mg PO q12hr
- Increase by increments of 200 mg/day; not to exceed 1600 mg/day
Dosage Modifications
Renal impairment
- Glomerular filtration rate <10 mL/min: Administer 75% of dose and monitor
- Peritoneal dialysis and hemodialysis: Administer 75% of dose and monitor
Hepatic impairment
- Use caution; drug is metabolized primarily in the liver
Restless Legs Syndrome (Off-label)
100-600 mg PO qHS for up to 5 weeks
Schizophrenia (Off-label)
200-1300 mg/day for 2.5-8 weeks
Postherpatic Neuralgia
100-200 mg PO qDay; may increase slowly to 1200 mg/day
Intravenous Carbamazepine (Orphan)
Orphan designation for treatment of epilepsy patients who cannot take anything by mouth
Orphan sponsor
- Lundbeck, LLC; Four Parkway North; Deerfield, IL 60015
Dosage Forms & Strengths
tablet, chewable (Epitol)
- 100mg
tablet, immediate-release (Tegretol)
- 200mg
tablet, extended-release (Tegretol XR)
- 100mg
- 200mg
- 400mg
capsule, extended-release (Equetro, Carbatrol)
- 100mg
- 200mg
- 300mg
oral suspension (Teril)
- 100mg/5mL
Epilepsy
Indicated for the treatment of partial seizures with complex symptomatology (eg, psychomotor, temporal lobe), generalized tonic-clonic seizures (grand mal), and mixed seizure patterns, which include the seizure types listed here or other partial or generalized seizures
<6 Years
- Initial (oral suspension): 10-20 mg/kg/day PO q6hr
- Initial (tablet): 10-20 mg/kg/day PO q8-12hr
- Maintenance: For tablets or suspension may divide frequency into 3-4 times daily not to exceed 35 mg/kg/day
6-12 Years
- Initial (oral suspension): 50 mg PO q6hr
- Initial (tablet, immediate- or extended-release): 100 mg PO q12hr; may increase qWeek by 100 mg/day
- Maintenance: 400-800 mg/day PO q6-8hr (immediate-release); q12hr (extended-release)
- Not to exceed 1000 mg/day
>12 Years
- Initial (oral suspension): 10 mL (200 mg) PO q6hr
- Initial (tablet, immediate- or extended-release tab/cap): 200 mg PO q12hr
- May increase by up to 200 mg/day qWeek; q12hr (extended-release tablet); q6-8hr (other formulations)
- 12-15 years: Dose not to exceed 1000 mg/day
- >15 years: Dose not to exceed 1200 mg/day
Dosage Modifications
Renal impairment
- Glomerular filtration rate <10 mL/min: Administer 75% of dose and monitor
- Peritoneal dialysis and hemodialysis: Administer 75% of dose and monitor
Hepatic impairment
- Use caution; drug is metabolized primarily in the liver
Dosing Considerations
Important to initiate slowly by advancing dose every 5-7 days to minimize GI upset and allow autoinduction of liver enzymes to occur (autoinduction is complete at 3-5 weeks)
Children <12 years who receive >400 mg/day may be converted to Carbatrol ER at the same dose, q12hr PO
Monitor: CBC, LFTs
Interactions
Interaction Checker
No Results
Contraindicated
Serious - Use Alternative
Significant - Monitor Closely
Minor
Contraindicated (46)
- apixaban
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of apixaban by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Contraindicated. Reduces anticoagulant effect by decreasing apixaban systemic exposure
- artemether/lumefantrine
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of artemether/lumefantrine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Contraindicated. Coadministration with strong CYP3A4 inducers can result in decreased serum concentrations and loss of antimalarial efficacy
- atazanavir
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of atazanavir by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Contraindicated.
- cabotegravir
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of cabotegravir by increasing metabolism. Contraindicated. Cabotegravir is metabolized by UGT1A1 and UGT1A9. Strong UGT1A1 or UGT1A9 inducers decrease cabotegravir systemic exposure, thereby increasing potential for loss of virologic response.
- cariprazine
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of cariprazine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Contraindicated. CYP3A4 is responsible for the formation and elimination of cariprazine's active metabolites. The effect of CYP3A4 inducers on cariprazine exposure has not been evaluated and the net effect is unclear.
- cobimetinib
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of cobimetinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Contraindicated. Avoid coadministration. Strong or moderate CYP3A inducers may decrease cobimetinib systemic exposure by >80% and reduce its efficacy.
- darunavir
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of darunavir by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Contraindicated. Coadministration with carbamazepine may result in loss of therapeutic effect and development of resistance to darunavir
- dienogest/estradiol valerate
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of dienogest/estradiol valerate by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Contraindicated. Women should not choose estradiol valerate/dienogest as their contraceptive while using strong CYP3A4 inducers due to potential decrease in contraceptive efficacy. Estradiol valerate/dienogest should not be used for at least 28 days after discontinuation of the inducer due to possibility of decreased contraceptive efficacy.
- doravirine
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of doravirine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Contraindicated. Coadministration of doravirine with a strong CYP3A inducer may decrease doravirine plasma concentrations and/or effects. Potential for loss of virologic response and possible resistance to doravirine.
- efavirenz
carbamazepine, efavirenz. Either decreases levels of the other by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Contraindicated. Coadministration of carbamazepine with NNRTIs may result in a loss of virologic response and possible resistance to the NNRTI. A decrease in AUC is observed for both carbamazepine (27%) and efavirenz (36%) when coadministered.
- elbasvir/grazoprevir
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of elbasvir/grazoprevir by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Contraindicated. The therapeutic effect of elbasvir/grazoprevir may be reduced if coadministered with strong CYP3A inducers and is therefore contraindicated.
- elvitegravir/cobicistat/emtricitabine/tenofovir DF
carbamazepine decreases levels of elvitegravir/cobicistat/emtricitabine/tenofovir DF by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Contraindicated. May lead to loss of virologic response and possible resistance.
- etravirine
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of etravirine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C9/10 metabolism. Contraindicated. Coadministration of carbamazepine with NNRTIs may result in a loss of virologic response and possible resistance to the NNRTI.
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of etravirine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Contraindicated. Coadministration of carbamazepine with NNRTIs may result in a loss of virologic response and possible resistance to the NNRTI. - fostemsavir
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of fostemsavir by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Contraindicated. Coadministration of fostemsavir (prodrug) with strong CYP3A4 inducers significantly decreases temsavir (active moiety) plasma concentrations, which may lead to loss of virologic response and resistance.
- irinotecan
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of irinotecan by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2B6 metabolism. Contraindicated.
- irinotecan liposomal
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of irinotecan liposomal by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2B6 metabolism. Contraindicated.
- isavuconazonium sulfate
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of isavuconazonium sulfate by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Contraindicated.
- isocarboxazid
carbamazepine increases toxicity of isocarboxazid by unknown mechanism. Contraindicated. D/C MAO inhibitor 2 weeks before.
- ledipasvir/sofosbuvir
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of ledipasvir/sofosbuvir by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Contraindicated. P-gp inducers decrease sofosbuvir levels, and therefore decrease conversion to sofosbuvir's active metabolite (GS-331007) responsible for 90% of pharmacologic effect
- lenacapavir
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of lenacapavir by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Contraindicated. Coadministration of lenacapavir with strong CYP3A inducers is contraindicated.
- linezolid
carbamazepine increases toxicity of linezolid by unknown mechanism. Contraindicated. D/C MAO inhibitor 2 weeks before.
- lonafarnib
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of lonafarnib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Contraindicated. Lonafarnib is a sensitive CYP3A4 substrate. Coadministration with strong or moderate CYP3A4 inducers is contraindicated.
- lorlatinib
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of lorlatinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Contraindicated. Coadministration of lorlatinib with strong CYP3A inducers is contraindicated. Discontinue the strong CYP3A inducer for 3 plasma half-lives before initiating lorlatinib.
- lumacaftor/ivacaftor
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of lumacaftor/ivacaftor by aldehyde dehydrogenase inhibition. Contraindicated. Strong CYP3A inducers have minimal effect on lumacaftor exposure, but decreased ivacaftor exposure (AUC) by 57%. This may reduce the effectiveness of lumacaftor/ivacaftor. Therefore, coadministration is not recommended.
- lumefantrine
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of lumefantrine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Contraindicated. Coadministration with strong CYP3A4 inducers can result in decreased serum concentrations and loss of antimalarial efficacy
- lurasidone
carbamazepine decreases levels of lurasidone by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Contraindicated. Contraindicated; decreases lurasidone Cmax by ~85%.
- mavacamten
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of mavacamten by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C19 metabolism. Contraindicated.
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of mavacamten by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Contraindicated. - naloxegol
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of naloxegol by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Contraindicated. Use of naloxegol with strong CYP3A4 inducers is not recommended
- nefazodone
nefazodone will increase the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Contraindicated.
nefazodone increases levels of carbamazepine by decreasing metabolism. Contraindicated.
carbamazepine decreases levels of nefazodone by increasing metabolism. Contraindicated. - nevirapine
carbamazepine decreases levels of nevirapine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Contraindicated. Coadministration of carbamazepine with NNRTIs may result in a loss of virologic response and possible resistance to the NNRTI.
- nirmatrelvir
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of nirmatrelvir by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Contraindicated. Nirmatrelvir, a CYP3A4 substrate, is contraindicated with strong CYP3A4 inducers. Significantly reduced nirmatrelvir plasma concentrations may be associated with potential for loss of virologic response and possible resistance. Do not initiate nirmatrelvir/ritonavir immediately after discontinuing a strong 3A4 inducer owing to time needed for systemic clearance of the inducer.
- nirmatrelvir/ritonavir
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of nirmatrelvir/ritonavir by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Contraindicated. Nirmatrelvir, a CYP3A4 substrate, is contraindicated with strong CYP3A4 inducers. Significantly reduced nirmatrelvir plasma concentrations may be associated with potential for loss of virologic response and possible resistance. Do not initiate nirmatrelvir/ritonavir immediately after discontinuing a strong 3A4 inducer owing to time needed for systemic clearance of the inducer.
- ombitasvir/paritaprevir/ritonavir & dasabuvir (DSC)
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of ombitasvir/paritaprevir/ritonavir & dasabuvir (DSC) by increasing metabolism. Contraindicated. Strong CYP2C8 inducers may reduce dasabuvir levels, and therefore decreased efficacy of Viekira Pak
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of ombitasvir/paritaprevir/ritonavir & dasabuvir (DSC) by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Contraindicated. Strong CYP3A4 inducers may reduce partiaprevir and ritonavir levels, and therefore decreased efficacy of Viekira Pak - panobinostat
carbamazepine decreases levels of panobinostat by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Contraindicated. Strong CYP3A4 inducers can reduce panobinostat levels by ~70% and lead to treatment failure.
- phenelzine
carbamazepine increases toxicity of phenelzine by unknown mechanism. Contraindicated. D/C MAO inhibitor 2 weeks before.
- pirfenidone
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of pirfenidone by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP1A2 metabolism. Contraindicated. Use of strong CYP1A2 inducers should be discontinued before initiating pirfenidone and avoided during treatment
- praziquantel
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of praziquantel by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Contraindicated.
- procarbazine
carbamazepine increases toxicity of procarbazine by unknown mechanism. Contraindicated. D/C MAO inhibitor 2 weeks before.
- regorafenib
carbamazepine, regorafenib. affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Contraindicated. Strong CYP3A4 inducers decrease regorafenib levels and increase exposure of the active metabolite M-5.
- rilpivirine
carbamazepine decreases levels of rilpivirine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Contraindicated. Coadministration of carbamazepine with NNRTIs may result in a loss of virologic response and possible resistance to the NNRTI.
- roflumilast
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of roflumilast by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Contraindicated. Coadministration not recommended; strong cytochrome P450 enzyme inducers decrease systemic exposure to roflumilast and may reduce the therapeutic effectiveness
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of roflumilast by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP1A2 metabolism. Contraindicated. Coadministration not recommended; strong cytochrome P450 enzyme inducers decrease systemic exposure to roflumilast and may reduce the therapeutic effectiveness - selegiline
carbamazepine increases toxicity of selegiline by unknown mechanism. Contraindicated. D/C MAO inhibitor 2 weeks before.
- selegiline transdermal
carbamazepine increases toxicity of selegiline transdermal by unknown mechanism. Contraindicated. D/C MAO inhibitor 2 weeks before.
- tranylcypromine
carbamazepine increases toxicity of tranylcypromine by unknown mechanism. Contraindicated. D/C MAO inhibitor 2 weeks before.
- vandetanib
carbamazepine decreases levels of vandetanib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Contraindicated. Avoid coadministration with potent CYP3A4 inducers; these drugs reduce exposure to vandetanib by up to 40%.
- voriconazole
carbamazepine decreases levels of voriconazole by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Contraindicated.
Serious - Use Alternative (260)
- abemaciclib
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of abemaciclib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Coadministration of abemaciclib with strong CYP3A4 inducers reduces plasma concentration of abemaciclib and its metabolites.
- abrocitinib
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of abrocitinib by increasing metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Abrocitinib is a CYP2C9 and CYP2C19 substrate. Drugs that are strong inducers of CYP2C19 or CYP2C9 decreases the combined exposure of abrocitinib and its active metabolites, resulting in loss of or reduced clinical response.
- acalabrutinib
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of acalabrutinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid coadministration of acalabrutinib with strong CYP3A inducers. If a strong CYP3A inducer must be used, increase acalabrutinib dose to 200 mg twice daily.
- adagrasib
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of adagrasib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
adagrasib will increase the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid coadministration of adagrasib, a CYP3A4 inhibitor, with sensitive CYP3A substrates unless otherwise recommended in the prescribing information for these substrates. - afatinib
carbamazepine decreases levels of afatinib by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Increase afatinib daily dose by 10 mg as tolerated if chronic therapy with P-gp inducer required; resume previous afatinib dose 2-3 days after P-gp inducer discontinued.
- almotriptan
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of almotriptan by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- alosetron
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of alosetron by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP1A2 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- alpelisib
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of alpelisib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid coadministration of alpelisib (CYP3A4 substrate) with strong CYP3A4 inducers.
- alprazolam
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of alprazolam by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- amiodarone
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of amiodarone by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- apalutamide
apalutamide will decrease the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Coadministration of apalutamide, a strong CYP3A4 inducer, with drugs that are CYP3A4 substrates can result in lower exposure to these medications. Avoid or substitute another drug for these medications when possible. Evaluate for loss of therapeutic effect if medication must be coadministered. Adjust dose according to prescribing information if needed.
- apremilast
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of apremilast by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Coadministration with strong CYP inducers results in a significant decrease of systemic exposure of apremilast, which may result in loss of efficacy
- aprepitant
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of aprepitant by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- aripiprazole
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of aripiprazole by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. If carbamazepine is started in a patient already taking aripiprazole, the aripiprazole dose should be doubled; reduce aripiprazole dose if carbamazepine is discontinued
- atorvastatin
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of atorvastatin by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- avapritinib
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of avapritinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- axitinib
carbamazepine decreases levels of axitinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Selection of concomitant medication with no or minimal CYP3A4 induction potential is recommended.
- bazedoxifene/conjugated estrogens
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of bazedoxifene/conjugated estrogens by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- bedaquiline
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of bedaquiline by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid coadministration of bedaquiline with strong CYP3A4 inducers due to potential for decreased therapeutic effect
- bictegravir
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of bictegravir by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Coadministration of strong CYP3A and UGT1A1 inducers can substantially decrease bictegravir plasma concentrations. This may result in the loss of therapeutic effect and development of resistance to bictegravir. Coadministration with another anticonvulsant should be considered.
- bosutinib
carbamazepine decreases levels of bosutinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Strong CYP3A4 inducers decreased bosutinib plasma concentration by ~85% .
- bremelanotide
bremelanotide will decrease the level or effect of carbamazepine by Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Bremelanotide may slow gastric emptying and potentially reduces the rate and extent of absorption of concomitantly administered oral medications. Avoid use when taking any oral drug that is dependent on threshold concentrations for efficacy. Interactions listed are representative examples and do not include all possible clinical examples.
- brigatinib
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of brigatinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Coadministration with strong CYP3A4 inducers may decrease brigatinib efficacy.
brigatinib will decrease the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Brigatinib induces CYP3A4 in vitro. Coadministration with CYP3A4 substrates, particularly those with a narrow therapeutic index, can result in decreased concentrations and loss of efficacy. If unable to avoid coadministration, monitor CYP3A4 substrate levels and adjust dose as needed. - budesonide
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of budesonide by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- buspirone
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of buspirone by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- cabozantinib
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of cabozantinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid coadministration of cabozantinib with strong CYP3A4 inducers. If a strong CYP3A4 inducer is required, increase cabozantinib dose by 40 mg/day (Cometriq) or by 20 mg/day (Cabometyx). Resume previous dose 2-3 days after strong CYP3A4 inducer discontinued.
- calcitriol
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of calcitriol by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- capivasertib
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of capivasertib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Strong or moderate CYP3A inducers decrease capivasertib exposure, which may reduce efficacy.
- capmatinib
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of capmatinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- ceritinib
carbamazepine decreases levels of ceritinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
ceritinib will increase the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. - cilostazol
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of cilostazol by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- cinacalcet
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of cinacalcet by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- clarithromycin
clarithromycin will increase the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Monitor plasma levels when used concomitantly
- clonazepam
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of clonazepam by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- clopidogrel
carbamazepine will increase the level or effect of clopidogrel by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. CYP3A4 inducers may increase the metabolism of clopidogrel to its active metabolite. Monitor patients for potential increase in antiplatelet effects when CYP3A4 inducers are used in combination with clopidogrel
- clozapine
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of clozapine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
carbamazepine, clozapine. Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Increased risk of agranulocytosis. - cobicistat
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of cobicistat by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. If coadministration is necessary, monitor for lack or loss of virologic response from cobicistat
- colchicine
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of colchicine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- conivaptan
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of conivaptan by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- conjugated estrogens
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of conjugated estrogens by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- conjugated estrogens, vaginal
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of conjugated estrogens, vaginal by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- copanlisib
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of copanlisib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid coadministration of copanlisib with strong CYP3A4 inducers.
- cortisone
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of cortisone by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- dabigatran
carbamazepine decreases levels of dabigatran by increasing metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. The concomitant use of dabigatran and P-gp inducers should generally be avoided.
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of dabigatran by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid coadministration. P-gp inducers reduce systemic exposure of dabigatran - dabrafenib
carbamazepine decreases levels of dabrafenib by increasing metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Strong CYP2C8 inducers may decrease dabrafenib levels.
carbamazepine decreases levels of dabrafenib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. - dantrolene
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of dantrolene by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- darifenacin
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of darifenacin by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- darolutamide
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of darolutamide by Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Darolutamide is a P-gp and CYP3A4 substrate. Avoid coadminstration of darolutamide with combined P-gp and strong or moderate CYP3A4 inducers.
- dasatinib
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of dasatinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- deflazacort
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of deflazacort by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid coadministration of deflazacort with moderate or strong CYP3A4 inducers.
- dexamethasone
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of dexamethasone by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- diazepam
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of diazepam by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- dihydroergotamine
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of dihydroergotamine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- dihydroergotamine intranasal
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of dihydroergotamine intranasal by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- disulfiram
carbamazepine, disulfiram. Either increases toxicity of the other by Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Comment: Pretomanid regimen associated with hepatotoxicity. Avoid alcohol and hepatotoxic agents, including herbal supplements and drugs other than bedaquiline and linezolid.
- dolutegravir
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of dolutegravir by increasing metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid coadministration; insufficient data to recommend dosage adjustment
- dronedarone
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of dronedarone by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- duloxetine
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of duloxetine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP1A2 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- duvelisib
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of duvelisib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Coadministration with a strong CYP3A inducer decreases duvelisib area under the curve (AUC), which may reduce duvelisib efficacy.
- edoxaban
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of edoxaban by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid coadministration of edoxaban with potent P-gp inducers
- elacestrant
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of elacestrant by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- eletriptan
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of eletriptan by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- eliglustat
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of eliglustat by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Strong CYP3A inducers significantly decreases eliglustat exposure; coadministration not recommended
- eluxadoline
carbamazepine increases levels of eluxadoline by decreasing metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Decrease eluxadoline dose to 75 mg PO BID if coadministered with OATP1B1 inhibitors. .
- elvitegravir
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of elvitegravir by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid; coadministration with CYP3A inducers may result in decreased plasma concentrations of elvitegravir and/or a concomitantly administered protease inhibitor and lead to loss of therapeutic effect and to possible resistance
- encorafenib
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of encorafenib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- entrectinib
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of entrectinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- enzalutamide
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of enzalutamide by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- erdafitinib
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of erdafitinib by altering metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid coadministration of strong CYP2C9 or CYP3A4 inducers with erdafitinib.
- ergotamine
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of ergotamine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- erlotinib
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of erlotinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- erythromycin base
erythromycin base will increase the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Monitor plasma levels when used concomitantly
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of erythromycin base by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. - erythromycin ethylsuccinate
erythromycin ethylsuccinate will increase the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Monitor plasma levels when used concomitantly
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of erythromycin ethylsuccinate by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. - erythromycin lactobionate
erythromycin lactobionate will increase the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Monitor plasma levels when used concomitantly
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of erythromycin lactobionate by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. - erythromycin stearate
erythromycin stearate will increase the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Monitor plasma levels when used concomitantly
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of erythromycin stearate by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. - esomeprazole
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of esomeprazole by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C19 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- estradiol
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of estradiol by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- estrogens conjugated synthetic
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of estrogens conjugated synthetic by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- estropipate
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of estropipate by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- ethinylestradiol
ethinylestradiol will increase the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. The efficacy of hormonal contraceptives may be reduced. Use of a nonhormonal contraceptive is recommended.
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of ethinylestradiol by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. - etonogestrel
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of etonogestrel by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- everolimus
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of everolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- fedratinib
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of fedratinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Effect of coadministering a strong CYP3A4 inducer with fedratinib has not been studied.
- felodipine
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of felodipine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- fesoterodine
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of fesoterodine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- fexinidazole
carbamazepine will increase the level or effect of fexinidazole by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. CYP450 inducers may significantly increase plasma concentrations of fexinidazole?s active metabolites: fexinidazole sulfoxide (M1) and fexinidazole sulfone (M2). M2 plasma concentrations associated with increased QT prolongation risks.
fexinidazole will increase the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Fexinidazole inhibits CYP3A4. Coadministration may increase risk for adverse effects of CYP3A4 substrates. - finerenone
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of finerenone by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- fludrocortisone
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of fludrocortisone by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- fosamprenavir
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of fosamprenavir by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- fosaprepitant
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of fosaprepitant by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- fostamatinib
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of fostamatinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- fruquintinib
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of fruquintinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- futibatinib
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of futibatinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Coadministration of futibatinib with drugs that are dual P-gp and strong CYP3A inducers may decrease futibatinib efficacy.
- ganaxolone
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of ganaxolone by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid coadministration of ganaxolone with moderate or strong CYP3A4 inducers. If coadministration unavoidable, consider increasing ganaxolone dose; however, do not exceed maximum daily dose for weight.
- gepirone
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of gepirone by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- gilteritinib
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of gilteritinib by Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Gilteritinib is a P-gp and CYP3A4 substrates. Coadministration of gilteritinib with a combined P-gp and strong CYP3A inducer decreases gilteritinib exposure and efficacy.
- glasdegib
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of glasdegib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid coadministration of glasdegib with strong CYP3A inducers.
- glecaprevir/pibrentasvir
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of glecaprevir/pibrentasvir by increasing metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Coadministration of carbamazepine (a strong CYP3A4 and P-gp inducer) with glecaprevir/pibrentasvir may significantly decrease glecaprevir/pibrentasvir plasma concentrations and AUC. Potential for loss of therapeutic effect.
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of glecaprevir/pibrentasvir by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. - haloperidol
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of haloperidol by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- hydrochlorothiazide
carbamazepine, hydrochlorothiazide. Either increases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Increased risk of systemic hyponatremia.
- hydrocortisone
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of hydrocortisone by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- hydroxyprogesterone caproate (DSC)
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of hydroxyprogesterone caproate (DSC) by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- ibrutinib
carbamazepine decreases levels of ibrutinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Strong CYP3A inducers decrease ibrutinib plasma concentrations by ~10-fold.
- idelalisib
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of idelalisib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid coadministration; strong CYP3A4 inducers significantly decrease idelalisib systemic exposure
idelalisib will increase the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Idelalisib is a strong CYP3A inhibitor; avoid coadministration with sensitive CYP3A substrates - iloperidone
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of iloperidone by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- indinavir
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of indinavir by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- infigratinib
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of infigratinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- irinotecan
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of irinotecan by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- irinotecan liposomal
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of irinotecan liposomal by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- isosorbide dinitrate
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of isosorbide dinitrate by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- isosorbide mononitrate
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of isosorbide mononitrate by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- istradefylline
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of istradefylline by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid coadministration of istradefylline with strong CYP3A4 inducers.
- itraconazole
itraconazole will increase the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Not recommended 2 weeks before, during, and 2 weeks after itraconazole.
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of itraconazole by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Not recommended 2 weeks before, during, and 2 weeks after itraconazole. - ivabradine
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of ivabradine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid coadministration of ivabradine with moderate CYP3A4 inducers.
- ivacaftor
carbamazepine decreases levels of ivacaftor by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid coadministration with strong CYP3A4 inducers; systemic exposure of ivacaftor substantially reduced (ie, ~9-fold).
- ivosidenib
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of ivosidenib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Coadministration of ivosidenib with strong CYP3A4 inducers decreased ivosidenib plasma concentrations.
ivosidenib will decrease the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. - ixabepilone
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of ixabepilone by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- ixazomib
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of ixazomib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid coadministration of ixazomib with strong CYP3A inducers. Strong inducers have been shown to decrease ixazomib Cmax by 54% and AUC by 74%.
- ketoconazole
ketoconazole will increase the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid combination for 2 weeks before and during ketoconazole use if possible. Monitor plasma levels when used concomitantly.
- lapatinib
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of lapatinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. If carbamazepine is started in a patient already taking lapatinib, gradually titrate lapatinib dose upward; reduce lapatinib dose if carbamazepine is discontinued
- larotrectinib
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of larotrectinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. If coadministration of larotrectinib with strong CYP3A4 inducers is unavoidable, double larotrectinib dose. Resume prior larotrectinib dose once CYP3A4 inducer discontinued for 3-5 half-lives
- lefamulin
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of lefamulin by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid coadministration of lefamulin with strong or moderate CYP3A inducers unless the benefit outweighs risks. Monitor for reduced efficacy.
- lemborexant
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of lemborexant by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- leniolisib
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of leniolisib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- letermovir
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of letermovir by Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Coadministration of letermovir with UCT1A1/3 inducers is not recommended.
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of letermovir by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Coadministration of letermovir with P-gp inducers is not recommended. - levoketoconazole
levoketoconazole will increase the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid combination for 2 weeks before and during ketoconazole use if possible. Monitor plasma levels when used concomitantly.
- lomitapide
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of lomitapide by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- lopinavir
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of lopinavir by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
lopinavir will increase the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. - loratadine
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of loratadine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- lorlatinib
lorlatinib will decrease the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Contraindicated.
- losartan
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of losartan by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- lovastatin
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of lovastatin by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- lumacaftor/ivacaftor
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of lumacaftor/ivacaftor by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- lumateperone
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of lumateperone by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- lurbinectedin
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of lurbinectedin by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- macimorelin
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of macimorelin by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Potential for false positive test results if macimorelin and strong CYP3A4 inducers are coadministered. Discontinue strong CYP3A4 inducer, allowing for sufficient washout time, before testing.
- macitentan
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of macitentan by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid coadministering macitentan with strong CYP3A4 inducers
- maraviroc
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of maraviroc by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- mestranol
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of mestranol by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
carbamazepine decreases levels of mestranol by increasing metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. May result in loss of contraceptive efficacy. - methadone
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of methadone by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- methimazole
methimazole, carbamazepine. Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Increased risk of agranulocytosis.
- methylprednisolone
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of methylprednisolone by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- metoclopramide intranasal
carbamazepine, metoclopramide intranasal. Either increases effects of the other by Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Comment: Avoid use of metoclopramide intranasal or interacting drug, depending on importance of drug to patient.
- midazolam
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of midazolam by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- midostaurin
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of midostaurin by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Strong CYP3A4 inducers may decrease midostaurin concentrations resulting in reduced efficacy.
- mifepristone
mifepristone will increase the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of mifepristone by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. - mobocertinib
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of mobocertinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
mobocertinib will decrease the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. If use is unavoidable, increase CYP3A4 substrate dosage in accordance with its prescribing information. - naldemedine
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of naldemedine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid coadministration with strong CYP3A4 inducers.
- nefazodone
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of nefazodone by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Contraindicated.
- nelfinavir
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of nelfinavir by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- neratinib
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of neratinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid coadministration of neratinib with strong/moderate CYP3A4 inducers.
- netupitant/palonosetron
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of netupitant/palonosetron by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Netupitant is mainly metabolized by CYP3A4; avoid use in patients who are chronically using a strong CYP3A4 inducer
- nicardipine
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of nicardipine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- nilotinib
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of nilotinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- nintedanib
carbamazepine decreases levels of nintedanib by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid coadministration, particularly for P-gp inducers that are also CYP3A4 inducers; nintedanib is a substrate of P-gp and to a less extent CYP3A4.
- nirogacestat
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of nirogacestat by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- nisoldipine
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of nisoldipine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- norethindrone
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of norethindrone by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid coadministration unless benefit outweighs risk. When coadministered, hormonal contraceptives are not a reliable method of effective birth control. Concomitant use may increase incidence of menstruation associated adverse effects (amenorrhea, dysmenorrhea, menorrhagia).
- norethindrone acetate
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of norethindrone acetate by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid coadministration unless benefit outweighs risk. When coadministered, hormonal contraceptives are not a reliable method of effective birth control. Concomitant use may increase incidence of menstruation associated adverse effects (amenorrhea, dysmenorrhea, menorrhagia).
- norethindrone transdermal
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of norethindrone transdermal by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid coadministration unless benefit outweighs risk. When coadministered, hormonal contraceptives are not a reliable method of effective birth control. Concomitant use may increase incidence of menstruation associated adverse effects (amenorrhea, dysmenorrhea, menorrhagia).
- norgestrel
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of norgestrel by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Contraceptive failure is possible owing to decreased serum concentration of norgestrel. Advise patients to use an alternative method of contraception or a back-up method during coadministration, and to continue back-up contraception for 28 days after discontinuing the strong CYP3A4 inducer to ensure contraceptive reliability
- olanzapine/samidorphan
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of olanzapine/samidorphan by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Strong CYP3A4 inducers decrease levels of olanzapine and samidorphan by~50% and ~75% respectively.
- olaparib
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of olaparib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid coadministration of olaparib with strong CYP3A4 inducers.
- olopatadine intranasal
carbamazepine and olopatadine intranasal both increase sedation. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Coadministration increases risk of CNS depression, which can lead to additive impairment of psychomotor performance and cause daytime impairment.
- olutasidenib
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of olutasidenib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Strong or moderate CYP3A inducers decrease olutasidenib (a CYP3A4 substrate) plasma concentrations and efficacy.
olutasidenib will decrease the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid coadministration of olutasidenib (a CYP3A4 inducer) with sensitive CYP3A substrates unless otherwise instructed in substrates prescribing information. If unavoidable, monitor for loss of therapeutic effect of sensitive CYP3A4 substrates. - omaveloxolone
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of omaveloxolone by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- omeprazole
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of omeprazole by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C19 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- osilodrostat
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of osilodrostat by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- osimertinib
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of osimertinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid concomitant use of osimertinib with strong CYP3A inducers.
- ozanimod
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of ozanimod by Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Coadministration of ozanimod (a CYP2C8 substrate) with strong CYP2C8 inducers decreases the exposure of the active metabolites (CC112273 and CC1084037) of ozanimod, which may decrease the effiicacy of ozanimod. Therefore, coadministration of ozanimod with strong CYP2C8 inducers is not recommended.
- pacritinib
pacritinib will increase the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- palbociclib
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of palbociclib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Strong CYP3A inducers decrease palbociclib plasma exposure by ~85%.
- palovarotene
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of palovarotene by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- pazopanib
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of pazopanib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- pemigatinib
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of pemigatinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- perampanel
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of perampanel by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- pexidartinib
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of pexidartinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
carbamazepine and pexidartinib both increase Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Pexidartinib can cause hepatotoxicity. Avoid coadministration of pexidartinib with other products know to cause hepatoxicity.
pexidartinib will decrease the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Coadministration of pexidartinib (a CYP3A4 inducer) with sensitive CYP3A substrates may lead to serious therapeutic failures. If concomitant use is unavoidable, increase the CYP3A substrate dosage in accordance with approved product labeling. - pirtobrutinib
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of pirtobrutinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- pomalidomide
carbamazepine decreases levels of pomalidomide by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
carbamazepine decreases levels of pomalidomide by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP1A2 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
carbamazepine decreases levels of pomalidomide by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. - ponatinib
carbamazepine decreases levels of ponatinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid unless the coadministration outweighs the possible risk of ponatinib underexposure; monitor for signs of reduced efficacy.
- ponesimod
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of ponesimod by Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Not recommended. Based on limited data, coadministration of strong CYP3A4 and UGT1A1 inducers (eg, rifampin, phenytoin, carbamazepine) may decrease systemic exposure of ponesimod. The clinical relevance is unclear.
- pralsetinib
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of pralsetinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. If unable to avoid, double current pralsetinib dose starting on Day 7 of coadministration with strong CYP3A inducer. After inducer has been discontinued for at least 14 days, resume previous pralsetinib dose.
- prednisolone
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of prednisolone by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- prednisone
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of prednisone by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- pretomanid
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of pretomanid by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Pretomanid is a CYP3A4 substrate. Avoid coadministration of strong or moderate CYP3A4 inducers.
carbamazepine, pretomanid. Either increases toxicity of the other by Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Comment: Pretomanid regimen associated with hepatotoxicity. Avoid alcohol and hepatotoxic agents, including herbal supplements and drugs other than bedaquiline and linezolid. - primaquine
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of primaquine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- progesterone intravaginal gel
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of progesterone intravaginal gel by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- progesterone micronized
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of progesterone micronized by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- progesterone, natural
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of progesterone, natural by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- propofol
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of propofol by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2B6 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- propylthiouracil
propylthiouracil, carbamazepine. Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Increased risk of agranulocytosis.
- quetiapine
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of quetiapine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- quinidine
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of quinidine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- quizartinib
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of quizartinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- ranolazine
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of ranolazine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- repaglinide
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of repaglinide by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- repotrectinib
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of repotrectinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
repotrectinib will decrease the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Repotrectinib is a CYP3A4 inducer. Avoid coadministration with CYP3A substrates where minimal concentration changes can cause reduced efficacy, unless otherwise recommended their prescribing information. - ribociclib
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of ribociclib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Coadministration of ribociclib with strong CYP3A inducers should be avoided.
- rifabutin
rifabutin will decrease the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- rifampin
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- rimegepant
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of rimegepant by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- ripretinib
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of ripretinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Coadministration with a strong CYP3A inhibitor will decrease systemic exposure to ripretinib and its active metabolite (DP-5439), which may decrease risk of adverse reactions.
- ritlecitinib
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of ritlecitinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Coadministration with strong CYP3A inducers may decrease ritlecitinib AUC and peak plasma concentration, which may result in loss of or reduced efficacy.
- ritonavir
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of ritonavir by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- rolapitant
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of rolapitant by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Long-term coadministration of strong CYP3A4 inducers with rolapitant may significantly decrease rolapitant efficacy.
- romidepsin
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of romidepsin by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Coadministration with strong 3A4 inducers should be avoided if possible.
- ropeginterferon alfa 2b
ropeginterferon alfa 2b, carbamazepine. Either increases toxicity of the other by Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Comment: Myelosuppressive agents can produce additive myelosuppression. Avoid use and monitor patients receiving the combination for effects of excessive myelosuppression.
- saquinavir
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of saquinavir by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- selinexor
selinexor, carbamazepine. unspecified interaction mechanism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Patients treated with selinexor may experience neurological toxicities. Avoid taking selinexor with other medications that may cause dizziness or confusion.
- selpercatinib
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of selpercatinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- selumetinib
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of selumetinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- silodosin
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of silodosin by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- simvastatin
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of simvastatin by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- siponimod
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of siponimod by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Coadministration of siponimod with a drug that causes moderate CYP2C9 plus a moderate or strong CYP3A4 inducer is not recommended. Coadministration with moderate or strong CYP3A4 inducers alone is not recommended for patients with CYP2C9*1/*3 and*2/*3 genotype.
- sirolimus
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of sirolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- sofosbuvir
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of sofosbuvir by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. P-gp inducers decrease sofosbuvir levels, and therefore decrease conversion to sofosbuvir's active metabolite (GS-331007) responsible for 90% of pharmacologic effect
- sofosbuvir/velpatasvir
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of sofosbuvir/velpatasvir by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Sofosbuvir and velpatasvir are substrates of the drug transporter P-gp. Potent P-gp inducers may significantly decrease sofosbuvir and velpatasvir plasma concentrations, leading to potentially reduced therapeutic effect.
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of sofosbuvir/velpatasvir by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2B6 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Velpatasvir is a substrate of CYP2B6, CYP2C8, and CYP3A4. Drugs that are moderate-to-potent inducers of CYP2B6, CYP2C8, or CYP3A4 may significantly decrease velpatasvir plasma concentrations, leading to potentially reduced therapeutic effect.
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of sofosbuvir/velpatasvir by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Velpatasvir is a substrate of CYP2B6, CYP2C8, and CYP3A4. Drugs that are moderate-to-potent inducers of CYP2B6, CYP2C8, or CYP3A4 may significantly decrease velpatasvir plasma concentrations, leading to potentially reduced therapeutic effect. - solifenacin
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of solifenacin by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- sonidegib
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of sonidegib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid coadministration of sonidegib with strong or moderate CYP3A4 inducers.
- sorafenib
carbamazepine decreases levels of sorafenib by increasing metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of sorafenib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. - sotagliflozin
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of sotagliflozin by Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Glucuronidation by UGT1A9, to form the 3-O-glucuronide, was identified as a major metabolic pathway for sotagliflozin. Coadministration of UGT1A9 inducers may decrease exposure to sotagliflozin, which may decrease efficacy.
- sotorasib
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of sotorasib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
sotorasib will decrease the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. If use is unavoidable, refer to the prescribing information of the CYP3A4 substrate for dosage modifications - sparsentan
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of sparsentan by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- St John's Wort
St John's Wort will decrease the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- stiripentol
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of stiripentol by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. If unable to avoid coadministration of stiripentol with strong CYP3A4 inducers, increase stiripentol dose.
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of stiripentol by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C19 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. If unable to avoid coadministration of stiripentol with strong CYP1A2 inducers, increase stiripentol dose. - sunitinib
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of sunitinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- tacrolimus
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Monitor tacrolimus levels and adjust dose accordingly
- tamsulosin
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of tamsulosin by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- tazemetostat
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of tazemetostat by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- temsirolimus
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of temsirolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- tetracycline
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of tetracycline by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- tezacaftor
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of tezacaftor by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- theophylline
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of theophylline by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
theophylline decreases levels of carbamazepine by increasing metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. - tiagabine
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of tiagabine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- tipranavir
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of tipranavir by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- tivozanib
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of tivozanib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- tizanidine
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of tizanidine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP1A2 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- tolterodine
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of tolterodine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- tolvaptan
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of tolvaptan by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- trabectedin
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of trabectedin by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- triamcinolone acetonide injectable suspension
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of triamcinolone acetonide injectable suspension by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- triazolam
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of triazolam by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- tucatinib
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of tucatinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of tucatinib by Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Coadministration of tucatinib (a CYP2C8 substrate) with a strong or moderate CYP2C8 inducer decreases tucatinib plasma concentrations.
tucatinib will increase the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid concomitant use of tucatinib with CYP3A substrates, where minimal concentration changes may lead to serious or life-threatening toxicities. If unavoidable, reduce CYP3A substrate dose according to product labeling. - ubrogepant
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of ubrogepant by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- ulipristal
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of ulipristal by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- upadacitinib
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of upadacitinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid upadacitinib coadministration with strong CYP3A4 inducers.
- valbenazine
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of valbenazine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Concomitant use not recommended.
- vardenafil
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of vardenafil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- velpatasvir
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of velpatasvir by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2B6 metabolism. Contraindicated.
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of velpatasvir by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. - vemurafenib
carbamazepine decreases levels of vemurafenib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- venetoclax
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of venetoclax by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid coadministration of venetoclax with strong or moderate CYP3A inducers. Consider alternative treatment with agents that have less CYP3A induction.
- verapamil
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of verapamil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- voclosporin
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of voclosporin by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- vonoprazan
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of vonoprazan by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- vorapaxar
carbamazepine decreases levels of vorapaxar by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- vortioxetine
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of vortioxetine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- voxelotor
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of voxelotor by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Voxelotor is primarily metabolized by CYP3A4. Avoid coadministration with moderate or strong CYP3A4 inducers. If unable to avoid coadministration, increase voxelotor dose (see Dosage Modifications).
voxelotor will increase the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Voxelotor increases systemic exposure of sensitive CYP3A4 substrates. Avoid coadministration with sensitive CYP3A4 substrates with a narrow therapeutic index. Consider dose reduction of the sensitive CYP3A4 substrate(s) if unable to avoid. - voxilaprevir
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of voxilaprevir by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- zanubrutinib
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of zanubrutinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid coadministration of zanubutinib with strong CYP3A4 inducers.
- zuranolone
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of zuranolone by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
Monitor Closely (368)
- abiraterone
carbamazepine decreases levels of abiraterone by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Avoid coadministration of abiraterone with strong CYP3A4 inducers; if a strong CYP3A4 inducer must be used, increase abiraterone dosage frequency from once daily to twice daily.
- alfentanil
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of alfentanil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- alfuzosin
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of alfuzosin by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- alosetron
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of alosetron by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- amitriptyline
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of amitriptyline by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- amlodipine
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of amlodipine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- amobarbital
amobarbital will decrease the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- antithrombin alfa
carbamazepine decreases levels of antithrombin alfa by increasing metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- antithrombin III
carbamazepine decreases levels of antithrombin III by increasing metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- apalutamide
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of apalutamide by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. No initial dose adjustment
- aprepitant
aprepitant will increase the level or effect of carbamazepine by decreasing metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Monitor plasma levels when used concomitantly
- argatroban
carbamazepine decreases levels of argatroban by increasing metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- armodafinil
armodafinil will decrease the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of armodafinil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. - artemether/lumefantrine
artemether/lumefantrine will decrease the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- artesunate
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of artesunate by increasing metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Coadministration may decrease AUC and peak plasma concentration of active artesunate metabolite (DHA) by inducing UGT. Monitor for decreased efficacy.
- atazanavir
atazanavir will increase the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Monitor plasma levels when used concomitantly
- atogepant
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of atogepant by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Recommended atogepant dosage with concomitant use of strong or moderate CYP3A4 inducers is 30 mg or 60 mg qDay.
- atorvastatin
carbamazepine increases toxicity of atorvastatin by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: OATP1B1 inhibitors may increase risk of myopathy.
- avanafil
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of avanafil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. For patients with ED, monitor response carefully because of potential for decreased effectiveness
- avatrombopag
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of avatrombopag by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. When treating ITP, coadministration of avatrombopag with a moderate or strong dual CYP2C9/3A4 inducer requires an increased avatrombopag starting dose. Refer to drug monograph for specific recommendations.
- bazedoxifene/conjugated estrogens
carbamazepine decreases levels of bazedoxifene/conjugated estrogens by increasing metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. A reduction in bazedoxifene exposure may be associated with an increase risk of endometrial hyperplasia.
- belumosudil
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of belumosudil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Increase belumosudil dosage to 200 mg PO BID when coadministered with strong CYP3A inducers.
- belzutifan
belzutifan will decrease the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. If unable to avoid coadministration of belzutifan with sensitive CYP3A4 substrates, consider increasing the sensitive CYP3A4 substrate dose in accordance with its prescribing information.
- bemiparin
carbamazepine decreases levels of bemiparin by increasing metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- bendamustine
carbamazepine decreases levels of bendamustine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP1A2 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Concentrations of active metabolites may be increased.
- benzhydrocodone/acetaminophen
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of benzhydrocodone/acetaminophen by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Caution when discontinuing CYP3A4 inducers that are coadministered with benzhydrocodone (prodrug of hydrocodone); plasma concentrations of hydrocodone may increase and can result in potentially fatal respiratory depression.
- benzphetamine
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of benzphetamine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- berotralstat
carbamazepine decreases levels of berotralstat by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
berotralstat will increase the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Monitor or titrate substrate dose when berotralstat is coadministered with narrow therapeutic index drugs that are CYP3A substrates. - bexagliflozin
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of bexagliflozin by Other (see comment). Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Bexagliflozin is a major substrate of UGT1A9. If coadministered with a UGT1A9 inducer, consider adding another antihyperglycemic agent in patients requiring additional glycemic control.
- bexarotene
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of bexarotene by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- bivalirudin
carbamazepine decreases levels of bivalirudin by increasing metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- blinatumomab
blinatumomab increases levels of carbamazepine by decreasing metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Treatment initiation causes transient release of cytokines that may suppress CYP450 enzymes; highest drug-drug interaction risk is during the first 9 days of the first cycle and the first 2 days of the 2nd cycle in patients who are receiving concomitant CYP450 substrates, particularly those with a narrow therapeutic index.
- bortezomib
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of bortezomib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- bosentan
bosentan will decrease the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of bosentan by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. - brentuximab vedotin
carbamazepine decreases levels of brentuximab vedotin by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- brexanolone
brexanolone, carbamazepine. Either increases toxicity of the other by sedation. Use Caution/Monitor.
- brexpiprazole
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of brexpiprazole by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Double brexpiprazole dose over 1-2 weeks if administered with a strong CYP3A4 inducer.
- brivaracetam
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of brivaracetam by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C19 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Brivaracetam plasma concentration decreased by 26%.
brivaracetam, carbamazepine. decreasing metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Brivaracetam reversibly inhibits epoxide hydrolase resulting in an increased concentration of carbamazepine epoxide, an active metabolite of carbamazepine. The carbamazepine epoxide plasma concentration increased up to 198%. May require carbamazepine dose reduction. . - brodalumab
brodalumab, carbamazepine. Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: Formation of CYP450 enzymes can be altered by increased levels of certain cytokines during chronic inflammation; thus, brodalumab could normalize the formation of CYP450 enzymes. Upon initiation or discontinuation of brodalumab in patients who are receiving concomitant CYP450 substrates, particularly those with a narrow therapeutic index, consider monitoring for therapeutic effect.
- bromocriptine
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of bromocriptine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- budesonide
budesonide will decrease the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- buprenorphine
carbamazepine decreases levels of buprenorphine by increasing metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Carbamazepine increases metabolism of buprenorphine; monitor for decreased efficacy.
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of buprenorphine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. - buprenorphine buccal
carbamazepine decreases levels of buprenorphine buccal by increasing metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Carbamazepine increases metabolism of buprenorphine; monitor for decreased efficacy.
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of buprenorphine buccal by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. - buprenorphine subdermal implant
carbamazepine decreases levels of buprenorphine subdermal implant by increasing metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Carbamazepine increases metabolism of buprenorphine; monitor for decreased efficacy.
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of buprenorphine subdermal implant by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Monitor patients already on buprenorphine subdermal implant who require newly-initiated treatment with CYP3A4 inducer for signs and symptoms of withdrawal. If the dose of the concomitant CYP3A4 inducer cannot be reduced or discontinued, implant removal may be necessary and the patient should then be treated with a buprenorphine dosage form that permits dose adjustments. If a CYP3A4 inducer is discontinued in a patient who has been stabilized on buprenorphine, monitor the patient for overmedication. - buprenorphine transdermal
carbamazepine decreases levels of buprenorphine transdermal by increasing metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Carbamazepine increases metabolism of buprenorphine; monitor for decreased efficacy.
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of buprenorphine transdermal by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. - buprenorphine, long-acting injection
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of buprenorphine, long-acting injection by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Patients who transfer to buprenorphine long-acting injection from transmucosal buprenorphine coadministered with CYP3A4 inducers should be monitored to ensure buprenorphine plasma levels are adequate. If the buprenorphine dose is inadequate and the CYP3A4 inducer cannot be reduced or discontinued, transition the patient back to a buprenorphine formulation that permits dose adjustments.
- bupropion
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of bupropion by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2B6 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- butabarbital
butabarbital will decrease the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- butalbital
butalbital will decrease the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- cabazitaxel
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of cabazitaxel by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Coadministration of strong CYP3A4 inducers may decrease cabazitaxel concentrations. Avoid coadministration.
- calcifediol
carbamazepine, calcifediol. affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Drugs that stimulate microsomal hydroxylation reduce the half-life of calcifediol.
- canagliflozin
carbamazepine decreases levels of canagliflozin by increasing metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Coadministration with potent UGT enzyme inducers: Consider increasing dose to 300 mg qDay if 100 mg/day tolerate and additional glycemic control required (eGFR must be >60 mL/min/1.73 m2 to increase dose); if eGFR <60 mL/min/1.73 m2, consider using a different antihyperglycemic agent.
- cannabidiol
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of cannabidiol by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Consider an increase in cannabidiol dosage (based on clinical response and tolerability) when coadministered with a strong CYP3A4 inducer.
- carvedilol
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of carvedilol by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C9/10 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- caspofungin
carbamazepine decreases levels of caspofungin by increasing metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- cenobamate
cenobamate will decrease the level or effect of carbamazepine by unspecified interaction mechanism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Concomitant use of carbamazepine with multiple doses of cenobamate 200 mg qDay decreased carbamazepine mean Cmax and AUC by 23%. Increase carbamazepine dosage as needed when used concomitantly with cenobamate.
cenobamate will decrease the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Increase dose of CYP3A4 substrate, as needed, when coadministered with cenobamate.
cenobamate, carbamazepine. Either increases effects of the other by sedation. Use Caution/Monitor. - cevimeline
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of cevimeline by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- chlordiazepoxide
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of chlordiazepoxide by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- chloroquine
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of chloroquine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- cimetidine
cimetidine will increase the level or effect of carbamazepine by decreasing metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Monitor plasma levels when used concomitantly
- ciprofloxacin
ciprofloxacin will increase the level or effect of carbamazepine by decreasing metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Monitor plasma levels when used concomitantly
- citalopram
carbamazepine decreases levels of citalopram by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. The possibility that carbamazepine might increase the clearance of citalopram should be considered when both drugs are coadministered.
- clobazam
carbamazepine, clobazam. Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: Concomitant administration can increase the potential for CNS effects (e.g., increased sedation or respiratory depression).
- clomipramine
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of clomipramine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP1A2 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of clomipramine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. - clorazepate
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of clorazepate by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- clozapine
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of clozapine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP1A2 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- cobicistat
cobicistat will increase the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- conivaptan
conivaptan will increase the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- cortisone
cortisone will decrease the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- crizotinib
carbamazepine decreases levels of crizotinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Concomitant use of strong CYP3A inducers should be avoided. .
crizotinib increases levels of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Coadministration of crizotinib with CYP3A substrates with narrow therapeutic indices should be avoided. - crofelemer
crofelemer increases levels of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Crofelemer has the potential to inhibit CYP3A4 at concentrations expected in the gut; unlikely to inhibit systemically because minimally absorbed.
- cyclophosphamide
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of cyclophosphamide by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2B6 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- cyclosporine
cyclosporine will increase the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of cyclosporine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. - dabrafenib
dabrafenib will decrease the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- dalteparin
carbamazepine decreases levels of dalteparin by increasing metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- danazol
danazol will increase the level or effect of carbamazepine by decreasing metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Monitor plasma levels when used concomitantly
danazol will increase the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. - dantrolene
dantrolene will increase the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Monitor plasma levels when used concomitantly
- daprodustat
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of daprodustat by Other (see comment). Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. CYP2C8 inducers may decrease daprodustat exposure, which may result in loss of efficacy. Monitor hemoglobin and adjust daprodustat dose when initiating or stopping therapy with CYP2C8 inducers during treatment
- dapsone
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of dapsone by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- daridorexant
carbamazepine and daridorexant both increase sedation. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Coadministration increases risk of CNS depression, which can lead to additive impairment of psychomotor performance and cause daytime impairment.
- darifenacin
darifenacin will increase the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- darunavir
darunavir will increase the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Monitor plasma levels when used concomitantly
- dasatinib
dasatinib will increase the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- deferasirox
deferasirox will decrease the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Caution is advised. Combination use may lead to increased or decreased carbamazepine levels.
- desogestrel
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of desogestrel by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Advise patients to use alternative contraceptive method during coadministration; continue alternative contraception for 28 days after discontinuing therapy to ensure contraception reliability
- deutetrabenazine
carbamazepine and deutetrabenazine both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor.
- dexamethasone
dexamethasone will decrease the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- dexlansoprazole
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of dexlansoprazole by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- DHEA, herbal
DHEA, herbal will increase the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- diazepam
diazepam increases levels of carbamazepine by decreasing metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
carbamazepine decreases levels of diazepam by increasing metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. - diazepam intranasal
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of diazepam intranasal by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C19 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Strong or moderate CYP2C19 inducers may increase rate of diazepam elimination; therefore, efficacy of diazepam may be decreased.
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of diazepam intranasal by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Strong or moderate CYP3A4 inducers may increase rate of diazepam elimination; therefore, efficacy of diazepam may be decreased. - difelikefalin
difelikefalin and carbamazepine both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor.
- diltiazem
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of diltiazem by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- disopyramide
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of disopyramide by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- docetaxel
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of docetaxel by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- donepezil
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of donepezil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- doxepin cream
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of doxepin cream by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- doxorubicin
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of doxorubicin by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- doxorubicin liposomal
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of doxorubicin liposomal by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- doxycycline
carbamazepine decreases levels of doxycycline by increasing metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- dronabinol
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of dronabinol by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C9/10 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Dronabinol is a CYP2C9 substrate.
carbamazepine will increase the level or effect of dronabinol by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Dronabinol is a CYP3A4 substrate. - dronedarone
dronedarone will increase the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- drospirenone
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of drospirenone by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Advise patients to use alternative contraceptive method during coadministration; continue alternative contraception for 28 days after discontinuing therapy to ensure contraception reliability
- dulaglutide
dulaglutide, carbamazepine. Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: Dulaglutide slows gastric emptying and may impact absorption of concomitantly administered oral medications; be particularly cautious when coadministered with drugs that have a narrow therapeutic index.
- dupilumab
dupilumab, carbamazepine. Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: Formation of CYP450 enzymes can be altered by increased levels of certain cytokines during chronic inflammation; thus, dupilumab could normalize the formation of CYP450 enzymes. Upon initiation or discontinuation of dupilumab in patients who are receiving concomitant CYP450 substrates, particularly those with a narrow therapeutic index, consider monitoring for therapeutic effect.
- dutasteride
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of dutasteride by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- duvelisib
duvelisib will increase the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. will increase the level or effect of
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of duvelisib by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor. - efavirenz
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of efavirenz by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2B6 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- elagolix
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of elagolix by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
elagolix will decrease the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Elagolix is a weak-to-moderate CYP3A4 inducer. Monitor CYP3A substrates if coadministered. Consider increasing CYP3A substrate dose if needed. - elranatamab
elranatamab will increase the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Elranatamab causes cytokine release syndrome (CRS) that may suppress activity of CYP enzymes, resulting in increased exposure of CYP substrates. This is more likely to occur from initiation of elranatamab step-up dosing up to 14 days after the first treatment dose and during and after CRS.
- eltrombopag
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of eltrombopag by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP1A2 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of eltrombopag by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C9/10 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. - eluxadoline
eluxadoline increases levels of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Caution when CYP3A substrates that have a narrow therapeutic index are coadministered with eluxadoline.
- elvitegravir/cobicistat/emtricitabine/tenofovir DF
elvitegravir/cobicistat/emtricitabine/tenofovir DF increases levels of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Cobicistat is a CYP3A4 inhibitor; contraindicated with CYP3A4 substrates for which elevated plasma concentrations are associated with serious and/or life-threatening events.
- enalapril
enalapril increases levels of carbamazepine by decreasing metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- encorafenib
encorafenib, carbamazepine. affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Encorafenib both inhibits and induces CYP3A4 at clinically relevant plasma concentrations. Coadministration of encorafenib with sensitive CYP3A4 substrates may result in increased toxicity or decreased efficacy of these agents.
- enfortumab vedotin
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of enfortumab vedotin by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- enoxaparin
carbamazepine decreases levels of enoxaparin by increasing metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- enzalutamide
enzalutamide will decrease the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- epcoritamab
epcoritamab, carbamazepine. affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Epcoritamab causes release of cytokines that may suppress activity of CYP enzymes, resulting in increased exposure of CYP substrates. For certain CYP substrates, minimal changes in their concentration may lead to serious adverse reactions. If needed, modify therapy as recommended in the substrate's prescribing information. .
- eplerenone
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of eplerenone by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- escitalopram
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of escitalopram by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- esketamine intranasal
esketamine intranasal, carbamazepine. Either increases toxicity of the other by sedation. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- eslicarbazepine acetate
eslicarbazepine acetate, carbamazepine. Either decreases effects of the other by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. May need dose adjustment for eslicarbazepine or carbamazepine.Concomitant administration of eslicarbazepine and carbamazepine may increase the incidence of diplopia and dizziness. .
carbamazepine, eslicarbazepine acetate. Either decreases levels of the other by increasing metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Dosage adjustment of either drug may be needed.
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of eslicarbazepine acetate by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. May need dose adjustment for eslicarbazepine or carbamazepine. - esomeprazole
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of esomeprazole by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- estradiol vaginal
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of estradiol vaginal by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- estrogens esterified
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of estrogens esterified by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- eszopiclone
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of eszopiclone by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- ethosuximide
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of ethosuximide by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- ethotoin
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of ethotoin by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C9/10 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- etoposide
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of etoposide by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- eucalyptus
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of eucalyptus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- exemestane
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of exemestane by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. For patients receiving exemestane with a potent CYP3A4 inducer the recommended dose of exemestane is 50 mg daily after a meal.
- fedratinib
fedratinib will increase the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Adjust dose of drugs that are CYP3A4 substrates as necessary.
- felbamate
carbamazepine decreases levels of felbamate by increasing metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Toxicity increased with combination.
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of felbamate by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. - felodipine
felodipine increases levels of carbamazepine by decreasing metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- fentanyl
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of fentanyl by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Coadministration of fentanyl with CYP3A4 inducers could lead to a decrease in fentanyl plasma concentrations, lack of efficacy or, possibly, development of a withdrawal syndrome in a patient who has developed physical dependence to fentanyl. After stopping a CYP3A4 inducer, as the effects of the inducer decline, the fentanyl plasma concentration will increase which could increase or prolong both the therapeutic and adverse effects.
- fentanyl intranasal
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of fentanyl intranasal by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Coadministration of fentanyl with CYP3A4 inducers could lead to a decrease in fentanyl plasma concentrations, lack of efficacy or, possibly, development of a withdrawal syndrome in a patient who has developed physical dependence to fentanyl. After stopping a CYP3A4 inducer, as the effects of the inducer decline, the fentanyl plasma concentration will increase which could increase or prolong both the therapeutic and adverse effects.
- fentanyl transdermal
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of fentanyl transdermal by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Coadministration of fentanyl with CYP3A4 inducers could lead to a decrease in fentanyl plasma concentrations, lack of efficacy or, possibly, development of a withdrawal syndrome in a patient who has developed physical dependence to fentanyl. After stopping a CYP3A4 inducer, as the effects of the inducer decline, the fentanyl plasma concentration will increase which could increase or prolong both the therapeutic and adverse effects.
- fentanyl transmucosal
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of fentanyl transmucosal by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Coadministration of fentanyl with CYP3A4 inducers could lead to a decrease in fentanyl plasma concentrations, lack of efficacy or, possibly, development of a withdrawal syndrome in a patient who has developed physical dependence to fentanyl. After stopping a CYP3A4 inducer, as the effects of the inducer decline, the fentanyl plasma concentration will increase which could increase or prolong both the therapeutic and adverse effects.
- ferric maltol
ferric maltol, carbamazepine. Either increases levels of the other by unspecified interaction mechanism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Coadministration of ferric maltol with certain oral medications may decrease the bioavailability of either ferric maltol and some oral drugs. For oral drugs where reductions in bioavailability may cause clinically significant effects on its safety or efficacy, separate administration of ferric maltol from these drugs. Duration of separation may depend on the absorption of the medication concomitantly administered (eg, time to peak concentration, whether the drug is an immediate or extended release product).
- finasteride
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of finasteride by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- flibanserin
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of flibanserin by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Strong CYP3A4 inducers substantially decrease flibanserin systemic exposure.
- fluconazole
fluconazole will increase the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Monitor plasma levels when used concomitantly
- fludrocortisone
fludrocortisone will decrease the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- fluoxetine
fluoxetine will increase the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Monitor plasma levels when used concomitantly
- fluoxymesterone
fluoxymesterone increases toxicity of carbamazepine by decreasing metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- flurazepam
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of flurazepam by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- fluticasone furoate
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of fluticasone furoate by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- fluticasone inhaled
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of fluticasone inhaled by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- fluvastatin
carbamazepine increases toxicity of fluvastatin by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: OATP1B1 inhibitors may increase risk of myopathy.
- fluvoxamine
fluvoxamine will increase the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Monitor plasma levels when used concomitantly
- fondaparinux
carbamazepine decreases levels of fondaparinux by increasing metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- fosamprenavir
fosamprenavir will increase the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Monitor plasma levels when used concomitantly
- fosaprepitant
fosaprepitant will increase the level or effect of carbamazepine by decreasing metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Monitor plasma levels when used concomitantly
- fosphenytoin
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of fosphenytoin by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C9/10 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
fosphenytoin will decrease the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. - galantamine
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of galantamine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- gefitinib
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of gefitinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Increase gefitinib to 500 mg daily if coadministered with a strong CYP3A4 inducer. Resume gefitinib dose at 250 mg/day 7 days after discontinuing the strong inducer.
- givinostat
givinostat will increase the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Givinostat is a weak CYP3A4 inhibitor. Closely monitor if coadministered with orally administered CYP3A4 sensitive substrates for which a small change in substrate plasma concentration may lead to serious toxicities.
- glofitamab
glofitamab, carbamazepine. affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Glofitamab causes release of cytokines that may suppress activity of CYP enzymes, resulting in increased exposure of CYP substrates. For certain CYP substrates, minimal changes in their concentration may lead to serious adverse reactions. If needed, modify therapy as recommended in the substrate's prescribing information. .
- glyburide
carbamazepine decreases levels of glyburide by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C9/10 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Strong CYP2C9 inducers may increase glyburide metabolism.
- glycerol phenylbutyrate
glycerol phenylbutyrate will decrease the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Glycerol phenylbutyrate is a weak inducer of CYP3A4. Monitor for decreased efficacy of CYP3A4 substrates that have a narrow therapeutic index.
- grapefruit
grapefruit will increase the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- griseofulvin
griseofulvin will decrease the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- guanfacine
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of guanfacine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Strong or moderate CYP3A4 inducers significantly reduce guanfacine plasma concentrations and elimination half-life. If coadministered, more frequent dosing of the IR product may be required to achieve or maintain the desired hypotensive response. For patients with ADHD, FDA-approved labeling for ER guanfacine recommends that, if coadministered, doubling the recommended dose of guanfacine should be considered.
- guselkumab
guselkumab, carbamazepine. Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: Formation of CYP450 enzymes can be altered by increased levels of certain cytokines during chronic inflammation; thus, normalizing the formation of CYP450 enzymes. Upon initiation or discontinuation of guselkumab in patients who are receiving concomitant CYP450 substrates, particularly those with a narrow therapeutic index, consider monitoring for therapeutic effect.
- haloperidol
carbamazepine decreases levels of haloperidol by increasing metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- heparin
carbamazepine decreases levels of heparin by increasing metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- hydrocodone
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of hydrocodone by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Caution when discontinuing CYP3A4 inducers that are coadministered with hydrocodone; plasma concentrations of hydrocodone may increase and can result in potentially fatal respiratory depression
- hydrocortisone
hydrocortisone will decrease the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- ibuprofen
ibuprofen will increase the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Monitor plasma levels when used concomitantly
- ibuprofen IV
ibuprofen IV will increase the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Monitor plasma levels when used concomitantly
- ibuprofen/famotidine
ibuprofen/famotidine will increase the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Monitor plasma levels when used concomitantly
- ifosfamide
carbamazepine increases effects of ifosfamide by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2B6 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Coadministration of ifosfamide with CYP2B6 inducers may increase metabolism of ifosfamide to its metabolite. Monitor for increased effects/toxicities if combined with CYP2B6 inducers.
carbamazepine increases toxicity of ifosfamide by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. CYP3A4 inducers may increase the metabolism of ifosfamide to its active alkylating metabolites. CYP3A4 inducers may increase the formation of the neurotoxic/nephrotoxic ifosfamide metabolite, chloroacetaldehyde. Closely monitor patients taking ifosfamide with CYP3A4 inducers for toxicities and consider dose adjustment. - iloperidone
iloperidone increases levels of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Iloperidone is a time-dependent CYP3A inhibitor and may lead to increased plasma levels of drugs predominantly eliminated by CYP3A4.
- imatinib
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of imatinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- imipramine
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of imipramine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP1A2 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of imipramine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. - indinavir
indinavir will increase the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Monitor plasma levels when used concomitantly
- iptacopan
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of iptacopan by increasing metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. CYP2C8 inducers may reduce efficacy of iptacopan (a CYP2C8 substrate).
- isavuconazonium sulfate
isavuconazonium sulfate will increase the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- isoniazid
isoniazid will increase the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Monitor plasma levels when used concomitantly
- isradipine
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of isradipine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- istradefylline
istradefylline will increase the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Istradefylline 40 mg/day increased peak levels and AUC of CYP3A4 substrates in clinical trials. This effect was not observed with istradefylline 20 mg/day. Consider dose reduction of sensitive CYP3A4 substrates.
- ixekizumab
ixekizumab, carbamazepine. Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: Formation of CYP450 enzymes can be altered by increased levels of certain cytokines during chronic inflammation; thus, ixekizumab could normalize the formation of CYP450 enzymes. Upon initiation or discontinuation of ixekizumab in patients who are receiving concomitant CYP450 substrates, particularly those with a narrow therapeutic index, consider monitoring for therapeutic effect.
- ketamine
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of ketamine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2B6 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of ketamine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. - ketoconazole
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of ketoconazole by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- lacosamide
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of lacosamide by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
carbamazepine increases toxicity of lacosamide by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: Coadministration of lacosamide with sodium channel-blocking antiseizure drugs may increase the risk for AV block, bradycardia, or ventricular tachyarrhythmias. Monitor ECG before beginning lacosamide and after lacosamide is titrated to steady-state. - lamotrigine
carbamazepine decreases levels of lamotrigine by increasing metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- lansoprazole
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of lansoprazole by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of lansoprazole by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C19 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. - lapatinib
lapatinib will increase the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- larotrectinib
larotrectinib will increase the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- lasmiditan
lasmiditan, carbamazepine. Either increases effects of the other by sedation. Use Caution/Monitor. Coadministration of lasmiditan and other CNS depressant drugs, including alcohol have not been evaluated in clinical studies. Lasmiditan may cause sedation, as well as other cognitive and/or neuropsychiatric adverse reactions.
- lemborexant
lemborexant, carbamazepine. Either increases effects of the other by sedation. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Dosage adjustment may be necessary if lemborexant is coadministered with other CNS depressants because of potentially additive effects.
- lenacapavir
lenacapavir will increase the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Lencapavir (a moderate CYP3A4 inhibitor) may increase CYP3A4 substrates initiated within 9 months after last SC dose of lenacapavir, which may increase potential risk of adverse reactions of CYP3A4 substrates.
- lesinurad (DSC)
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of lesinurad (DSC) by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C9/10 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- letermovir
carbamazepine increases levels of letermovir by decreasing metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Coadminstration of letermovir, an OATP1B1/3 substrate, with OATP1B1/3 inhibitors may increase letermovir plasma concentrations.
letermovir increases levels of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. - levamlodipine
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of levamlodipine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. No information is available on the quantitative effects of CYP3A4 inducers on amlodipine. Closely monitor blood pressure when amlodipine is coadministered with CYP3A4 inducers.
- levoketoconazole
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of levoketoconazole by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- levonorgestrel intrauterine
carbamazepine decreases levels of levonorgestrel intrauterine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- levonorgestrel oral
carbamazepine decreases levels of levonorgestrel oral by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- levonorgestrel oral/ethinylestradiol/ferrous bisglycinate
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of levonorgestrel oral/ethinylestradiol/ferrous bisglycinate by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. The efficacy of hormonal contraceptives may be reduced. Use an alternative method of contraception or a backup method when enzyme inducers are used with combined hormonal contraceptives (CHCs), and continue backup contraception for 28 days after discontinuing enzyme inducer to ensure contraceptive reliability.
- lidocaine
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of lidocaine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP1A2 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- linagliptin
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of linagliptin by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Use of alternative treatments is strongly recommended when linagliptin is to be administered with a CYP3A4 inducer.
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of linagliptin by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor. Use of alternative treatments is strongly recommended when linagliptin is to be administered with a P-gp inducer. - linezolid
carbamazepine decreases levels of linezolid by increasing metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- lithium
carbamazepine, lithium. Mechanism: unknown. Use Caution/Monitor. Risk of neurotoxicity.
- lomustine
lomustine, carbamazepine. Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Lomustine may enhance the toxicities of myelosuppressive agents. Monitor for increased risk of myelosuppression.
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of lomustine by increasing metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Coadministration of enzyme inducing antiepileptics with lomustine may cause a decrease in plasma concentration and reduced efficacy of lomustine. - lonapegsomatropin
lonapegsomatropin will decrease the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Limited published data indicate that growth hormone treatment increases cytochrome P450 (CYP450)-mediated antipyrine clearance. Caution with sensitive CYP substrates
- losartan
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of losartan by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C9/10 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- loxapine
loxapine will increase the level or effect of carbamazepine by decreasing metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Monitor plasma levels when used concomitantly
- lumacaftor/ivacaftor
lumacaftor/ivacaftor will decrease the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Lumacaftor is a strong inducer of CYP3A. Avoid coadministration with sensitive CYP3A substrates or CYP3A substrates with a narrow therapeutic index.
- lumefantrine
lumefantrine will decrease the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- lurasidone
lurasidone, carbamazepine. Either increases toxicity of the other by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: Potential for increased CNS depressant effects when used concurrently; monitor for increased adverse effects and toxicity.
- marijuana
marijuana will increase the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of marijuana by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. - medroxyprogesterone
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of medroxyprogesterone by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Contraceptirve failure possible
- mefloquine
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of mefloquine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- mesterolone
mesterolone increases toxicity of carbamazepine by decreasing metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- methylphenidate
carbamazepine decreases effects of methylphenidate by unspecified interaction mechanism. Use Caution/Monitor. Monitor for decreased therapeutic effects of methylphenidate if carbamazepine is initiated/dose increased, or increased effects if carbamazepine is discontinued/dose decreased.
- methylphenidate transdermal
methylphenidate transdermal will increase the level or effect of carbamazepine by decreasing metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Consider decreasing the dose of these drugs when given coadministered with methylphenidate. Monitor for drug toxiticities when initiating or discontinuing methylphenidate.
- methylprednisolone
methylprednisolone will decrease the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- metronidazole
metronidazole will increase the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- mexiletine
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of mexiletine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP1A2 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- miconazole vaginal
miconazole vaginal will increase the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- midazolam intranasal
midazolam intranasal, carbamazepine. Either increases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Concomitant use of barbiturates, alcohol, or other CNS depressants may increase the risk of hypoventilation, airway obstruction, desaturation, or apnea and may contribute to profound and/or prolonged drug effect.
- mifepristone
carbamazepine, mifepristone. Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: Carbamazepine may decrease mifepristone levels via CYP3A4 induction; additionally, mifepristone may increase carbamazepine levels by inhibiting CYP2C8/2C9.
- mipomersen
mipomersen, carbamazepine. Either increases toxicity of the other by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: Both drugs have potential to increase hepatic enzymes; monitor LFTs.
- mirtazapine
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of mirtazapine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- mitotane
mitotane decreases levels of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Mitotane is a strong inducer of cytochrome P-4503A4; monitor when coadministered with CYP3A4 substrates for possible dosage adjustments.
- modafinil
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of modafinil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- montelukast
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of montelukast by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- nateglinide
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of nateglinide by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C9/10 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- nelfinavir
nelfinavir will increase the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Monitor plasma levels when used concomitantly
- nifedipine
nifedipine will increase the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of nifedipine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. - nilotinib
nilotinib will increase the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- nimodipine
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of nimodipine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- nitrendipine
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of nitrendipine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- norelgestromin
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of norelgestromin by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Advise patients to use alternative contraceptive method during coadministration; continue alternative contraception for 28 days after discontinuing therapy to ensure contraception reliability
- norgestimate
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of norgestimate by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Advise patients to use alternative contraceptive method during coadministration; continue alternative contraception for 28 days after discontinuing therapy to ensure contraception reliability
- olanzapine
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of olanzapine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP1A2 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- oliceridine
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of oliceridine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. If coadministration with a CYP3A4 inducer is necessary, consider increasing oliceridine dose until stable drug effects are achieved; monitor for signs of opioid withdrawal. If inducer is discontinued, consider oliceridine dosage reduction and monitor for signs of respiratory depression.
- omeprazole
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of omeprazole by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- ondansetron
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of ondansetron by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP1A2 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of ondansetron by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. - oritavancin
oritavancin will decrease the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Oritavancin is a weak CYP3A4 inducer; caution if coadministered with CYP3A4 substrates that have a narrow therapeutic index
- orlistat
orlistat decreases levels of carbamazepine by inhibition of GI absorption. Applies only to oral form of both agents. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Risk of convulsions.
- osilodrostat
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of osilodrostat by Other (see comment). Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Osilodrostat is a CYP3A4 and CYP2B6 subtrate. Monitor cortisol concentration and patient?s signs and symptoms during coadministration and discontinuation with strong CYP3A4 and/or CYP2B6 inducers. Adjust dose of osilodrostat if necessary.
- ospemifene
carbamazepine decreases levels of ospemifene by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
carbamazepine decreases levels of ospemifene by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C19 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
carbamazepine decreases levels of ospemifene by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C9/10 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. - oxandrolone
oxandrolone increases toxicity of carbamazepine by decreasing metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- oxcarbazepine
oxcarbazepine will decrease the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- oxybutynin
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of oxybutynin by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
oxybutynin will increase the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Monitor plasma levels when used concomitantly - oxycodone
carbamazepine decreases levels of oxycodone by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- oxymetholone
oxymetholone increases toxicity of carbamazepine by decreasing metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- paclitaxel
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of paclitaxel by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of paclitaxel by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Paclitaxel levels/efficacy may decrease when coadministered with CYP2C8 inducers - paclitaxel protein bound
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of paclitaxel protein bound by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of paclitaxel protein bound by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Paclitaxel levels/efficacy may decrease when coadministered with CYP2C8 inducers - palbociclib
palbociclib will increase the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. The dose of sensitive CYP3A substrates with a narrow therapeutic index may need to be reduced if coadministered with palbociclib
- paliperidone
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of paliperidone by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Paliperidone dose may need to be increased when coadministered with strong inducers of both CYP3A4 and P-gp
- pantoprazole
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of pantoprazole by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- parecoxib
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of parecoxib by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C9/10 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of parecoxib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. - paricalcitol
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of paricalcitol by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- pentobarbital
pentobarbital will decrease the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- phenindione
carbamazepine decreases levels of phenindione by increasing metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- phenobarbital
phenobarbital will decrease the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- phenytoin
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of phenytoin by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C9/10 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
phenytoin will decrease the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. - pimavanserin
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of pimavanserin by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Avoid coadministration if possible. Monitor for reduced pimavanserin efficacy. An increase in pimavanserin dosage may be needed.
- pimozide
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of pimozide by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- pioglitazone
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of pioglitazone by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- pirtobrutinib
pirtobrutinib will increase the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Pirtobrutinib (a CYP3A4 inhibitor) may increase plasma concentrations of sensitive CYP3A4 substrate which may increase the risk of adverse reactions related to these substrates.
- pitavastatin
carbamazepine increases toxicity of pitavastatin by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: OATP1B1 inhibitors may increase risk of myopathy.
- pitolisant
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of pitolisant by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Pitolisant exposure is decreased by 50% if coadministered with strong CYP3A4 inducers. For patients stable on pitolisant 8.9 mg/day or 17.8 mg/day, double the pitolisant dose (ie, 17.8 mg or 35.6 mg, respectively) over 7 days. If the strong CYP3A4 inducer is discontinued, reduce pitolisant dosage by half.
pitolisant will decrease the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Pitolisant is a borderline/weak inducer of CYP3A4. Monitor sensitive CYP3A4 substrates for reduced effectiveness if coadministered. - polatuzumab vedotin
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of polatuzumab vedotin by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Polatuzumab undergoes catabolism to small peptides, amino acids, monomethyl auristatin E (MMAE), and unconjugated MMAE-related catabolites. MMAE is a CYP3A4 substrate. Coadministration of polatuzumab vedotin with a strong CYP3A4 inducer may decrease unconjugated MMAE AUC.
- posaconazole
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
carbamazepine decreases levels of posaconazole by increasing metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. - pravastatin
carbamazepine increases toxicity of pravastatin by Other (see comment). Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Comment: OATP1B1 inhibitors may increase risk of myopathy.
- prednisone
prednisone will decrease the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- primidone
primidone will decrease the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- promazine
promazine increases toxicity of carbamazepine by unspecified interaction mechanism. Use Caution/Monitor. Enhanced myelosuppression.
- propafenone
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of propafenone by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- protamine
carbamazepine decreases levels of protamine by increasing metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- quazepam
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of quazepam by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- quetiapine
quetiapine will increase the level or effect of carbamazepine by decreasing metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Monitor plasma levels when used concomitantly
- quinine
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of quinine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- quinupristin/dalfopristin
quinupristin/dalfopristin will increase the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- rabeprazole
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of rabeprazole by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- ramelteon
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of ramelteon by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP1A2 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of ramelteon by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. - ribociclib
ribociclib will increase the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Caution if ribociclib is coadministered with sensitive CYP3A4 substrates that have a narrow therapeutic index. Dose reduction for sensitive CYP3A4 substrates may be needed.
- rifabutin
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of rifabutin by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- rifapentine
rifapentine will decrease the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- riociguat
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of riociguat by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Data not available for dose adjustment
- risperidone
carbamazepine decreases levels of risperidone by increasing metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- ritlecitinib
ritlecitinib will increase the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Ritlecitinib inhibits CYP3A4 substrates; coadministration increases AUC and peak plasma concentration sensitive substrates, which may increase risk of adverse reactions. Additional monitoring and dosage adjustment may be needed in accordance with product labeling of CYP3A substrates.
- ritonavir
ritonavir will increase the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Monitor plasma levels when used concomitantly
- rivaroxaban
carbamazepine decreases levels of rivaroxaban by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Avoid concomitant use of rivaroxaban with drugs that are combined P-gp and strong CYP3A4 inducers. Consider increasing the rivaroxaban dose if these drugs must be coadministered.
- romidepsin
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of romidepsin by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
- ropinirole
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of ropinirole by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP1A2 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- rosuvastatin
carbamazepine increases toxicity of rosuvastatin by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: OATP1B1 inhibitors may increase risk of myopathy.
- rucaparib
rucaparib will increase the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Adjust dosage of CYP3A4 substrates, if clinically indicated.
- rufinamide
rufinamide will decrease the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
carbamazepine decreases levels of rufinamide by increasing metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. - ruxolitinib
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of ruxolitinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- ruxolitinib topical
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of ruxolitinib topical by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- sacubitril/valsartan
carbamazepine will increase the level or effect of sacubitril/valsartan by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. The results from an in vitro study with human liver tissue indicate that valsartan is a substrate of the hepatic uptake transporter OATP1B1; coadministration with OATP1B1 inhibitors may increase valsartan systemic exposure
- saquinavir
saquinavir will increase the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Monitor plasma levels when used concomitantly
- sarilumab
sarilumab, carbamazepine. Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: Formation of CYP450 enzymes can be altered by increased levels of cytokines such as IL-6. Elevated IL-6 concentration may down-regulate CYP activity, such as in patients with RA, and, hence, increase drug levels compared with subjects without RA. Blockade of IL-6 signaling by IL-6 antagonists (eg, sarilumab) might reverse the inhibitory effect of IL-6 and restore CYP activity, leading to decreased drug concentrations. Caution when initiating or discontinuing sarilumab if coadministered with CYP450 substrates, especially those with a narrow therapeutic index.
- saxagliptin
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of saxagliptin by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- schisandra
schisandra will increase the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- secobarbital
secobarbital will decrease the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- secukinumab
secukinumab, carbamazepine. Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: Formation of CYP450 enzymes can be altered by increased levels of certain cytokines during chronic inflammation; thus, secukinumab could normalize the formation of CYP450 enzymes. Upon initiation or discontinuation of secukinumab in patients who are receiving concomitant CYP450 substrates, particularly those with a narrow therapeutic index, consider monitoring for therapeutic effect.
- segesterone/ethinyl estradiol
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of segesterone/ethinyl estradiol by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Advise patients to use alternative contraceptive method during coadministration; continue alternative contraception for 28 days after discontinuing therapy to ensure contraception reliability
- selegiline
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of selegiline by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2B6 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- selexipag
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of selexipag by increasing metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Increase selexipag dose (up to 2-fold) if coadministered with strong CYP2C8 inducers.
- sevelamer
sevelamer decreases levels of carbamazepine by increasing elimination. Use Caution/Monitor.
- sildenafil
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of sildenafil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Potent CYP3A4 inducers are expected to cause substantial decreases in sildenafil plasma levels
- siltuximab
siltuximab, carbamazepine. Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: CYP450 activity in the liver is down regulated by infection and inflammation stimuli including cytokines (eg, IL-6); inhibition of IL-6 by siltuximab may restore CYP450 enzymatic activity; caution if coadministered with CYP substrates that have a narrow therapeutic index.
- simvastatin
carbamazepine will increase the level or effect of simvastatin by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. OATP1B1 inhibitors may increase risk of myopathy
- sodium sulfate/potassium chloride/magnesium sulfate/polyethylene glycol
carbamazepine, sodium sulfate/potassium chloride/magnesium sulfate/polyethylene glycol. Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: Caution when bowel preps are used with drugs that cause SIADH or NSAIDs; increased risk for water retention or electrolyte imbalance.
- somapacitan
somapacitan will decrease the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Limited published data indicate that growth hormone treatment increases cytochrome P450 (CYP450)-mediated antipyrine clearance. Caution with sensitive CYP substrates
- somatrogon
somatrogon will decrease the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Limited published data indicate that growth hormone treatment increases cytochrome P450 (CYP450)-mediated antipyrine clearance. Caution with sensitive CYP substrates
- somatropin
somatropin will decrease the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Limited published data indicate that growth hormone treatment increases cytochrome P450 (CYP450)-mediated antipyrine clearance. Caution with sensitive CYP substrates
- stiripentol
stiripentol, carbamazepine. affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Stiripentol is a CYP3A4 inhibitor and inducer. Monitor CYP3A4 substrates coadministered with stiripentol for increased or decreased effects. CYP3A4 substrates may require dosage adjustment.
- sufentanil
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of sufentanil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- sufentanil SL
carbamazepine decreases effects of sufentanil SL by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Coadministration of CYP3A4 inducers may decrease sufentanil levels and efficacy, possibly precipitating withdrawal syndrome in patients who have developed physical dependence to sufentanil. Discontinuation of concomitantly used CYP3A4 inducers may increase sufentanil plasma concentration.
- suvorexant
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of suvorexant by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Strong CYP3A4 inducers may decrease suvorexant efficacy; if increased suvorexant dose required, do not exceed 20 mg/day
- tacrolimus ointment
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of tacrolimus ointment by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- tadalafil
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of tadalafil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Avoid combination in pulmonary HTN patients. For patients with ED, monitor response to tadalafil carefully because of potential for decreased effectiveness.
- talquetamab
talquetamab will increase the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Talquetamab causes cytokine release syndrome (CRS) that may suppress activity of CYP enzymes, resulting in increased exposure of CYP substrates. This is more likely to occur from initiation of talquetamab step-up dosing up to 14 days after the first treatment dose and during and after CRS.
- tamoxifen
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of tamoxifen by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C9/10 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of tamoxifen by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. - tasimelteon
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of tasimelteon by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Avoid coadministration of tasimelteon with strong CYP3A4 inducers
- tazemetostat
tazemetostat will decrease the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- teclistamab
teclistamab will increase the level or effect of carbamazepine by altering metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Teclistamab causes release of cytokines that may suppress activity of CYP450 enzymes, resulting in increased exposure of CYP substrates. Monitor for increased concentrations or toxicities of sensitive CYP substrates. Adjust dose of CYP substrate drug as needed.
- tecovirimat
tecovirimat will decrease the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Tecovirimat is a weak CYP3A4 inducer. Monitor sensitive CYP3A4 substrates for effectiveness if coadministered.
- teduglutide
teduglutide increases levels of carbamazepine by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: Teduglutide may increase absorption of concomitant PO medications; caution with with drugs requiring titration or those with a narrow therapeutic index; dose adjustment may be necessary.
- telotristat ethyl
telotristat ethyl will decrease the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Telotristat ethyl induces CYP3A4 and may reduce systemic exposure of sensitive CYP3A4 substrates. Monitor for suboptimal efficacy and consider increasing the dose of the CYP3A4 substrate.
- teniposide
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of teniposide by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- terbinafine
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of terbinafine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C9/10 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of terbinafine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. - teriflunomide
teriflunomide increases levels of carbamazepine by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: Teriflunomide inhibits CYP2C8; caution when coadministered with CYP2C8 substrates.
- tesamorelin
tesamorelin will decrease the level or effect of carbamazepine by altering metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Monitor levels
- testosterone
testosterone increases toxicity of carbamazepine by decreasing metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- testosterone buccal system
testosterone buccal system increases toxicity of carbamazepine by decreasing metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- testosterone topical
testosterone topical increases toxicity of carbamazepine by decreasing metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- theophylline
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of theophylline by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP1A2 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- ticagrelor
carbamazepine decreases levels of ticagrelor by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Avoid use of ticagrelor with potent CYP3A inducers.
- ticlopidine
ticlopidine will increase the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Monitor plasma levels when used concomitantly
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of ticlopidine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. - tinidazole
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of tinidazole by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- tipranavir
tipranavir will increase the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Monitor plasma levels when used concomitantly
- tofacitinib
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of tofacitinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Loss of, or decreased response to tofacitinib may occur when coadministered with potent CYP3A4 inducers
- topiramate
topiramate will decrease the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
carbamazepine decreases levels of topiramate by increasing metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. - toremifene
carbamazepine decreases levels of toremifene by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. CYP3A4 inducers increase rate of toremifene metabolism, lowering the steady-state concentration in serum.
- tramadol
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of tramadol by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Decreased AUC of tramadol and the active metabolite (O-desmethyltramadol) when coadministered with strong CYP3A4 and CYP2B6 inducers
- trazodone
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of trazodone by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
trazodone will increase the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Monitor plasma levels when used concomitantly - trimipramine
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of trimipramine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- trofinetide
trofinetide will increase the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Monitor CYP3A4 substrates for which a small increase in plasma concentration may lead to serious toxicities if coadministered with trofinetide (a weak CYP3A4 inhibitor).
- turmeric
turmeric will increase the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- ustekinumab
ustekinumab, carbamazepine. Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: Formation of CYP450 enzymes can be altered by increased levels of certain cytokines during chronic inflammation; thus, normalizing the formation of CYP450 enzymes. Upon initiation or discontinuation of ustekinumab in patients who are receiving concomitant CYP450 substrates, particularly those with a narrow therapeutic index, consider monitoring for therapeutic effect.
- valoctocogene roxaparvovec
carbamazepine and valoctocogene roxaparvovec both increase Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Medications that may cause hepatotoxicity when combined with valoctogene roxaparvovec may potentiate the risk of elevated liver enzymes. Closely monitor these medications and consider alternative medications in case of potential drug interactions.
- valproic acid
valproic acid will increase the level or effect of carbamazepine by Mechanism: decreasing metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Valproic acid may increase or decrease carbamazepine levels.
carbamazepine decreases levels of valproic acid by increasing metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. - valsartan
carbamazepine will increase the level or effect of valsartan by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. The results from an in vitro study with human liver tissue indicate that valsartan is a substrate of the hepatic uptake transporter OATP1B1; coadministration with OATP1B1 inhibitors may increase valsartan systemic exposure
- vemurafenib
carbamazepine decreases levels of vemurafenib by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
- verapamil
verapamil will increase the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Monitor plasma levels when used concomitantly
- vilazodone
carbamazepine decreases levels of vilazodone by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Consider increasing vilazodone dose up to 2-fold (not to exceed 80 mg/day) when coadministered with strong CYP3A4 inducers for >14 days.
- viloxazine
viloxazine will increase the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Viloxazine (a weak CYP3A4 inhibitor) may increase systemic exposure of sensitive CYP3A4 substrates. Monitor and adjust dose of substrate as clinically indicated.
- vinblastine
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of vinblastine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- vincristine
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of vincristine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- vincristine liposomal
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of vincristine liposomal by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- vinorelbine
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of vinorelbine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- vonoprazan
vonoprazan will increase the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Vonoprazan is weak CYP3A inhibitor. Caution with sensitive CYP3A substrates.
- voriconazole
voriconazole will increase the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Monitor plasma levels when used concomitantly
- vortioxetine
carbamazepine decreases levels of vortioxetine by increasing metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Consider increasing the vortioxetine dose when coadministered with strong CYP inducers for >14 days; not to exceed 3 times original vortioxetine dose.
- warfarin
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of warfarin by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C9/10 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- zafirlukast
zafirlukast will increase the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- zaleplon
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of zaleplon by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- ziprasidone
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of ziprasidone by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- zolpidem
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of zolpidem by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- zonisamide
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of zonisamide by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
Minor (74)
- acetaminophen
carbamazepine decreases levels of acetaminophen by increasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown. Enhanced metabolism incr levels of hepatotoxic metabolites.
- acetaminophen IV
carbamazepine decreases levels of acetaminophen IV by increasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown. Enhanced metabolism incr levels of hepatotoxic metabolites.
- acetaminophen rectal
carbamazepine decreases levels of acetaminophen rectal by increasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown. Enhanced metabolism incr levels of hepatotoxic metabolites.
- acetazolamide
acetazolamide will increase the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- alosetron
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of alosetron by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C9/10 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- ambrisentan
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of ambrisentan by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- amitriptyline
carbamazepine decreases levels of amitriptyline by increasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- amoxapine
carbamazepine decreases levels of amoxapine by increasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- anastrozole
anastrozole will increase the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- antipyrine
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of antipyrine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP1A2 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- asenapine
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of asenapine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP1A2 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- atracurium
carbamazepine decreases effects of atracurium by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- biotin
carbamazepine decreases levels of biotin by unspecified interaction mechanism. Minor/Significance Unknown. Biotin supplementation may be necessary.
- bosentan
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of bosentan by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C9/10 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- bupropion
carbamazepine decreases levels of bupropion by increasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- caffeine
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of caffeine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP1A2 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- celecoxib
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of celecoxib by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C9/10 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- cisatracurium
carbamazepine decreases effects of cisatracurium by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- clomipramine
carbamazepine decreases levels of clomipramine by increasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- cyanocobalamin
carbamazepine decreases levels of cyanocobalamin by inhibition of GI absorption. Applies only to oral form of both agents. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- cyclophosphamide
cyclophosphamide will increase the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- desipramine
carbamazepine decreases levels of desipramine by increasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- desmopressin
carbamazepine, desmopressin. Mechanism: unknown. Minor/Significance Unknown. Carbamazepine may increase or decrease the duration of action of desmopressin.
- dexmethylphenidate
dexmethylphenidate increases effects of carbamazepine by decreasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- diclofenac
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of diclofenac by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C9/10 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- dosulepin
carbamazepine decreases levels of dosulepin by increasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- doxepin
carbamazepine decreases levels of doxepin by increasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- drospirenone
drospirenone will increase the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- ethotoin
carbamazepine, ethotoin. Mechanism: unspecified interaction mechanism. Minor/Significance Unknown. Carbamazepine may increase or decrease phenytoin levels.
- ezogabine
carbamazepine decreases levels of ezogabine by Mechanism: unknown. Minor/Significance Unknown. Upon discontinuation of carbamazepine, ezogabine clearance decreased by approximately 30%. Consider an increase in the ezogabine dose during concurrent use.
- flurbiprofen
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of flurbiprofen by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C9/10 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- fluvastatin
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of fluvastatin by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C9/10 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- folic acid
carbamazepine decreases levels of folic acid by unspecified interaction mechanism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- fosphenytoin
carbamazepine, fosphenytoin. Mechanism: unspecified interaction mechanism. Minor/Significance Unknown. Carbamazepine may increase or decrease phenytoin levels.
- frovatriptan
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of frovatriptan by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP1A2 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- green tea
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of green tea by increasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- ibuprofen
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of ibuprofen by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C9/10 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- ibuprofen IV
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of ibuprofen IV by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C9/10 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- imipramine
carbamazepine decreases levels of imipramine by increasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- isotretinoin
isotretinoin decreases levels of carbamazepine by increasing renal clearance. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- L-methylfolate
carbamazepine decreases levels of L-methylfolate by unspecified interaction mechanism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- levocarnitine
carbamazepine decreases levels of levocarnitine by unspecified interaction mechanism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- levothyroxine
carbamazepine decreases levels of levothyroxine by increasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- liothyronine
carbamazepine decreases levels of liothyronine by increasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- lofepramine
carbamazepine decreases levels of lofepramine by increasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- maprotiline
carbamazepine decreases levels of maprotiline by increasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- mebendazole
carbamazepine decreases levels of mebendazole by increasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- meloxicam
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of meloxicam by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C9/10 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- niacin
niacin increases levels of carbamazepine by decreasing renal clearance. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- nortriptyline
carbamazepine decreases levels of nortriptyline by increasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- omeprazole
omeprazole increases levels of carbamazepine by decreasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown. Monitor plasma levels when used concomitantly.
- oxcarbazepine
carbamazepine decreases levels of oxcarbazepine by increasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- pancuronium
carbamazepine decreases effects of pancuronium by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- perampanel
perampanel increases levels of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- phenytoin
carbamazepine, phenytoin. Mechanism: unspecified interaction mechanism. Minor/Significance Unknown. Carbamazepine may increase or decrease phenytoin levels.
- piroxicam
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of piroxicam by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C9/10 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- protriptyline
carbamazepine decreases levels of protriptyline by increasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- ramelteon
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of ramelteon by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C9/10 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- rapacuronium
carbamazepine decreases effects of rapacuronium by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- riluzole
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of riluzole by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP1A2 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- rocuronium
carbamazepine decreases effects of rocuronium by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- sage
sage decreases effects of carbamazepine by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Minor/Significance Unknown. Theoretical interaction; some species of sage may cause convulsions.
- serdexmethylphenidate/dexmethylphenidate
serdexmethylphenidate/dexmethylphenidate increases effects of carbamazepine by decreasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- sertraline
sertraline increases levels of carbamazepine by decreasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- succinylcholine
carbamazepine decreases effects of succinylcholine by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- sulfamethoxazole
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of sulfamethoxazole by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C9/10 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- thyroid desiccated
carbamazepine decreases levels of thyroid desiccated by increasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- tiagabine
carbamazepine decreases levels of tiagabine by increasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- tibolone
carbamazepine decreases levels of tibolone by increasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown. Theoretical interaction.
- tolbutamide
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of tolbutamide by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C9/10 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- trazodone
carbamazepine decreases levels of trazodone by increasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- trimipramine
carbamazepine decreases levels of trimipramine by increasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- vasopressin
carbamazepine increases effects of vasopressin by pharmacodynamic synergism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- vecuronium
carbamazepine decreases effects of vecuronium by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
Adverse Effects
>10%
Ataxia (15%)
Dizziness (44%)
Drowsiness (32%)
Nausea (29%)
Vomiting (18%)
1-10%
Dry mouth (8%)
Rare
MI
Stevens-Johnson syndrome
Hepatic failure
Punctate cortical lens opacities
Syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion (SIADH)
Frequency Not Defined
Hemopoietic system: Aplastic anemia, agranulocytosis, pancytopenia, bone marrow depression, thrombocytopenia, leukopenia, leukocytosis, eosinophilia, anemia, acute intermittent porphyria, variegate porphyria, porphyria cutanea tarda
Skin: Toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN) and Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS) (see Black Box Warnings), pruritic and erythematous rashes, urticaria, photosensitivity reactions, alterations in skin pigmentation, exfoliative dermatitis, erythema multiforme and nodosum, purpura, aggravation of disseminated lupus erythematosus, alopecia, hirsutism, diaphoresis, generalized exanthematous pustulosis, and onychomadesis
Cardiovascular system: Congestive heart failure, edema, aggravation of hypertension, hypotension, syncope and collapse, aggravation of coronary artery disease, arrhythmias and AV block, thrombophlebitis, thromboembolism, and adenopathy or lymphadenopathy
Liver: Abnormalities in liver function tests, cholestatic and hepatocellular jaundice, hepatitis; very rare cases of hepatic failure
Pancreatic: Pancreatitis
Respiratory System: Pulmonary hypersensitivity characterized by fever, dyspnea, pneumonitis, or pneumonia
Genitourinary System: Urinary frequency, acute urinary retention, oliguria with elevated blood pressure, azotemia, renal failure, and impotence (rare reports of impaired male fertility and/or abnormal spermatogenesis)
Laboratory: Albuminuria, glycosuria, elevated BUN, decreased plasma calcium, and microscopic deposits in the urine, decreased values of thyroid function tests
Nervous system: Dizziness, drowsiness, disturbances of coordination, confusion, headache, fatigue, blurred vision, visual hallucinations, transient diplopia, oculomotor disturbances, nystagmus, speech disturbances, abnormal involuntary movements, peripheral neuritis and paresthesias, depression with agitation, talkativeness, tinnitus, hyperacusis, isolated cases of neuroleptic malignant syndrome
Digestive system: Nausea, vomiting, gastric distress and abdominal pain, diarrhea, constipation, anorexia, and dryness of the mouth and pharynx, including glossitis, and stomatitis, liver damage
Eyes: Scattered punctate cortical lens opacities, increased intraocular pressure as well as conjunctivitis
Musculoskeletal system: Aching joints and muscles, and leg cramps
Metabolism: Fever and chills; SIADH; cases of frank water intoxication, with decreased serum sodium (hyponatremia) and confusion; decreased levels of plasma calcium leading to osteoporosis
Immune system disorders: Hypogammaglobulinemia
Other: Multiorgan hypersensitivity reactions occurring days to weeks or months after initiating treatment have been reported in rare cases, signs or symptoms may include fever, skin rashes, vasculitis, lymphadenopathy, disorders mimicking lymphoma, arthralgia, leukopenia, eosinophilia, hepatosplenomegaly and abnormal liver function tests
Warnings
Black Box Warnings
Serious and sometimes fatal dermatologic reactions, including toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN) and Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS), have been reported during treatment with carbamazepine; studies in patients of Chinese ancestry found a strong association between the risk of developing SJS/TEN and the presence of HLA-B*1502, an inherited allelic variant of the HLA-B gene; HLA-B*1502 is found almost exclusively in patients of Asian ancestry, with populations across broad areas of Asia producing such descendants; patients testing positive for the allele should not be treated with carbamazepine unless the benefit clearly outweighs the risk; patients with ancestry in genetically at-risk populations should be screened for the presence of HLA-B*1502 prior to initiation of treatment with carbamazepine
Aplastic anemia and agranulocytosis reported; patients with a previous history of adverse hematologic reaction to any drug may be at increased risk
Complete pretreatment hematological testing should be obtained as a baseline; if a patient in the course of treatment exhibits low or decreased white blood cell or platelet counts, the patient should be monitored closely; consider discontinuation of therapy if significant bone marrow depression develops
Contraindications
Documented hypersensitivity
History of bone marrow suppression
Administration of MAO inhibitors within last 14 days
Coadministration with nefazodone; carbamazepine decreases plasma levels of nefazodone and its active metabolite
Coadministration with NNRTIs (eg, delavirdine, efavirenz, etravirine, nevirapine, rilpivirine); carbamazepine induces CYP3A4 and may substantially reduce NNRTI serum concentration
Jaundice, hepatitis
Pregnancy (especially first trimester: risk of fetal carbamazepine syndrome)
Cautions
Monitor for notable changes in behavior that might indicate suicidal thoughts or depression and notify healthcare provider immediately if behavioral changes observed
Discontinue if significant bone marrow depression occurs
Withdraw gradually
Increased risk of agranulocytosis and aplastic anemia
May cause ECG abnormalities; use caution in patients with conduction abnormalities; AV heart block, including second and third-degree block, reported following carbamazepine treatment; effect occurred generally, but not solely, in patients with underlying EKG abnormalities or risk factors for conduction disturbances
Therapy should be prescribed only after critical benefit-to-risk appraisal in patients with a history of cardiac conduction disturbance, including second- and third-degree atrioventricular (AV) block; cardiac, hepatic, or renal damage; adverse hematologic or hypersensitivity reaction to other drugs including reactions to other anticonvulsants; or interrupted courses of therapy with carbamazepine
May exacerbate absence seizures; in the event of allergic or hypersensitivity reaction, more rapid substitution of alternative therapy may be necessary
Bipolar mania: Efficacy inconsistent; APA recommends use after failure of or if there is resistance to lithium and valproate
May cause psychosis/confusion/agitation; elderly patients are at greater risk
May render oral contraceptives ineffective
Higher risk of potentially fatal skin reactions (SJS/TEN) in patients of Asian ancestry (genetic testing recommended); increased risk of developing hypersensitivity reactions with presence of HLAA*3101 or HLA-B*1502, inherited allelic variants of the HLA-A and HLA-B gene (see Pharmacogenomics in the Pharmacology section);
Hyponatremia may occur and appears to be a result of SIADH; may be dose-related and elderly individuals are at greater risk
Associated with hypotension, bradycardia, AV block, and signs and symptoms of HF
Fatal dermatologic reactions, including toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN) and Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS), reported
Not a simple analgesic; do not use to relieve minor aches and pains
Suspension formulation contains sorbitol; not for administration to patients with rare hereditary problems of fructose intolerance
AV heart block, including second and third-degree block, reported following carbamazepine treatment; effect occurred generally, but not solely, in patients with underlying EKG abnormalities or risk factors for conduction disturbances
Rare cases of anaphylaxis and angioedema involving larynx, glottis, lips, and eyelids reported with first or subsequent doses; angioedema associated with laryngeal edema can be fatal; if a patient develops reactions after treatment discontinue therapy and start alternative treatment; patients should not be rechallenged with drug
Mild anticholinergic activity; use caution in patients with sensitivity to anticholinergic effects
Fever and chills, decreased levels of plasma calcium leading to osteoporosis, and hyperammonemia reported
Urinary frequency, acute urinary retention, oliguria with elevated blood pressure, azotemia, renal failure, and impotence may occur; albuminuria, glycosuria, elevated BUN, and microscopic deposits in urine also reported; there have been rare reports of impaired male fertility and/or abnormal spermatogenesis
Hepatic effects
- Hepatic effects reported ranging from slight elevations in liver enzymes to rare cases of hepatic failure
- In some cases, hepatic effects may progress despite discontinuation
- Rare instances of vanishing bile duct syndrome reported; consists of a variable clinical course ranging from fulminant to indolent, involving the destruction and disappearance of the intrahepatic bile ducts
- Some cases associated other immunoallergenic syndromes (eg, multiorgan hypersensitivity [DRESS syndrome], serious dermatologic reactions)
- DRESS typically, although not exclusively, presents with fever, rash, lymphadenopathy and/or facial swelling in association with other organ system involvement, such as hepatitis, nephritis, hematologic abnormalities, myocarditis, or myositis sometimes resembling an acute viral infection
- As an example there has been a report of vanishing bile duct syndrome associated with Stevens-Johnson syndrome, and in another case an association with fever and eosinophilia
- Baseline and periodic evaluations of liver function, particularly in patients with history of liver disease, must be performed during treatment with this drug since liver damage may occur; drug should be discontinued immediately in cases of aggravated liver dysfunction or active liver disease
Pregnancy & Lactation
Pregnancy
There is a pregnancy exposure registry that monitors pregnancy outcomes in women exposed to antiepileptic drugs (AEDs), during pregnancy; encourage women who receive therapy during pregnancy to enroll in the North American Antiepileptic Drug (NAAED) Pregnancy Registry; this can be done by calling the toll-free number 1-888-233-2334 or visiting http://www.aedpregnancyregistry.org, and must be done by the patient herself
Females of reproductive potential should be counseled on consistent use of effective nonhormonal contraception or barrier methods during treatment
Therapy can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman; an association between use of drug during pregnancy and congenital malformations, including spina bifida and malformations involving other body systems (e.g., craniofacial defects and cardiovascular malformations) shown; developmental delays reported
Women of childbearing potential should be informed of potential risk to fetus
Consideration should be given to discontinuing therapy in women who are pregnant or attempting to become pregnant if benefits of discontinuation outweigh risks of recurrent seizures; women with epilepsy should not discontinue therapy abruptly due to risk of status epilepticus and less severe seizures which may be life-threatening
There have been a few cases of neonatal seizures and/or respiratory depression associated with maternal carbamazepine in combination with other antiepileptic drugs; a few cases of neonatal vomiting, diarrhea, and/or decreased feeding have also been reported in association with maternal carbamazepine use; these symptoms may represent a neonatal withdrawal syndrome
Tests to detect birth defects using currently accepted procedures should be considered a part of routine prenatal care in childbearing women receiving carbamazepine; evidence suggests that folic acid supplementation prior to conception and during first trimester of pregnancy decreases risk for congenital neural tube defects in general population; not known whether risk of neural tube defects in offspring of women receiving therapy is reduced by folic acid supplementation, but dietary folic acid supplementation both prior to conception and during pregnancy should be recommended for patients in therapy
Animal data
- In animal studies, therapy during pregnancy resulted in developmental toxicity, including increased incidences of fetal malformations
Lactation
Drug and its epoxide metabolite are excreted in human milk; there are no data to assess effects of drug or its metabolites on milk production, or on breastfed infant, of mothers taking drug; developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for drug and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed infant from drug or from underlying maternal condition
Pregnancy Categories
A: Generally acceptable. Controlled studies in pregnant women show no evidence of fetal risk.
B: May be acceptable. Either animal studies show no risk but human studies not available or animal studies showed minor risks and human studies done and showed no risk. C: Use with caution if benefits outweigh risks. Animal studies show risk and human studies not available or neither animal nor human studies done. D: Use in LIFE-THREATENING emergencies when no safer drug available. Positive evidence of human fetal risk. X: Do not use in pregnancy. Risks involved outweigh potential benefits. Safer alternatives exist. NA: Information not available.Pharmacology
Mechanism of Action
Stabilizes inactivated state of sodium channels, thereby making neurons less excitable
May reduce activity of nucleus ventralis of the thalamus or decrease synaptic transmission or summation of temporal stimulation leading to neuronal discharge
Absorption
Bioavailability: 85% (oral suspension)
Peak serum time: 4.5 hr (immediate-release tablets); 3-12 hr (extended-release tablets); 1.5 hr (oral suspension)
Distribution
Protein bound: 75-90%
Vd: 1.5 L/kg (neonates); 1.9 L/kg (children); 0.59-2 L/kg (adults)
Metabolism
Via hepatic CYP3A4
Metabolites: Carbamazepine 10,11-epoxide
Enzymes induced: CYP1A2, CYP2C9, CYP3A4
Elimination
Half-life: 25-65 hr (initial dosing); decreases to 10-20 hr after autoinduction; 35-40 hr (extended release)
Excretion: Urine (72%); feces (28%)
Pharmacogenomics
HLA-B*1502
- It is estimated that 1 in 20 patients with HLA-B*1502 will have a severe dermatologic reaction (eg, TEN, SJS) when taking carbamazepine
- This allele occurs almost exclusively in patients with ancestry across broad areas of Asia, including Han Chinese, Filipinos, Malaysians, South Asian Indians, and Thais
HLA-A*3101
- Retrospective case-control studies in patients of European, Korean, and Japanese ancestry have found a moderate association between the risk of developing hypersensitivity reactions and the presence of HLAA*3101, an inherited allelic variant of the HLA-A gene, in patients using carbamazepine; these hypersensitivity reactions include Stevens Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis
- HLA-A*3101 is expected to be carried by more than 15% of patients of Japanese, Native American, Southern Indian (eg, Tamil Nadu) and some Arabic ancestry; up to about 10% in patients of Han Chinese, Korean, European, Latin American, and other Indian ancestry; and up to about 5% in African-Americans and patients of Thai, Taiwanese, and Chinese (Hong Kong) ancestry
Genetic testing laboratories
- The following companies provide genetic testing for HLA variants
- Kashi Clinical Laboratories (www.kashilab.com)
- LabCorp (http://www.labcorp.com/)
- Specialty Laboratories (http://www.specialtylabs.com)
- Quest (http://www.questdiagnostics.com)
Administration
Oral Administration
Take with food
Do not chew, crush, or cut extended-release tablets
IV Preparation
For IV use only
Must be diluted with 100 mL of a compatible diluent before infusion (ie, 0.9% NaCl, lactated Ringer’s solution, or D%W)
Transfer measured dose to 100 mL bag of compatible solution
Inspected visually for particulate matter, cloudiness, or discoloration prior to administration; if any of these are present, discard the solution
IV Administration
Administer IV over 30 minutes
Storage
IV (before dilution)
- Store at 20-25°C (68-77°F); excursions permitted to 15-30°C (59-86°F)
IV (after dilution)
- Controlled room temperature (20-25°C [68-77°F]): Maximum of 4 hr
- Refrigerated (2-8°C [36-46°F]): Maximum of 24 hr
Images
| BRAND | FORM. | UNIT PRICE | PILL IMAGE |
|---|---|---|---|
| Epitol oral - | 200 mg tablet | 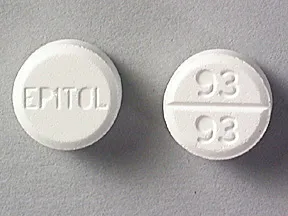 | |
| Carbatrol oral - | 200 mg capsule |  | |
| Carbatrol oral - | 100 mg capsule |  | |
| Carbatrol oral - | 300 mg capsule |  | |
| carbamazepine oral - | 400 mg tablet |  | |
| carbamazepine oral - | 200 mg tablet |  | |
| carbamazepine oral - | 100 mg capsule |  | |
| carbamazepine oral - | 200 mg tablet |  | |
| carbamazepine oral - | 200 mg tablet |  | |
| carbamazepine oral - | 300 mg capsule |  | |
| carbamazepine oral - | 100 mg/5 mL suspension |  | |
| carbamazepine oral - | 100 mg/5 mL suspension |  | |
| carbamazepine oral - | 100 mg chewable tablet |  | |
| carbamazepine oral - | 200 mg capsule | 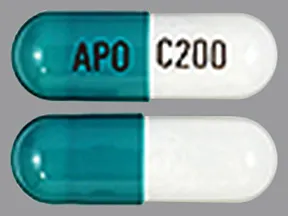 | |
| carbamazepine oral - | 200 mg tablet |  | |
| carbamazepine oral - | 200 mg/10 mL suspension | 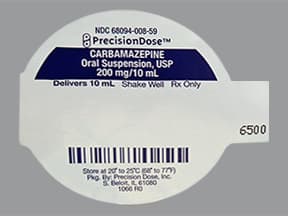 | |
| carbamazepine oral - | 400 mg tablet |  | |
| carbamazepine oral - | 300 mg capsule | 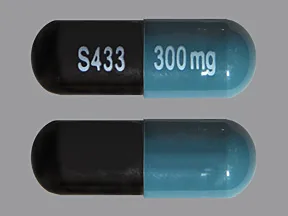 | |
| carbamazepine oral - | 200 mg tablet |  | |
| carbamazepine oral - | 200 mg tablet |  | |
| carbamazepine oral - | 100 mg chewable tablet |  | |
| carbamazepine oral - | 200 mg tablet |  | |
| carbamazepine oral - | 400 mg tablet |  | |
| carbamazepine oral - | 100 mg tablet |  | |
| carbamazepine oral - | 200 mg tablet |  | |
| carbamazepine oral - | 200 mg tablet |  | |
| carbamazepine oral - | 200 mg tablet |  | |
| carbamazepine oral - | 100 mg capsule |  | |
| carbamazepine oral - | 400 mg tablet |  | |
| carbamazepine oral - | 200 mg tablet |  | |
| carbamazepine oral - | 100 mg chewable tablet |  | |
| carbamazepine oral - | 200 mg tablet |  | |
| carbamazepine oral - | 100 mg tablet |  | |
| carbamazepine oral - | 100 mg/5 mL suspension |  | |
| carbamazepine oral - | 100 mg tablet |  | |
| carbamazepine oral - | 100 mg tablet | 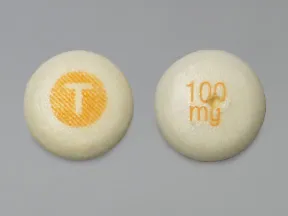 | |
| carbamazepine oral - | 100 mg capsule | 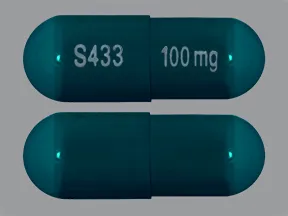 | |
| carbamazepine oral - | 200 mg capsule | 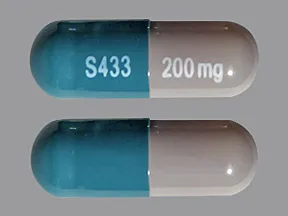 | |
| carbamazepine oral - | 200 mg capsule |  | |
| carbamazepine oral - | 300 mg capsule |  | |
| carbamazepine oral - | 100 mg tablet |  | |
| Tegretol oral - | 200 mg tablet | 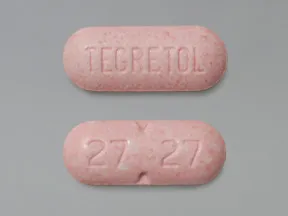 | |
| Tegretol oral - | 100 mg/5 mL suspension |  | |
| Tegretol XR oral - | 400 mg tablet |  | |
| Tegretol XR oral - | 200 mg tablet |  | |
| Tegretol XR oral - | 100 mg tablet |  |
Copyright © 2010 First DataBank, Inc.
Patient Handout
carbamazepine oral
CARBAMAZEPINE - ORAL
(KAR-ba-MAZ-e-peen)
COMMON BRAND NAME(S): Tegretol
WARNING: Carbamazepine may rarely cause very serious (possibly fatal) skin reactions. Some people in certain ethnic groups (such as people of Asian/South Asian descent) are at greater risk. Your doctor may order a blood test to measure your risk before you start this medication. If the blood test shows you are at greater risk, your doctor should discuss the risks and benefits of carbamazepine and other treatment choices with you. Such skin reactions have developed mostly within the first few months of treatment. Get medical help right away if you develop any of the following symptoms: skin rash/blisters/peeling, itching, or swelling. Ask your doctor or pharmacist for more details.This drug has rarely caused very serious blood disorders (aplastic anemia, agranulocytosis). Your doctor will monitor your blood counts to minimize the chance of these side effects. Keep all medical and lab appointments. Get medical help right away if any of these rare but very serious side effects occur: signs of infection (such as sore throat that doesn't go away, fever, swollen lymph nodes), unusual weakness/tiredness, shortness of breath, or easy bleeding/bruising.
USES: Carbamazepine is used to prevent and control seizures. This medication is known as an anticonvulsant or anti-epileptic drug. It is also used to relieve certain types of nerve pain (such as trigeminal neuralgia). This medication works by reducing the spread of seizure activity in the brain and restoring the normal balance of nerve activity.
HOW TO USE: Read the Medication Guide provided by your pharmacist before you start using carbamazepine and each time you get a refill. If you have any questions, ask your doctor or pharmacist.Take this medication by mouth with food as directed by your doctor. If you are using the chewable tablets, chew the tablets thoroughly before swallowing.If you are using the suspension form of this medication, shake the bottle well before each dose. Carefully measure the dose using a special measuring device/spoon. Do not use a household spoon because you may not get the correct dose. Separate doses of the suspension from other liquid medicines by at least 2 hours.The dosage is based on your medical condition and response to treatment. In children, the dosage is also based their weight. To reduce your risk of side effects, your doctor may direct you to start this medication at a low dose and gradually increase your dose. Follow your doctor's instructions carefully.Avoid eating grapefruit or drinking grapefruit juice while using this medication unless your doctor or pharmacist says you may do so safely. Grapefruit can increase the chance of side effects with this medicine. Ask your doctor or pharmacist for more details.Take this medication regularly to get the most benefit from it. To help you remember, take it at the same times each day. Keep taking this medication even if you feel well.Do not stop taking this medication without consulting your doctor. Some conditions (such as seizures) may become worse when this drug is suddenly stopped. Your dose may need to be gradually decreased.Tell your doctor if your condition does not get better or if it gets worse.
SIDE EFFECTS: See also Warning section.Nausea, vomiting, dizziness, drowsiness, constipation, dry mouth, or unsteadiness may occur. If any of these effects last or get worse, tell your doctor or pharmacist promptly.Remember that this medication has been prescribed because your doctor has judged that the benefit to you is greater than the risk of side effects. Many people using this medication do not have serious side effects.Tell your doctor right away if you have any serious side effects, including: headaches that are severe or don't go away, signs of liver problems (such as nausea/vomiting that doesn't stop, loss of appetite, stomach/abdominal pain, yellowing eyes/skin, dark urine), signs of kidney problems (such as change in the amount of urine), mouth sores, fainting, fast/slow/irregular heartbeat, unusual eye movements (nystagmus), vision changes (such as blurred vision), joint pain, swelling of the ankles/feet, pain/redness/swelling of the arms or legs, numbness/tingling of the hands/feet, signs of low levels of sodium in the blood (such as extreme drowsiness, mental/mood changes including confusion, seizures).A small number of people who take anticonvulsants for any condition (such as seizure, bipolar disorder, pain) may experience depression, suicidal thoughts/attempts, or other mental/mood problems. Tell your doctor right away if you or your family/caregiver notice any unusual/sudden changes in your mood, thoughts, or behavior including signs of depression, suicidal thoughts/attempts, thoughts about harming yourself.A very serious allergic reaction to this drug is rare. However, get medical help right away if you notice any symptoms of a serious allergic reaction, including: rash, itching/swelling (especially of the face/tongue/throat), severe dizziness, trouble breathing.This is not a complete list of possible side effects. If you notice other effects not listed above, contact your doctor or pharmacist.In the US -Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or at www.fda.gov/medwatch.In Canada - Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to Health Canada at 1-866-234-2345.
PRECAUTIONS: Before taking carbamazepine, tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are allergic to it; or to other anti-seizure medications (such as fosphenytoin, oxcarbazepine, phenobarbital, phenytoin, primidone) or tricyclic antidepressants (such as amitriptyline, desipramine); or if you have any other allergies. This product may contain inactive ingredients (such as sorbitol in the suspension), which can cause allergic reactions or other problems. Talk to your pharmacist for more details.Before using this medication, tell your doctor or pharmacist your medical history, especially of: decreased bone marrow function (bone marrow depression), blood disorders (such as porphyria, anemia), glaucoma, heart disease (such as coronary artery disease, heart failure, irregular heartbeat), kidney disease, liver disease, mental/mood disorders (such as depression), mineral imbalances (such as low levels of sodium or calcium in the blood ).This drug may make you dizzy or drowsy. Alcohol or marijuana (cannabis) can make you more dizzy or drowsy. Do not drive, use machinery, or do anything that needs alertness until you can do it safely. Avoid alcoholic beverages. Talk to your doctor if you are using marijuana (cannabis).This medication may make you more sensitive to the sun. Limit your time in the sun. Avoid tanning booths and sunlamps. Use sunscreen and wear protective clothing when outdoors. Get medical help right away if you get sunburned or have skin blisters/redness.The chewable tablets or suspension may contain sugar. Caution is advised if you have diabetes or any other condition that requires you to limit/avoid sugar in your diet. Ask your doctor or pharmacist about using this product safely.Before having surgery, tell your doctor or dentist about all the products you use (including prescription drugs, nonprescription drugs, and herbal products).Older adults may be more sensitive to the side effects of this drug, especially, confusion, unsteadiness, or irregular heartbeat. Confusion and unsteadiness can increase the risk of falling. Older adults may also be at greater risk of developing a type of mineral imbalance (low levels of sodium in the blood), especially if they are also taking "water pills" (diuretics).During pregnancy, this medication should be used only when clearly needed. It may harm an unborn baby. However, since untreated seizures are a serious condition that can harm both a pregnant woman and her unborn baby, do not stop taking this medication unless directed by your doctor. If you are planning pregnancy, become pregnant, or think you may be pregnant, discuss with your doctor right away the benefits and risks of using this medication during pregnancy. If you are pregnant, prenatal care that includes tests for birth defects is recommended. Since birth control pills, patches, implants, and injections may not work if used with this medication (see also Drug Interactions section), discuss reliable forms of birth control with your doctor.This medication passes into breast milk. Consult your doctor before breastfeeding.
DRUG INTERACTIONS: See also How to Use section.Drug interactions may change how your medications work or increase your risk for serious side effects. This document does not contain all possible drug interactions. Keep a list of all the products you use (including prescription/nonprescription drugs and herbal products) and share it with your doctor and pharmacist. Do not start, stop, or change the dosage of any medicines without your doctor's approval.Some products that may interact with this drug include: certain azole antifungals (isavuconazonium, voriconazole), orlistat.Taking MAO inhibitors with this medication may cause a serious (possibly fatal) drug interaction. Avoid taking MAO inhibitors (isocarboxazid, linezolid, metaxalone, methylene blue, moclobemide, phenelzine, procarbazine, rasagiline, safinamide, selegiline, tranylcypromine) during treatment with this medication. Most MAO inhibitors should also not be taken for two weeks before treatment with this medication. Ask your doctor when to start or stop taking this medication.Other medications can affect the removal of carbamazepine from your body, which may affect how carbamazepine works. Examples include macrolide antibiotics (such as erythromycin), rifamycins (such as rifabutin), St. John's wort, among others.Carbamazepine can speed up the removal of other drugs from your body, which may affect how they work. Examples of affected drugs include artemether/lumefantrine, certain drugs used to prevent blood clots (anticoagulants such as apixaban, rivaroxaban), certain calcium channel blockers (such as nifedipine, nimodipine), nefazodone, HIV NNRTIs (such as efavirenz, etravirine, rilpivirine), praziquantel, ranolazine, among others.This medication may decrease the effectiveness of hormonal birth control such as pills, patch, or ring. This could cause pregnancy. Discuss with your doctor or pharmacist if you should use reliable backup birth control methods while taking this medication. Also tell your doctor if you have any new spotting or breakthrough bleeding, because these may be signs that your birth control is not working well.Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking other products that cause drowsiness including alcohol, marijuana (cannabis), antihistamines (such as cetirizine, diphenhydramine), drugs for sleep or anxiety (such as alprazolam, diazepam, zolpidem), muscle relaxants (such as carisoprodol, cyclobenzaprine), and opioid pain relievers (such as codeine, hydrocodone).Check the labels on all your medicines (such as allergy or cough-and-cold products) because they may contain ingredients that cause drowsiness. Ask your pharmacist about using those products safely.This medication may interfere with certain lab tests (such as thyroid function, some pregnancy tests), possibly causing false test results. Make sure lab personnel and all your doctors know you use this drug.
OVERDOSE: If someone has overdosed and has serious symptoms such as passing out or trouble breathing, call 911. Otherwise, call a poison control center right away. US residents can call their local poison control center at 1-800-222-1222. Canada residents can call a provincial poison control center. Symptoms of overdose may include: slowed breathing, loss of consciousness, muscle twitching, uncontrolled movements, very fast heartbeat.
NOTES: Do not share this medication with others.Lab and/or medical tests (such as complete blood count, blood mineral levels, kidney/liver function, eye exams, carbamazepine blood levels) should be done before you start taking this medication and while you are taking it. Keep all medical and lab appointments. Consult your doctor for more details.
MISSED DOSE: If you miss a dose, take it as soon as you remember. If it is near the time of the next dose, skip the missed dose. Take your next dose at the regular time. Do not double the dose to catch up.
STORAGE: Store at room temperature away from light and moisture. Do not store in the bathroom. Keep all medications away from children and pets.Do not flush medications down the toilet or pour them into a drain unless instructed to do so. Properly discard this product when it is expired or no longer needed. Consult your pharmacist or local waste disposal company.
MEDICAL ALERT: Your condition can cause complications in a medical emergency. For information about enrolling in MedicAlert, call 1-888-633-4298 (US) or 1-800-668-1507 (Canada).
Information last revised March 2024. Copyright(c) 2024 First Databank, Inc.
IMPORTANT: HOW TO USE THIS INFORMATION: This is a summary and does NOT have all possible information about this product. This information does not assure that this product is safe, effective, or appropriate for you. This information is not individual medical advice and does not substitute for the advice of your health care professional. Always ask your health care professional for complete information about this product and your specific health needs.
Formulary
Adding plans allows you to compare formulary status to other drugs in the same class.
To view formulary information first create a list of plans. Your list will be saved and can be edited at any time.
Adding plans allows you to:
- View the formulary and any restrictions for each plan.
- Manage and view all your plans together – even plans in different states.
- Compare formulary status to other drugs in the same class.
- Access your plan list on any device – mobile or desktop.



